Abstract
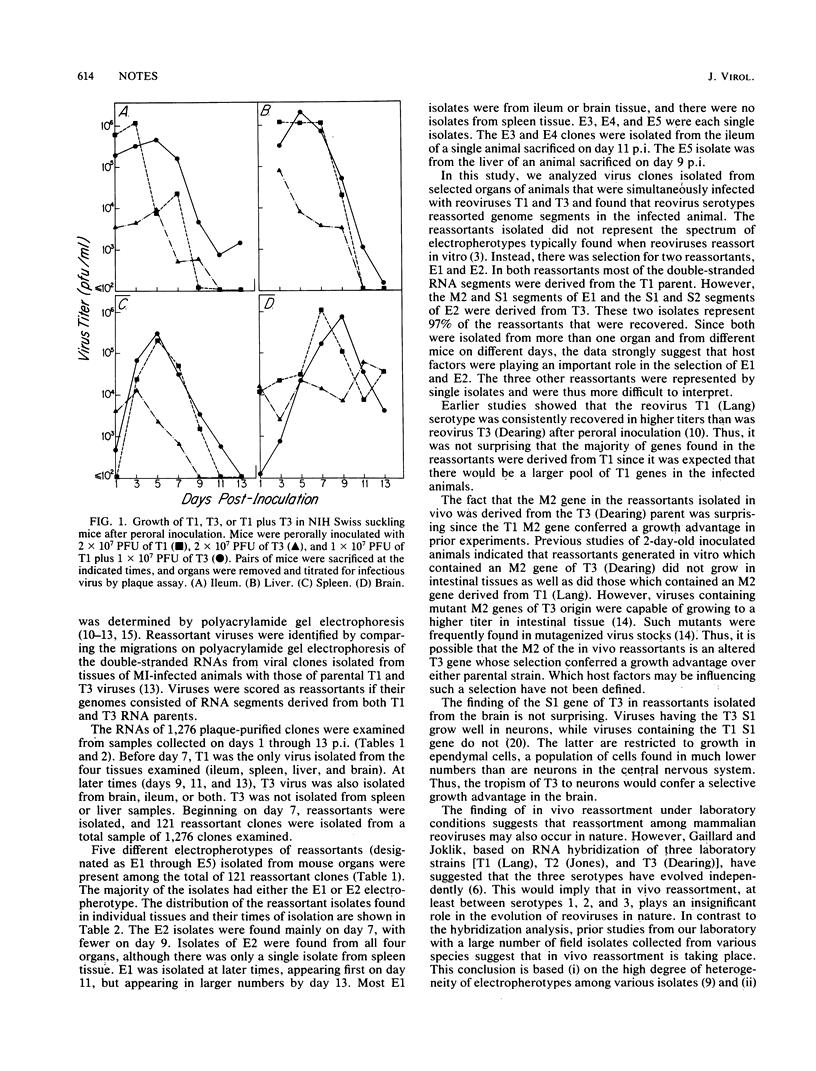
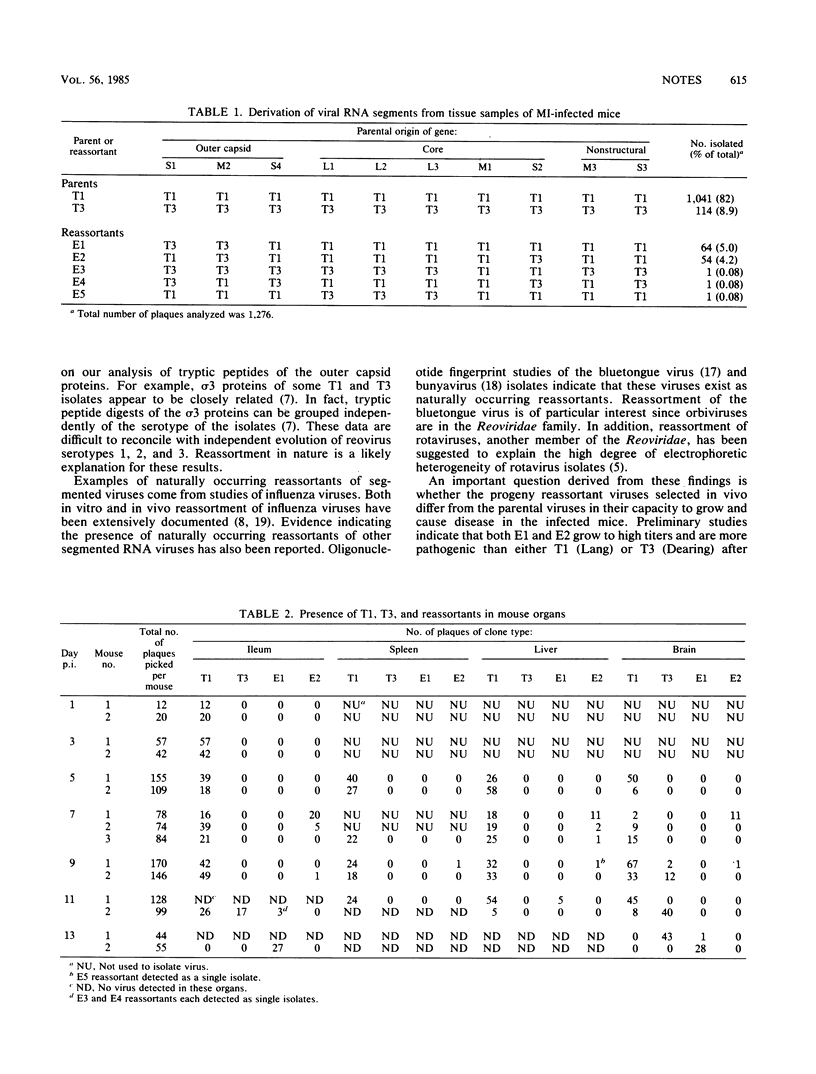
Reassortments between type 1 (Lang) and type 3 (Dearing) reoviruses were isolated from suckling mice infected perorally with an inoculum containing both type 1 and type 3 viruses. A total of five distinct reassortants (designated as E1 through E5) were isolated from animals during the course of the experiment. Two reassortants (E1 and E2) represented the majority of the reassortants isolated. The majority of genes of types E1 and E2 were derived from type 1 (Lang). However, E1 had an M2 gene and an S1 gene derived from type 3 (Dearing), while E2 had M2 and S2 genes derived from type 3 (Dearing). Thus, nonrandom reassortment between mammalian reoviruses can be demonstrated in vivo.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed R., Fields B. N. Role of the S4 gene in the establishment of persistent reovirus infection in L cells. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):605–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. K., Fields B. N. Use of an aberrant polypeptide as a marker in three-factor crosses: further evidence for independent reassortment as the mechanism of recombination between temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):345–362. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90341-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Fields B. N. Genetic studies on the mechanism of chemical and physical inactivation of reovirus. J Gen Virol. 1982 Nov;63(Pt 1):149–159. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-63-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. N., Greene M. I. Genetic and molecular mechanisms of viral pathogenesis: implications for prevention and treatment. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):19–23. doi: 10.1038/300019a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Perez I., White L., Perez M., Kalica A. R., Marquina R., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Genetic relatedness among human rotaviruses as determined by RNA hybridization. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):648–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.648-655.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard R. K., Jr, Joklik W. K. Quantitation of the relatedness of reovirus serotypes 1, 2, and 3 at the gene level. Virology. 1982 Nov;123(1):152–164. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90302-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentsch J. R., Fields B. N. Genetic diversity in natural populations of mammalian reoviruses: tryptic peptide analysis of outer capsid polypeptides of murine, bovine, and human type 1 and 3 reovirus strains. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):641–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.641-651.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw V. S., Bean W. J., Webster R. G., Sriram G. Genetic reassortment of influenza A viruses in the intestinal tract of ducks. Virology. 1980 Apr 30;102(2):412–419. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrdy D. B., Rosen L., Fields B. N. Polymorphism of the migration of double-stranded RNA genome segments of reovirus isolates from humans, cattle, and mice. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):104–111. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.104-111.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrdy D. B., Rubin D. H., Fields B. N. Molecular basis of reovirus neurovirulence: role of the M2 gene in avirulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1298–1302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman R. S., Wolf J. L., Finberg R., Trier J. S., Fields B. N. The sigma 1 protein determines the extent of spread of reovirus from the gastrointestinal tract of mice. Virology. 1983 Jan 30;124(2):403–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90356-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F., Cross R. K., Fields B. N. Genome RNAs and polypeptides of reovirus serotypes 1, 2, and 3. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):726–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.726-733.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. H., Fields B. N. Molecular basis of reovirus virulence. Role of the M2 gene. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):853–868. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Fields B. N. Reovirus inhibition of cellular RNA and protein synthesis: role of the S4 gene. Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Ramig R. F., Mustoe T. A., Fields B. N. A genetic map of reovirus. 1. Correlation of genome RNAs between serotypes 1, 2, and 3. Virology. 1978 Jan;84(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90218-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama K., Bishop D. H., Roy P. Analyses of the genomes of bluetongue viruses recovered in the United States. I. Oligonucleotide fingerprint studies that indicate the existence of naturally occurring reassortant BTV isolates. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):210–217. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90266-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushijima H., Clerx-Van Haaster C. M., Bishop D. H. Analyses of Patois group bunyaviruses: evidence for naturally occurring recombinant bunyaviruses and existence of immune precipitable and nonprecipitable nonvirion proteins induced in bunyavirus-infected cells. Virology. 1981 Apr 30;110(2):318–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Laver W. G., Air G. M., Schild G. C. Molecular mechanisms of variation in influenza viruses. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):115–121. doi: 10.1038/296115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Powers M. L., Fields B. N. Absolute linkage of virulence and central nervous system cell tropism of reoviruses to viral hemagglutinin. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):609–616. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


