Abstract
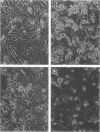
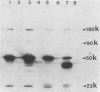
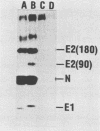
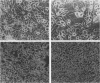
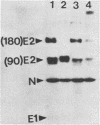
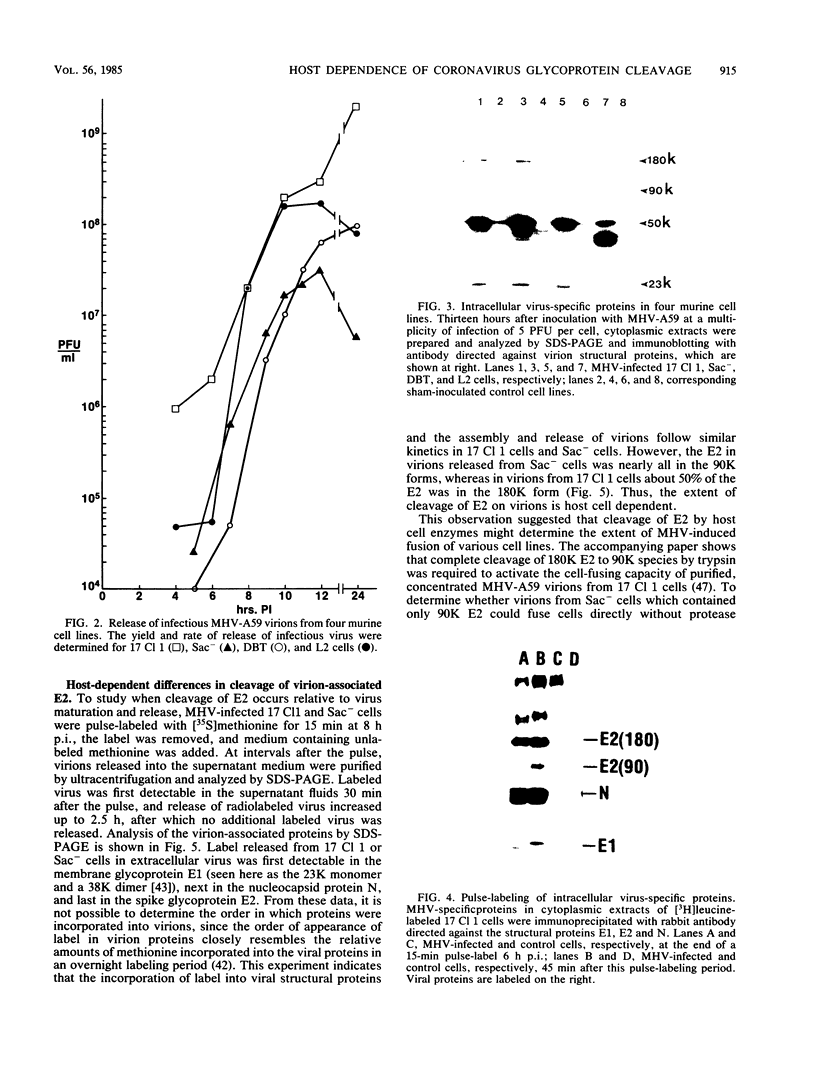
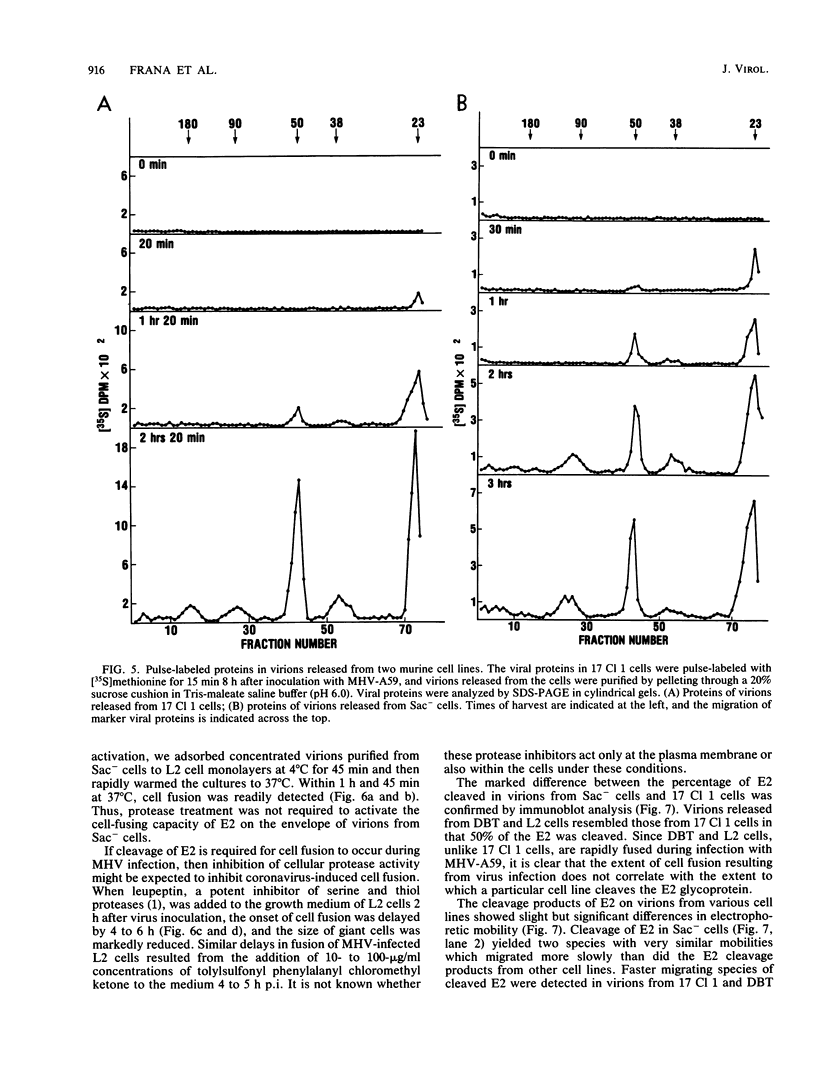
Cell fusion induced by infection with mouse hepatitis virus strain A59 (MHV-A59) varied markedly in extent and time course in four different murine cell lines. When inoculated at a multiplicity of 3 to 5 PFU per cell, the Sac-, L2, and DBT cell lines began to fuse by 7 h, were fused into confluent syncytia by 9 to 12 h, and peeled from the substrate by 10 to 14 h. These virulent virus-cell interactions were in striking contrast to the moderate interaction of MHV-A59 with the 17 Cl 1 cell line, in which only small syncytia were observed 18 h postinoculation, and greater than 50% of the cells remained unfused by 24 h. The yield of infectious virus produced by 17 Cl 1 cells was 10-fold higher than the yields from the other three cell lines. The processing of the nucleocapsid protein, the membrane glycoprotein E1, and the peplomeric glycoprotein E2 were found to differ significantly in the four cell lines. Since the E2 glycoprotein is responsible for virus-induced cell fusion, we attempted to correlate differences in cellular processing of E2 with differences in fusion of infected cells. The predominant intracellular form of E2 in all cell lines was the 180K species. Pulse-chase experiments showed that a small portion of the 17 Cl 1 cell-associated 180K E2 was cleaved by 1 h after synthesis to yield 90K E2, shown in the preceding paper to consist of two different glycoproteins called 90A and 90B (L. S. Sturman, C. S. Ricard, and K. V. Holmes, J. Virol. 56:904-911, 1985). This cleavage occurred shortly before the release of virions from cells, as shown by pulse-chase experiments. After budding at intracellular membranes, virions released into the medium by the four cell lines contained different ratios of 180K to 90K E2. Virions from Sac- cells, which contained 100% 90K E2, fused L2 cells rapidly without requiring virus replication, whereas virions from 17 Cl 1 cells, which had 50% 90K E2, required trypsin activation to induce rapid fusion (Sturman et al., J. Virol. 56:904-911, 1985). The addition of protease inhibitors to the medium markedly delayed L2 cell fusion induced by MHV infection. The extent of coronavirus-induced cell fusion does not depend solely upon the percent cleavage of the E2 glycoprotein by cellular proteases, since extensive fusion was induced by infection of L2 and DBT cells but not 17 Cl 1 cells, although all three cell lines cleaved E2 to the same extent.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleyard G., Tisdale M. Inhibition of the growth of human coronavirus 229E by leupeptin. J Gen Virol. 1985 Feb;66(Pt 2):363–366. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-2-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bang F. B. The use of a genetically incompatible combination of host and virus (MHV) for the study of mechanisms of host resistance. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;142:359–373. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0456-3_30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bang F. B., Warwick A. MOUSE MACROPHAGES AS HOST CELLS FOR THE MOUSE HEPATITIS VIRUS AND THE GENETIC BASIS OF THEIR SUSCEPTIBILITY. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Aug;46(8):1065–1075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.8.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Smith A. L. Mouse hepatitis virus strain--related patterns of tissue tropism in suckling mice. Arch Virol. 1984;81(1-2):103–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01309300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch F. X., Orlich M., Klenk H. D., Rott R. The structure of the hemagglutinin, a determinant for the pathogenicity of influenza viruses. Virology. 1979 May;95(1):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90414-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh D. Structural polypeptides of coronavirus IBV. J Gen Virol. 1981 Mar;53(Pt 1):93–103. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-53-1-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheley S., Morris V. L., Cupples M. J., Anderson R. RNA and polypeptide homology among murine coronaviruses. Virology. 1981 Dec;115(2):310–321. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90113-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins A. R., Knobler R. L., Powell H., Buchmeier M. J. Monoclonal antibodies to murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM) define the viral glycoprotein responsible for attachment and cell--cell fusion. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):358–371. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90095-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois-Dalcq M. E., Doller E. W., Haspel M. V., Holmes K. V. Cell tropism and expression of mouse hepatitis viruses (MHV) in mouse spinal cord cultures. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90092-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Fries E., Urbani L. J., Rothman J. E. Early and late functions associated with the Golgi apparatus reside in distinct compartments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7453–7457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Berk W., Nagai Y., Rott R., Klenk H. D. Mutational changes of the protease susceptibility of glycoprotein F of Newcastle disease virus: effects on pathogenicity. J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):135–147. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Bosch F. X., Linder D., Rott R., Klenk H. D. Proteolytic activation of the influenza virus hemagglutinin: The structure of the cleavage site and the enzymes involved in cleavage. Virology. 1981 Dec;115(2):361–374. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTLEY J. W., ROWE W. P. Tissue culture cytopathic and plaque assays for mouse hepatitis viruses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Jun;113:403–406. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano N., Fujiwara K., Hino S., Matumoto M. Replication and plaque formation of mouse hepatitis virus (MHV-2) in mouse cell line DBT culture. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1974;44(3):298–302. doi: 10.1007/BF01240618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. V., Choppin P. W. On the role of the response of the cell membrane in determining virus virulence. Contrasting effects of the parainfluenza virus SV5 in two cell types. J Exp Med. 1966 Sep 1;124(3):501–520. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.3.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. V., Doller E. W., Behnke J. N. Analysis of the functions of coronavirus glycoproteins by differential inhibition of synthesis with tunicamycin. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;142:133–142. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0456-3_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. V., Doller E. W., Sturman L. S. Tunicamycin resistant glycosylation of coronavirus glycoprotein: demonstration of a novel type of viral glycoprotein. Virology. 1981 Dec;115(2):334–344. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90115-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Rott R., Orlich M., Blödorn J. Activation of influenza A viruses by trypsin treatment. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):426–439. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90284-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koolen M. J., Osterhaus A. D., Van Steenis G., Horzinek M. C., Van der Zeijst B. A. Temperature-sensitive mutants of mouse hepatitis virus strain A59: isolation, characterization and neuropathogenic properties. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90211-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarowitz S. G., Choppin P. W. Enhancement of the infectivity of influenza A and B viruses by proteolytic cleavage of the hemagglutinin polypeptide. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):440–454. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90285-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarowitz S. G., Compans R. W., Choppin P. W. Proteolytic cleavage of the hemagglutinin polypeptide of influenza virus. Function of the uncleaved polypeptide HA. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):199–212. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90409-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas A., Flintoff W., Anderson R., Percy D., Coulter M., Dales S. In vivo and in vitro models of demyelinating diseases: tropism of the JHM strain of murine hepatitis virus for cells of glial origin. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):553–560. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90131-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Kawasaki K., Ohnishi S. Interaction of influenza virus hemagglutinin with target membrane lipids is a key step in virus-induced hemolysis and fusion at pH 5.2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4133–4137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh K., Dees J. H., Becker W. B., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Recovery in tracheal organ cultures of novel viruses from patients with respiratory disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):933–940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizzen L., Cheley S., Rao M., Wolf R., Anderson R. Fusion resistance and decreased infectability as major host cell determinants of coronavirus persistence. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):407–417. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90266-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Klenk H. D. Activation of precursors to both glycoporteins of Newcastle disease virus by proteolytic cleavage. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90412-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Klenk H. D., Rott R. Proteolytic cleavage of the viral glycoproteins and its significance for the virulence of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):494–508. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemann H., Boschek B., Evans D., Rosing M., Tamura T., Klenk H. D. Post-translational glycosylation of coronavirus glycoprotein E1: inhibition by monensin. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1499–1504. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01346.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemann H., Klenk H. D. Coronavirus glycoprotein E1, a new type of viral glycoprotein. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 25;153(4):993–1010. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90463-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb J. A., Bond C. W. Pathogenic murine coronaviruses. I. Characterization of biological behavior in vitro and virus-specific intracellular RNA of strongly neurotropic JHMV and weakly neurotropic A59V viruses. Virology. 1979 Apr 30;94(2):352–370. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90467-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottier P. J., Spaan W. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Translation of three mouse hepatitis virus strain A59 subgenomic RNAs in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):20–26. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.20-26.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Protease activation mutants of sendai virus. Activation of biological properties by specific proteases. Virology. 1976 Jan;69(1):265–277. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90213-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S. G., Wege H., Barthel A., ter Meulen V. Coronavirus JHM: cell-free synthesis of structural protein p60. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):10–17. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.10-17.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S., Wege H., Barthel A., ter Meulen V. Coronavirus JHM: intracellular protein synthesis. J Gen Virol. 1981 Mar;53(Pt 1):145–155. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-53-1-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S., Wege H., ter Meulen V. The structure and replication of coronaviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;99:131–163. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68528-6_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Sefton B. M. Coronavirus proteins: biogenesis of avian infectious bronchitis virus virion proteins. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):794–803. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.794-803.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz J., Rott R., Kaluza G. Enhancement of plaque formation and cell fusion of an enteropathogenic coronavirus by trypsin treatment. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1214–1222. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1214-1222.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V., Behnke J. Isolation of coronavirus envelope glycoproteins and interaction with the viral nucleocapsid. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):449–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.449-462.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V. Characterization of coronavirus II. Glycoproteins of the viral envelope: tryptic peptide analysis. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):650–660. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90489-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V. The molecular biology of coronaviruses. Adv Virus Res. 1983;28:35–112. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60721-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S. I. Structural proteins: effects of preparative conditions on the migration of protein in polyacrylamide gels. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):637–649. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90488-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Ricard C. S., Holmes K. V. Proteolytic cleavage of the E2 glycoprotein of murine coronavirus: activation of cell-fusing activity of virions by trypsin and separation of two different 90K cleavage fragments. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):904–911. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.904-911.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Takemoto K. K. Enhanced growth of a murine coronavirus in transformed mouse cells. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):501–507. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.501-507.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi F., Yamada A., Fujiwara K. Factors involved in the age-dependent resistance of mice infected with low-virulence mouse hepatitis virus. Arch Virol. 1979;62(4):333–340. doi: 10.1007/BF01318107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell D. A., Almeida J. D. Direct electron-microscopy of organ culture for the detection and characterization of viruses. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;22(3):417–425. doi: 10.1007/BF01242962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Siddell S., ter Meulen V. The biology and pathogenesis of coronaviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;99:165–200. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68528-6_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Matlin K., Helenius A. Cell fusion by Semliki Forest, influenza, and vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):674–679. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikura H., Tejima S. Role of protease in mouse hepatitis virus-induced cell fusion. Studies with a cold-sensitive mutant isolated from a persistent infection. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90178-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]