Abstract
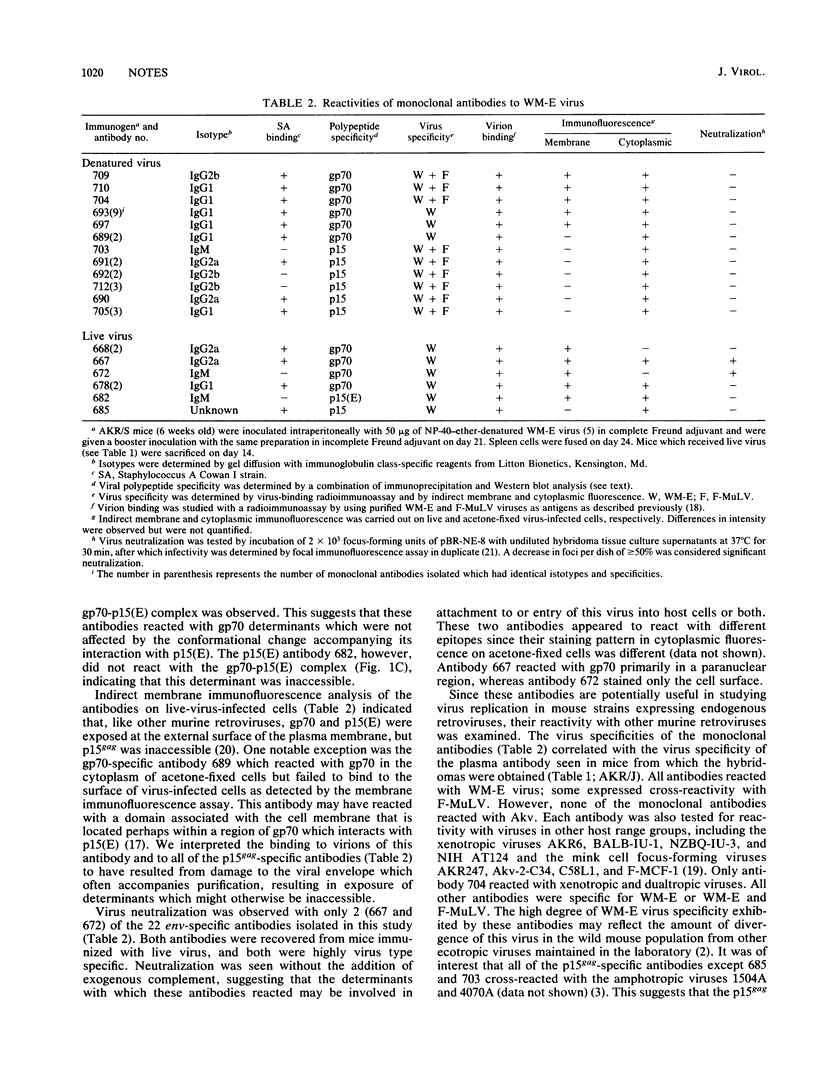
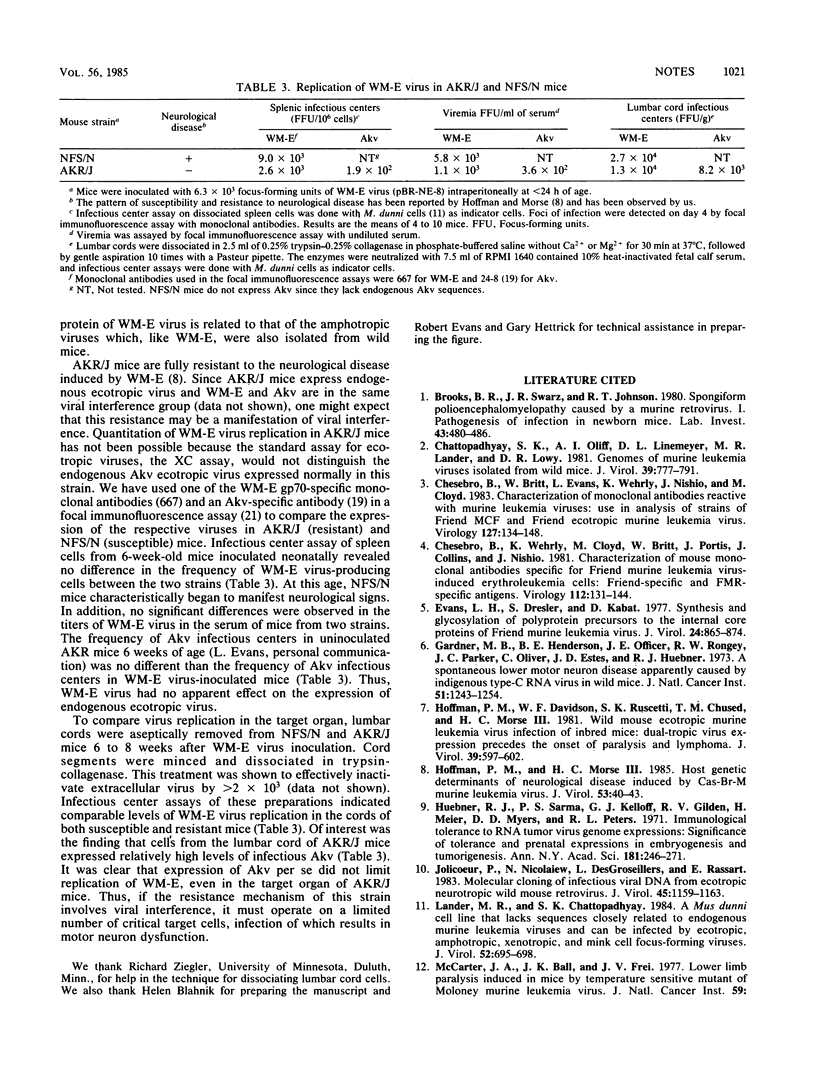
We used AKR/J mice to produce monoclonal antibodies specific for a neurotropic ecotropic (WM-E) virus initially isolated from wild mice. The rationale for this approach involved the observation that these mice were immunologically hyporesponsive to endogenous ecotropic virus (Akv) but fully responsive to type-specific determinants of WM-E. Hybridoma cell lines derived from mice immunized with both denatured and viable virus produced antibodies with specificity for three viral membrane-associated polypeptides, gp70, p15(E), and p15gag. Epitopes specific for WM-E virus were detected in each of these polypeptides. Cross-reactivity with Friend ecotropic virus (Friend murine leukemia virus) was observed with some gp70- and p15gag-specific antibodies, but no reactivity with endogenous Akv ecotropic virus was seen. The majority of these antibodies did not react with either xenotropic or mink cell focus-forming viruses. Two WM-E-specific anti-gp70 antibodies reacting with different determinants had virus-neutralizing activity in the absence of complement, suggesting that the respective epitopes may participate in receptor binding or virus penetration events. We used these monoclonal antibodies in initial studies to examine the replication of WM-E virus in neonatally inoculated AKR/J mice which are fully resistant to the paralytic disease induced by this virus. Since these mice express high levels of endogenous ecotropic virus, standard assays for ecotropic virus cannot be used to study this question. We present evidence that the resistance to disease does not involve a resistance to virus replication, since these mice expressed levels of viremia and virus replication in spleen and lumbar spinal cord comparable to susceptible NFS/N mice at a time when the latter began to manifest clinical signs of lower-motor-neuron pathology.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooks B. R., Swarz J. R., Johnson R. T. Spongiform polioencephalomyelopathy caused by a murine retrovirus. I. Pathogenesis of infection in newborn mice. Lab Invest. 1980 Nov;43(5):480–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Oliff A. I., Linemeyer D. L., Lander M. R., Lowy D. R. Genomes of murine leukemia viruses isolated from wild mice. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):777–791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.777-791.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Britt W., Evans L., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Cloyd M. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies reactive with murine leukemia viruses: use in analysis of strains of friend MCF and Friend ecotropic murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):134–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Cloyd M., Britt W., Portis J., Collins J., Nishio J. Characterization of mouse monoclonal antibodies specific for Friend murine leukemia virus-induced erythroleukemia cells: friend-specific and FMR-specific antigens. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90619-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Dresler S., Kabat D. Synthesis and glycosylation of polyprotein precursors to the internal core proteins of Friend murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1977 Dec;24(3):865–874. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.3.865-874.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B., Henderson B. E., Officer J. E., Rongey R. W., Parker J. C., Oliver C., Estes J. D., Huebner R. J. A spontaneous lower motor neuron disease apparently caused by indigenous type-C RNA virus in wild mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Oct;51(4):1243–1254. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.4.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. M., Davidson W. F., Ruscetti S. K., Chused T. M., Morse H. C., 3rd Wild mouse ecotropic murine leukemia virus infection of inbred mice: dual-tropic virus expression precedes the onset of paralysis and lymphoma. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):597–602. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.597-602.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. M., Morse H. C., 3rd Host genetic determinants of neurological disease induced by Cas-Br-M murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):40–43. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.40-43.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P., Nicolaiew N., DesGroseillers L., Rassart E. Molecular cloning of infectious viral DNA from ecotropic neurotropic wild mouse retrovirus. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1159–1163. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1159-1163.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander M. R., Chattopadhyay S. K. A Mus dunni cell line that lacks sequences closely related to endogenous murine leukemia viruses and can be infected by ectropic, amphotropic, xenotropic, and mink cell focus-forming viruses. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):695–698. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.695-698.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Jensen F., Dixon F. J., Lampert P. W. Pathogenesis of the slow disease of the central nervous system associated with wild mouse virus. II. Role of virus and host gene products. Virology. 1980 Nov;107(1):180–193. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90283-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Jensen F., Elder J., Dixon F. J., Lampert P. W. Pathogenesis of the slow disease of the central nervous system associated with wild mouse virus. III. Role of input virus and MCF recombinants in disease. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):154–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Lampert P. W., Lee S., Dixon F. J. Pathogenesis of the slow disease of the central nervous system associated with WM 1504 E virus. I. Relationship of strain susceptibility and replication to disease. Am J Pathol. 1977 Jul;88(1):193–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Vogt V. M. Identification of retrovirus matrix proteins by lipid-protein cross-linking. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 15;131(4):819–837. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter A., Honnen W. J. Topography of murine leukemia virus envelope proteins: characterization of transmembrane components. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):1056–1060. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.1056-1060.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis J. L., McAtee F. J., Cloyd M. W. Monoclonal antibodies to xenotropic and MCF murine leukemia viruses derived during the graft-versus-host reaction. Virology. 1982 Apr 15;118(1):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis J. L., McAtee F. J. Monoclonal antibodies derived during graft-versus-host reaction. II. Antibodies detect unique determinants common to many MCF viruses. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):96–105. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90464-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satake M., Luftig R. B. Comparative immunofluorescence of murine leukemia virus-derived membrane-associated antigens. Virology. 1983 Jan 30;124(2):259–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90343-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Nishio J., Wehrly K., Lodmell D., Chesebro B. Use of a focal immunofluorescence assay on live cells for quantitation of retroviruses: distinction of host range classes in virus mixtures and biological cloning of dual-tropic murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):110–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Soong M. M., MacLeod R., Gallick G. E., Yuen P. H. A group of temperature-sensitive mutants of Moloney leukemia virus which is defective in cleavage of env precursor polypeptide in infected cells also induces hind-limb paralysis in newborn CFW/D mice. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):513–518. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



