Abstract
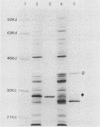
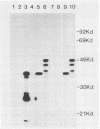
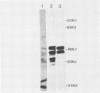
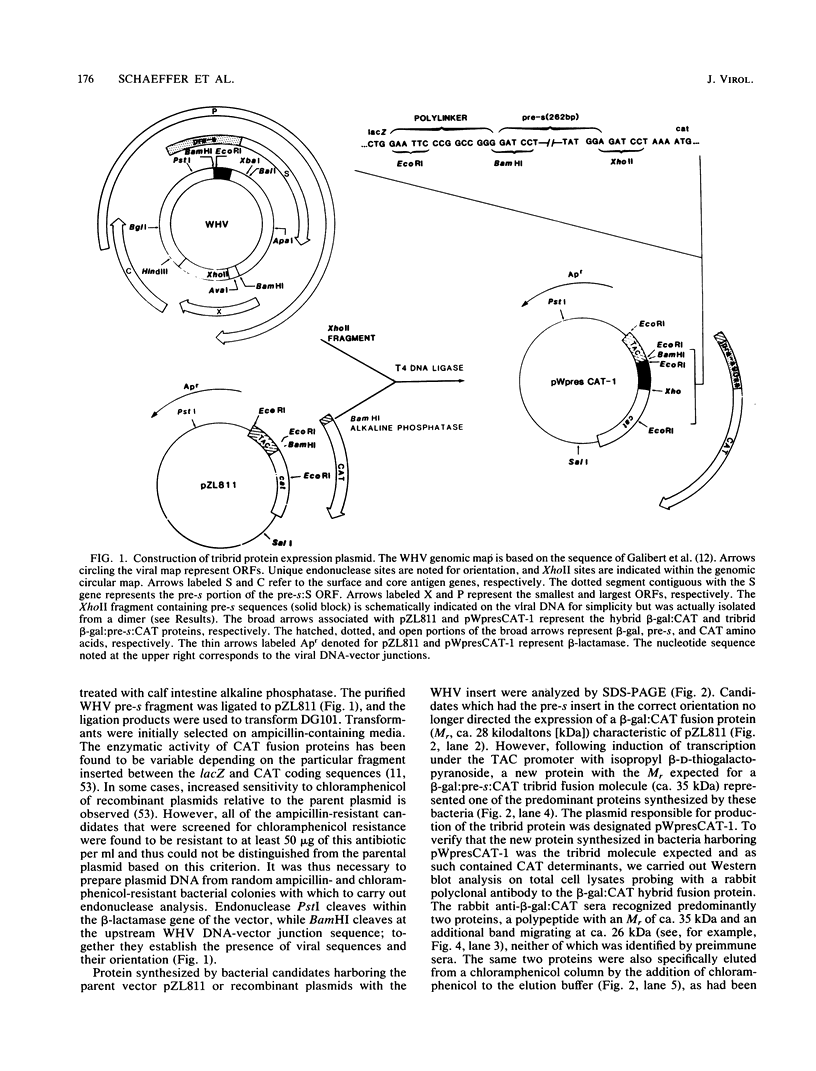
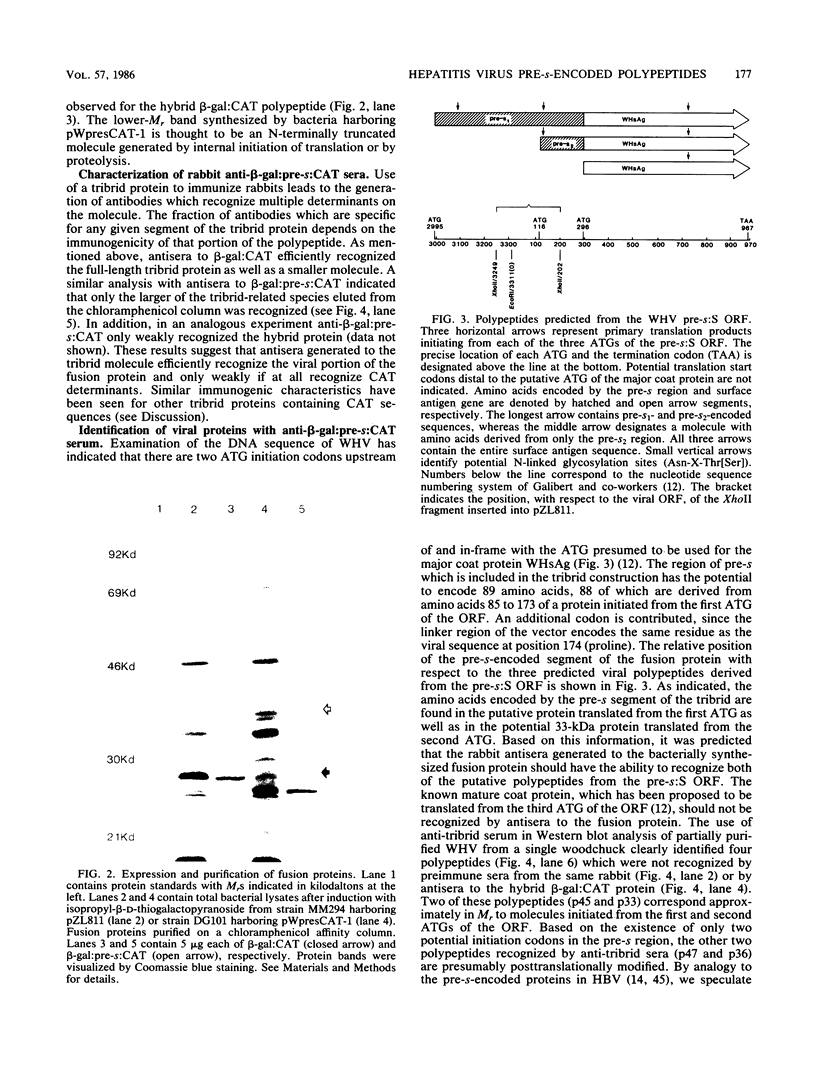
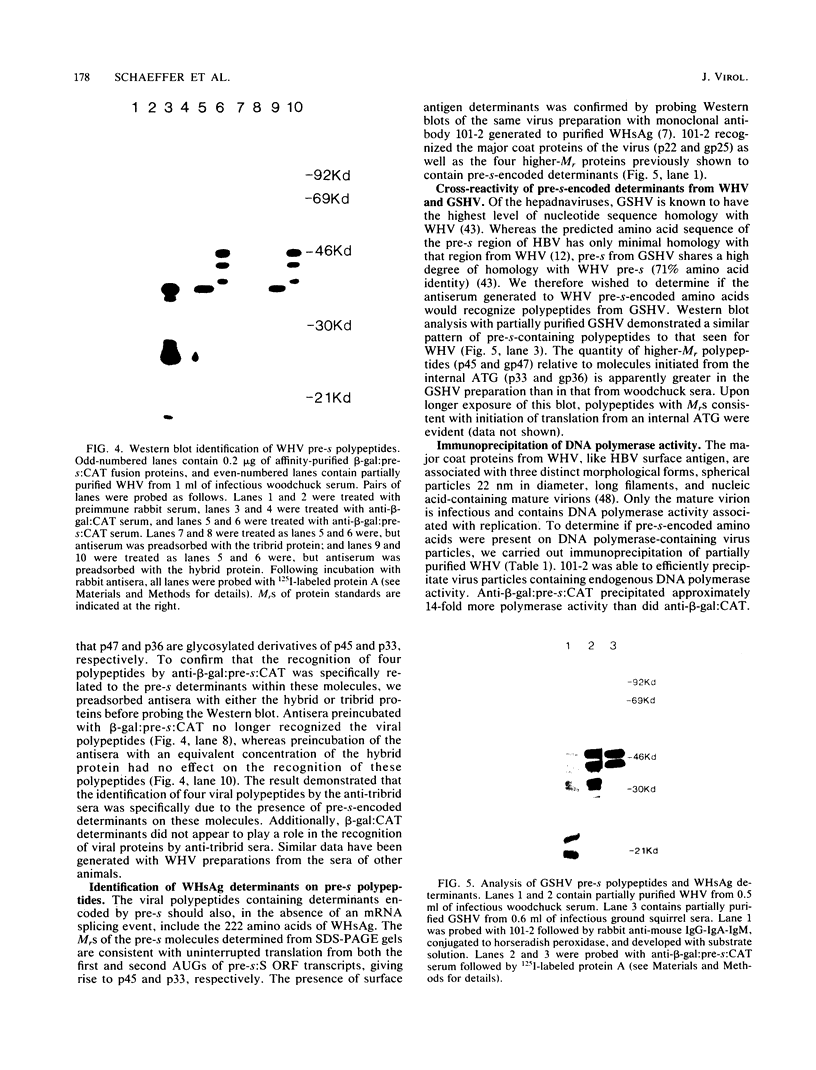
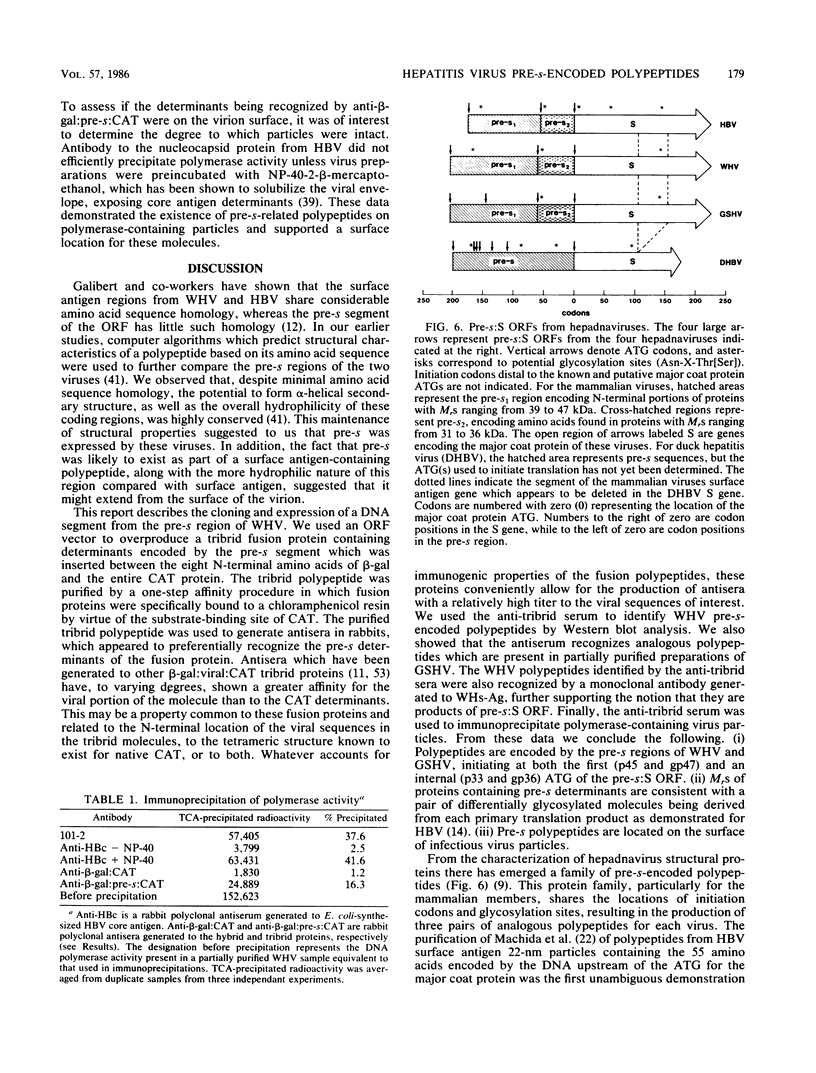
A segment from the pre-s region of the woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV) was inserted into an open reading frame vector allowing for the expression in Escherichia coli of viral determinants as part of a fusion protein. The bacterially synthesized fusion molecule contained eight amino acids from beta-galactosidase (beta-gal) at the N terminus, followed by 89 pre-s-encoded amino acids and 219 amino acids of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) at the C terminus (beta-gal:pre-s:CAT). This tribrid protein was used to generate antiserum which had a significant titer to the viral portion of the fusion polypeptide. Anti-beta-gal:pre-s:CAT was used in Western blot analysis to identify viral proteins containing pre-s-encoded determinants. Antiserum to the tribrid molecule recognized four WHV polypeptides with molecular masses of 33, 36, 45, and 47 kilodaltons, each of which was also recognized by a monoclonal antibody to WHV surface antigen. Using the same anti-tribrid serum, we also identified analogous polypeptides from ground squirrel hepatitis virus. The antiserum was also used to immunoprecipitate virus particles containing endogenous DNA polymerase activity, indicating that pre-s determinants are found on the surface of mature virions. Based on previous computer studies and the location of pre-s-encoded molecules on the surface of virus particles, a role in hepadnavirus host cell entry is suggested for these polypeptides.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alton N. K., Vapnek D. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chloramphenicol resistance transposon Tn9. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):864–869. doi: 10.1038/282864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amann E., Brosius J., Ptashne M. Vectors bearing a hybrid trp-lac promoter useful for regulated expression of cloned genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90222-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Will H., Hernandez N., Schaller H. Signals regulating hepatitis B surface antigen transcription. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):336–338. doi: 10.1038/305336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote P. J., Jr, Dapolito G. M., Shih J. W., Gerin J. L. Surface antigenic determinants of mammalian "hepadnaviruses" defined by group- and class-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):135–142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.135-142.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feitelson M. A., Marion P. L., Robinson W. S. The nature of polypeptides larger in size than the major surface antigen components of hepatitis b and like viruses in ground squirrels, woodchucks, and ducks. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):76–90. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingeroth J. D., Weis J. J., Tedder T. F., Strominger J. L., Biro P. A., Fearon D. T. Epstein-Barr virus receptor of human B lymphocytes is the C3d receptor CR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4510–4514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friefeld B. R., Korn R., de Jong P. J., Sninsky J. J., Horwitz M. S. The 140-kDa adenovirus DNA polymerase is recognized by antibodies to Escherichia coli-synthesized determinants predicted from an open reading frame on the adenovirus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2652–2656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Chen T. N., Mandart E. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned woodchuck hepatitis virus genome: comparison with the hepatitis B virus sequence. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):51–65. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.51-65.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Mandart E., Fitoussi F., Tiollais P., Charnay P. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):646–650. doi: 10.1038/281646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heermann K. H., Goldmann U., Schwartz W., Seyffarth T., Baumgarten H., Gerlich W. H. Large surface proteins of hepatitis B virus containing the pre-s sequence. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):396–402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.396-402.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Yanase Y., Nojiri T., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. A receptor for polymerized human and chimpanzee albumins on hepatitis B virus particles co-occurring with HBeAg. Gastroenterology. 1979 Feb;76(2):242–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenkei R., Onica D., Ghetie V. Receptors for polymerized albumin on liver cells. Experientia. 1977 Aug 15;33(8):1046–1047. doi: 10.1007/BF01945961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz T. L., Burrage T. G., Smith A. L., Crick J., Tignor G. H. Is the acetylcholine receptor a rabies virus receptor? Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):182–184. doi: 10.1126/science.7053569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida A., Kishimoto S., Ohnuma H., Baba K., Ito Y., Miyamoto H., Funatsu G., Oda K., Usuda S., Togami S. A polypeptide containing 55 amino acid residues coded by the pre-S region of hepatitis B virus deoxyribonucleic acid bears the receptor for polymerized human as well as chimpanzee albumins. Gastroenterology. 1984 May;86(5 Pt 1):910–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida A., Kishimoto S., Ohnuma H., Miyamoto H., Baba K., Oda K., Nakamura T., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. A hepatitis B surface antigen polypeptide (P31) with the receptor for polymerized human as well as chimpanzee albumins. Gastroenterology. 1983 Aug;85(2):268–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandart E., Kay A., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned duck hepatitis B virus genome: comparison with woodchuck and human hepatitis B virus sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):782–792. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.782-792.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L., Oshiro L. S., Regnery D. C., Scullard G. H., Robinson W. S. A virus in Beechey ground squirrels that is related to hepatitis B virus of humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2941–2945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Seal G., Summers J. Virus of Pekin ducks with structural and biological relatedness to human hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):829–836. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.829-836.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M., Yuan R. DNA restriction enzyme from E. coli. Nature. 1968 Mar 23;217(5134):1110–1114. doi: 10.1038/2171110a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. H., Marion P. L., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B viral DNA-RNA hybrid molecules in particles from infected liver are converted to viral DNA molecules during an endogenous DNA polymerase reaction. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):64–72. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90330-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millman I., Halbherr T., Simmons H. Immunological cross-reactivities of woodchuck and hepatitis B viral antigens. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):752–757. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.752-757.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Strick N., Taylor P., Stevens C. E. Hepatitis B virus contains pre-S gene-encoded domains. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):154–156. doi: 10.1038/315154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogston C. W., Jonak G. J., Rogler C. E., Astrin S. M., Summers J. Cloning and structural analysis of integrated woodchuck hepatitis virus sequences from hepatocellular carcinomas of woodchucks. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):385–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Onda H., Sasada R., Igarashi K., Sugino Y., Nishioka K. The complete nucleotide sequences of the cloned hepatitis B virus DNA; subtype adr and adw. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1747–1757. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J., Rutter W. J. Hybrid hepatitis B virus-host transcripts in a human hepatoma cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):83–87. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasek M., Goto T., Gilbert W., Zink B., Schaller H., MacKay P., Leadbetter G., Murray K. Hepatitis B virus genes and their expression in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):575–579. doi: 10.1038/282575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. L., Nath N., Gavilanes F. Structure of hepatitis B surface antigen. Correlation of subtype with amino acid sequence and location of the carbohydrate moiety. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10414–10420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H., Shih J. W., Gerin J. L., Wong D. C., Hoyer B. H., London W. T., Sly D. L., Purcell R. H. Woodchuck hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation of histologic with virologic observations. Hepatology. 1981 Mar-Apr;1(2):91–98. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pourcel C., Louise A., Gervais M., Chenciner N., Dubois M. F., Tiollais P. Transcription of the hepatitis B surface antigen gene in mouse cells transformed with cloned viral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):100–105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.100-105.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S., Greenman R. L. DNA polymerase in the core of the human hepatitis B virus candidate. J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1231–1236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1231-1236.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S., Robinson H. L. DNA polymerase in defective Rous sarcoma virus. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):457–462. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90278-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer E., Sninsky J. J. Predicted secondary structure similarity in the absence of primary amino acid sequence homology: hepatitis B virus open reading frames. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2902–2906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schottel J. L., Bibb M. J., Cohen S. N. Cloning and expression in streptomyces lividans of antibiotic resistance genes derived from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):360–368. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.360-368.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger C., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequence of an infectious molecularly cloned genome of ground squirrel hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):367–375. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.367-375.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibbe W., Gerlich W. H. Structural relationships between minor and major proteins of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):626–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.626-628.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Smolec J. M., Snyder R. A virus similar to human hepatitis B virus associated with hepatitis and hepatoma in woodchucks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4533–4537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J. Three recently described animal virus models for human hepatitis B virus. Hepatology. 1981 Mar-Apr;1(2):179–183. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmis K. N., Cabello F., Cohen S. N. Cloning and characterization of EcoRI and HindIII restriction endonuclease-generated fragments of antibiotic resistance plasmids R6-5 and R6. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jun 14;162(2):121–137. doi: 10.1007/BF00267869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong D. T., Nath N., Sninsky J. J. Identification of hepatitis B virus polypeptides encoded by the entire pre-s open reading frame. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):223–231. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.223-231.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaidenzaig Y., Shaw W. V. Affinity and hydrophobic chromatography of three variants of chloramphenicol acetyltransferases specified by R factors in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1976 Mar 1;62(3):266–271. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]