Abstract
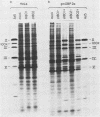
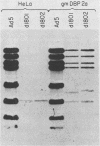
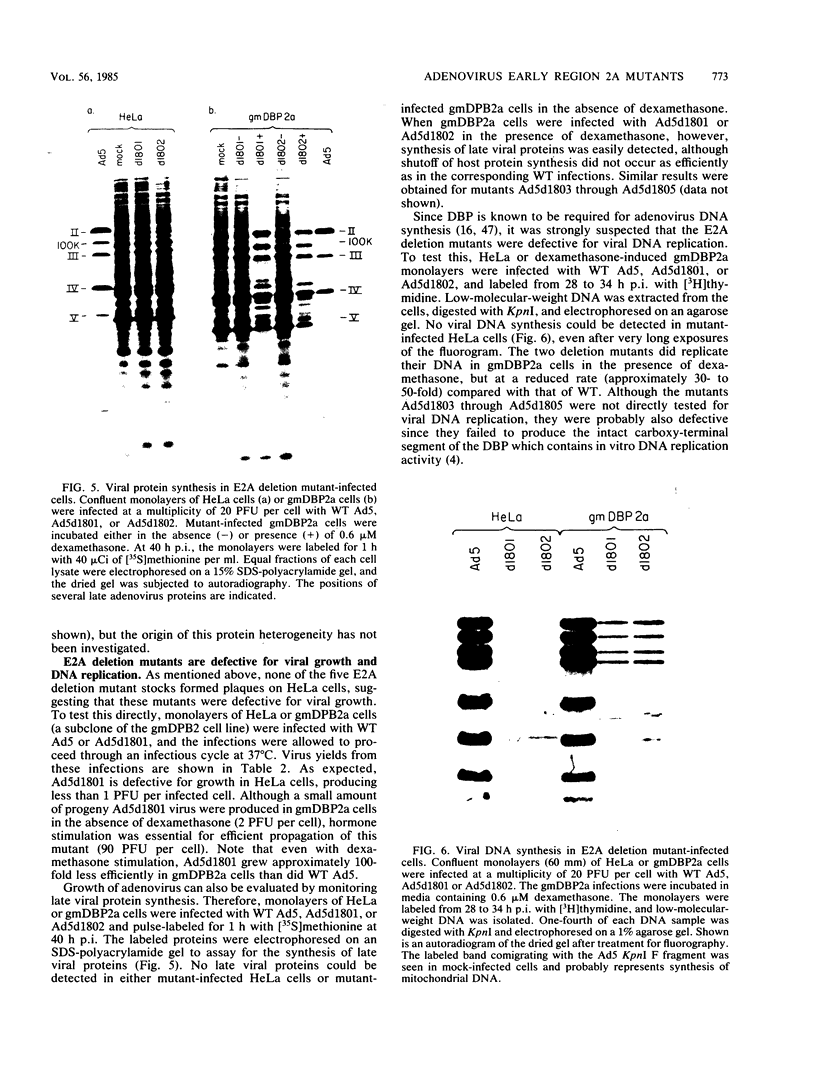
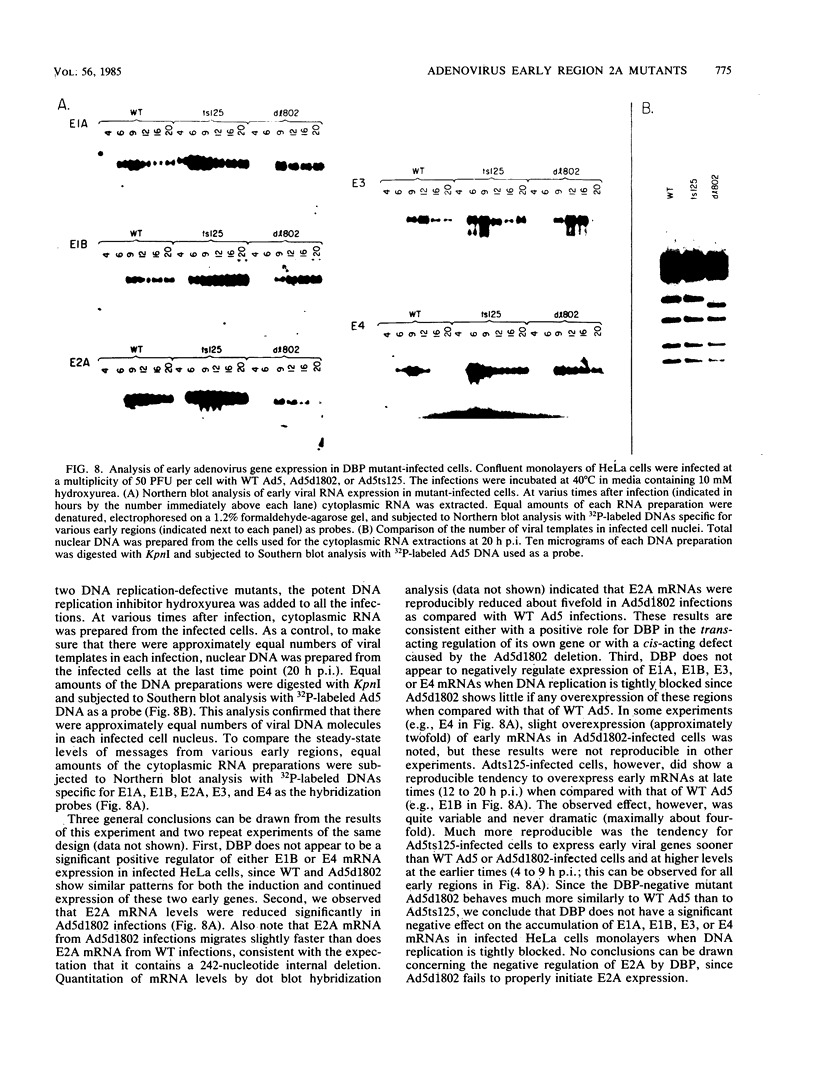
A genetic system is described which allows the isolation and propagation of adenovirus mutants containing lesions in early region 2A (E2A), the gene encoding the multifunctional adenovirus DNA-binding protein (DBP). A cloned E2A gene was first mutagenized in vitro and then was introduced into the viral genome by in vivo recombination. The E2A mutants were propagated by growth in human cell lines which express an integrated copy of the DBP gene under the control of a dexamethasone-inducible promoter (D. F. Klessig, D. E. Brough, and V. Cleghon, Mol. Cell. Biol. 4:1354-1362, 1984). The protocol was used to construct five adenovirus mutants, Ad5d1801 through Ad5d1805, which contained deletions in E2A. One of the mutants, Ad5d1802, made no detectable DBP and thus represents the first DBP-negative adenovirus mutant, while the four other mutants made truncated DBP-related polypeptides. All five mutants were completely defective for growth and plaque formation on HeLa cell monolayers. Furthermore, the two mutants which were tested, Ad5d1801 and Ad5d1802, did not replicate their DNA in HeLa cells. The mutant Ad5d1804 encoded a truncated DBP-related protein which contained an entire amino-terminal domain derived from the host range mutant Ad5hr404, a variant of Ad5 which multiplies efficiently in monkey cells. While results of a previous study suggest that the amino-terminal domain of DBP could act independently of the carboxyl-terminal domain to enhance late gene expression in monkey cells, the Ad5d1804 polypeptide failed to relieve the block to late viral protein synthesis in monkey cells. The mutant Ad5d1802 was used to study the role of DBP in the regulation of early adenovirus gene expression in infected HeLa cells. These experiments show that E2A mRNA levels are consistently reduced approximately fivefold in Ad5d1802-infected cells, suggesting either a role for DBP in the expression of its own gene or a cis-acting defect caused by the E2A deletion. DBP does not appear to play a significant role in the regulation of adenovirus early regions 1A, 1B, 3, or 4 mRNA levels in infected HeLa cell monolayers since wild-type Ad5- and Ad5d1802-infected cells showed very little difference in the patterns of expression of these genes.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. W., Hardy M. M., Dunn J. J., Klessig D. F. Independent, spontaneous mutants of adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrid Ad2+ND3 that grow efficiently in monkey cells possess indentical mutations in the adenovirus type 2 DNA-binding protein gene. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):31–39. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.31-39.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Klessig D. F. Altered mRNA splicing in monkey cells abortively infected with human adenovirus may be responsible for inefficient synthesis of the virion fiber polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4023–4027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Klessig D. F. Posttranscriptional block to synthesis of a human adenovirus capsid protein in abortively infected monkey cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):31–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariga H., Klein H., Levine A. J., Horwitz M. S. A cleavage product of the adenovirus DNA binding protein is active in DNA replication in vitro. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90510-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrand J. E. Mapping of adenovirus type 5 temperature-sensitive mutations by marker rescue in enhanced double DNA infections. J Gen Virol. 1978 Dec;41(3):573–586. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-3-573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselbergs F. A., Mathews M. B., Smart J. E. Structural characterization of the proteins encoded by adenovirus early region 2A. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 15;163(2):177–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babich A., Nevins J. R. The stability of early adenovirus mRNA is controlled by the viral 72 kd DNA-binding protein. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90206-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum S. G., Horwitz M. S., Maizel J. V., Jr Studies of the mechanism of enhancement of human adenovirus infection in monkey cells by simian virus 40. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):211–219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.211-219.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter T. H., Blanton R. A. Autoregulation of adenovirus type 5 early gene expression II. Effect of temperature-sensitive early mutations on virus RNA accumulation. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):450–456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.450-456.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter T. H., Blanton R. A. Possible role of the 72,000 dalton DNA-binding protein in regulation of adenovirus type 5 early gene expression. J Virol. 1978 Feb;25(2):664–674. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.2.664-674.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Ostrove J. M., Kelly T. J., Jr Initiation of adenovirus DNA replication: detection of covalent complexes between nucleotide and the 80-kilodalton terminal protein. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):265–270. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.265-270.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadurai G., Chinnadurai S., Green M. Enhanced infectivity of adenovirus type 2 DNA and a DNA-protein complex. J Virol. 1978 Apr;26(1):195–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.1.195-199.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber M. S., Baum S. G. Transcription of adenovirus RNA in permissive and nonpermissive infections. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):136–148. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.136-148.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey G., Lewis J. B., Grodzicker T., Bothwell A. Characterization of a fused protein specified by the adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrid Ad2+ND1 dp2. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):201–217. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.201-217.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friefeld B. R., Krevolin M. D., Horwitz M. S. Effects of the adenovirus H5ts125 and H5ts107 DNA binding proteins on DNA replication in vitro. Virology. 1983 Jan 30;124(2):380–389. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90354-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friefeld B. R., Lichy J. H., Field J., Gronostajski R. M., Guggenheimer R. A., Krevolin M. D., Nagata K., Hurwitz J., Horwitz M. S. The in vitro replication of adenovirus DNA. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;110:221–255. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46494-2_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost E., Williams J. Mapping temperature-sensitive and host-range mutations of adenovirus type 5 by marker rescue. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg H. S., Ensinger M. J., Kauffman R. S., Mayer A. J., Lundholm U. Cell transformation: a study of regulation with types 5 and 12 adenovirus temperature-sensitive mutants. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):419–426. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicker T., Lewis J. B., Anderson C. W. Conditional lethal mutants of adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrids. II. Ad2+ND1 host-range mutants that synthesize fragments of the Ad2+ND1 30K protein. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):559–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.559-571.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa H., Kingston R. E., Sharp P. A. Inhibition of adenovirus early region IV transcription in vitro by a purified viral DNA binding protein. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):545–547. doi: 10.1038/302545a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein H., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. Structure-function relationships of the adenovirus DNA-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11051–11060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Anderson C. W. Block to multiplication of adenovirus serotype 2 in monkey cells. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1650–1668. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1650-1668.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Brough D. E., Cleghon V. Introduction, stable integration, and controlled expression of a chimeric adenovirus gene whose product is toxic to the recipient human cell. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1354–1362. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Chow L. T. Incomplete splicing and deficient accumulation of the fiber messenger RNA in monkey cells infected by human adenovirus type 2. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 15;139(2):221–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Grodzicker T., Cleghon V. Construction of human cell lines which contain and express the adenovirus DNA binding protein gene by cotransformation with the HSV-1 tk gene. Virus Res. 1984;1(2):169–188. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Grodzicker T. Mutations that allow human Ad2 and Ad5 to express late genes in monkey cells map in the viral gene encoding the 72K DNA binding protein. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):957–966. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90335-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Quinlan M. P. Genetic evidence for separate functional domains on the human adenovirus specified, 72 kd, DNA binding protein. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):263–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Van Schaik F. M., Sussenbach J. S. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding adenovirus type 2 DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4493–4500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., van Schaik F. M., Sussenbach J. S. Structure and organization of the gene coding for the DNA binding protein of adenovirus type 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 25;9(18):4439–4457. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.18.4439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Atkins J. F., Baum P. R., Solem R., Gesteland R. F., Anderson C. W. Location and identification of the genes for adenovirus type 2 early polypeptides. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):141–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90264-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Enomoto T., Lichy J. H., Hurwitz J. Adenovirus DNA replication in vitro: identification of a host factor that stimulates synthesis of the preterminal protein-dCMP complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6438–6442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Winkler J. J. Regulation of early adenovirus transcription: a protein product of early region 2 specifically represses region 4 transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1893–1897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas J. C., Sarnow P., Girard M., Levine A. J. Host range temperature-conditional mutants in the adenovirus DNA binding protein are defective in the assembly of infectious virus. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):228–239. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90474-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice S. A., Klessig D. F. The function(s) provided by the adenovirus-specified, DNA-binding protein required for viral late gene expression is independent of the role of the protein in viral DNA replication. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):35–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.35-49.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Westphal H. A cascade of adenovirus early functions is required for expression of adeno-associated virus. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90367-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossini M. The role of adenovirus early region 1A in the regulation of early regions 2A and 1B expression. Virology. 1983 Nov;131(1):49–58. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90532-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter N. M., Davies W., Anderson C. W. Adenovirus coded deoxyribonucleic acid binding protein. Isolation, physical properties, and effects of proteolytic digestion. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2802–2810. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. P., Mathews M. B. DNA replication and the early to late transition in adenovirus infection. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90362-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornow J., Polvino-Bodnar M., Santangelo G., Cole C. N. Two separable functional domains of simian virus 40 large T antigen: carboxyl-terminal region of simian virus 40 large T antigen is required for efficient capsid protein synthesis. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):415–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.415-424.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vliet P. C., Sussenbach J. S. An adenovirus type 5 gene function required for initiation of viral DNA replication. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):415–426. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90443-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. F., Gharpure M., Ustacelebi S., McDonald S. Isolation of temperature-sensitive mutants of adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1971 May;11(2):95–101. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-11-2-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willians J. F., Young C. S., Austin P. E. Genetic analysis of human adenovirus type 5 in permissive and nonpermissive cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):427–437. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vliet P. C., Levine A. J. DNA-binding proteins specific for cells infected by adenovirus. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 12;246(154):170–174. doi: 10.1038/newbio246170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]