Abstract
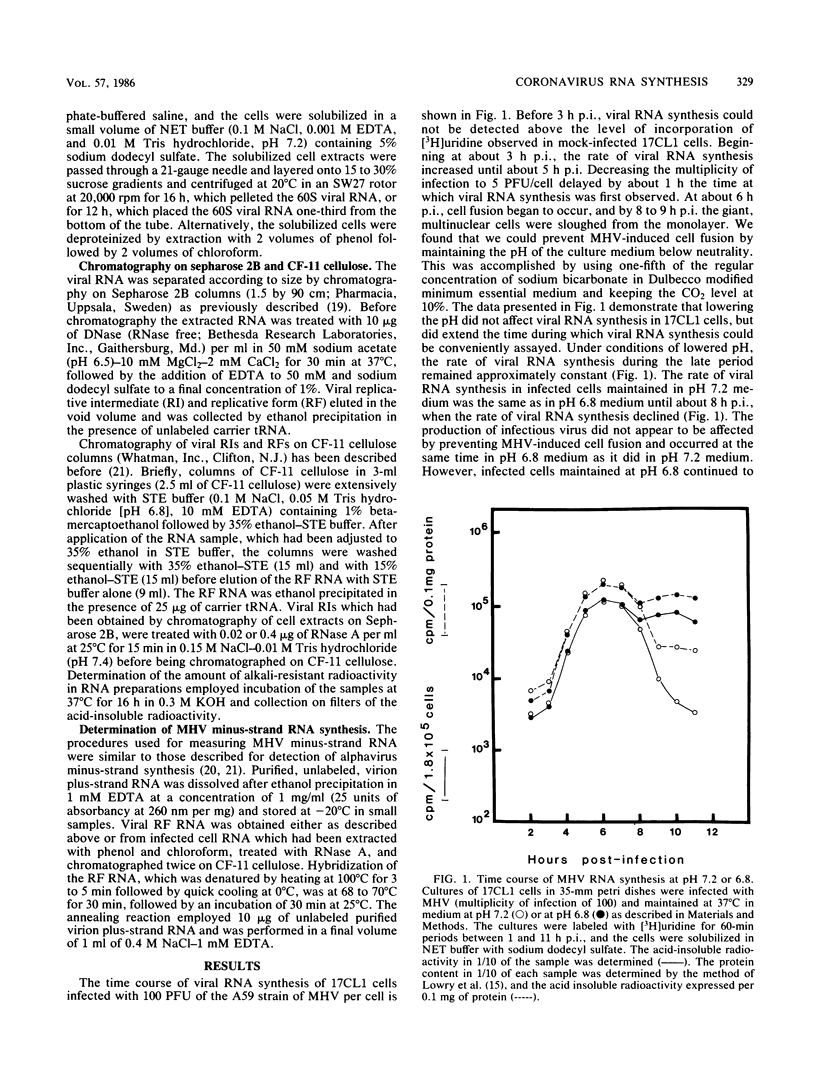
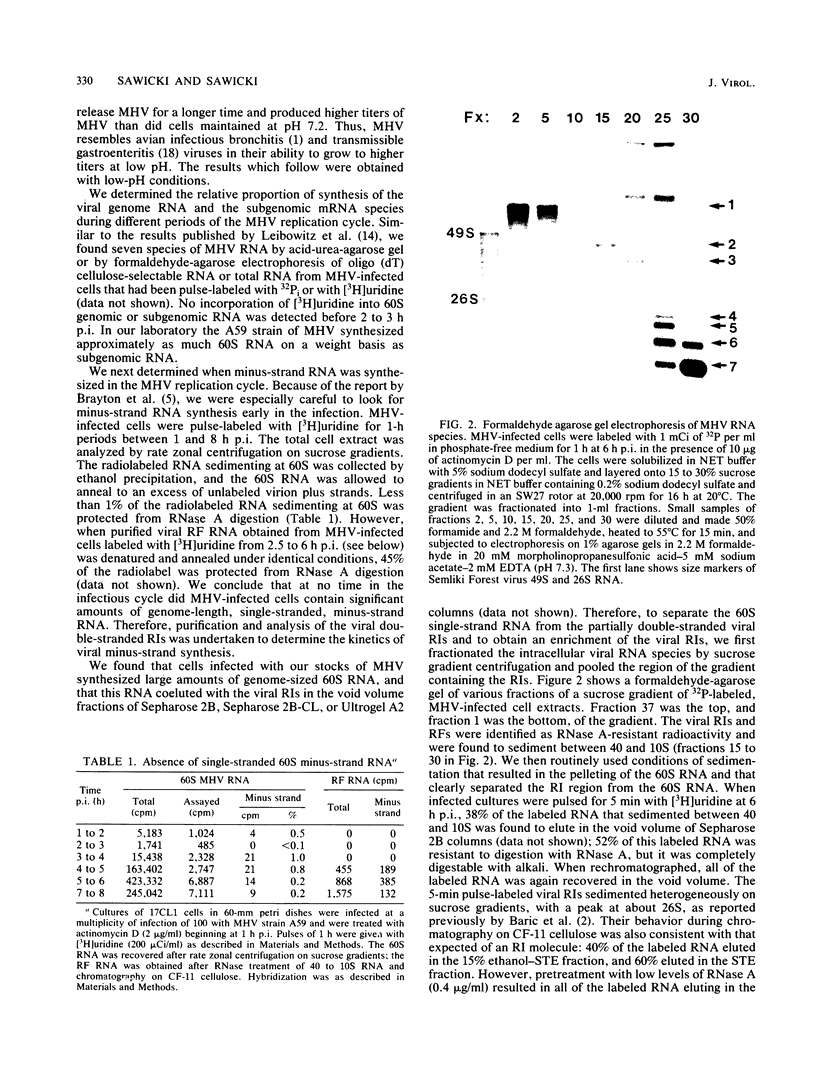
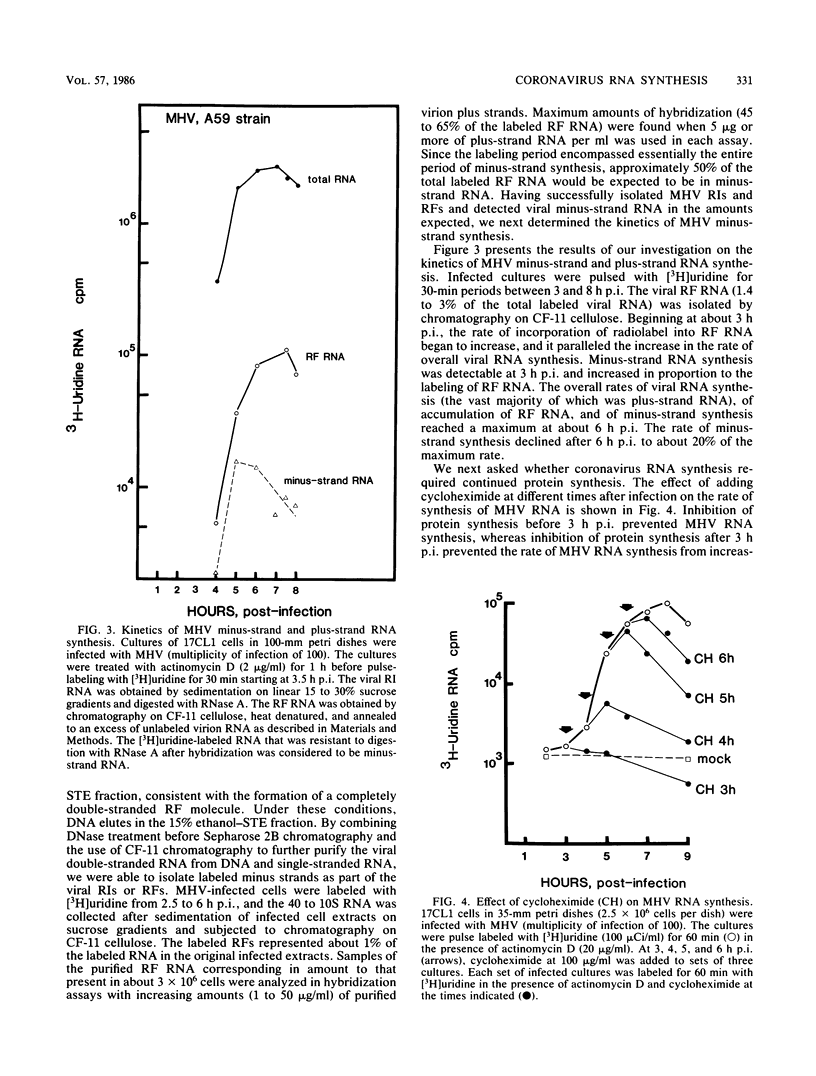
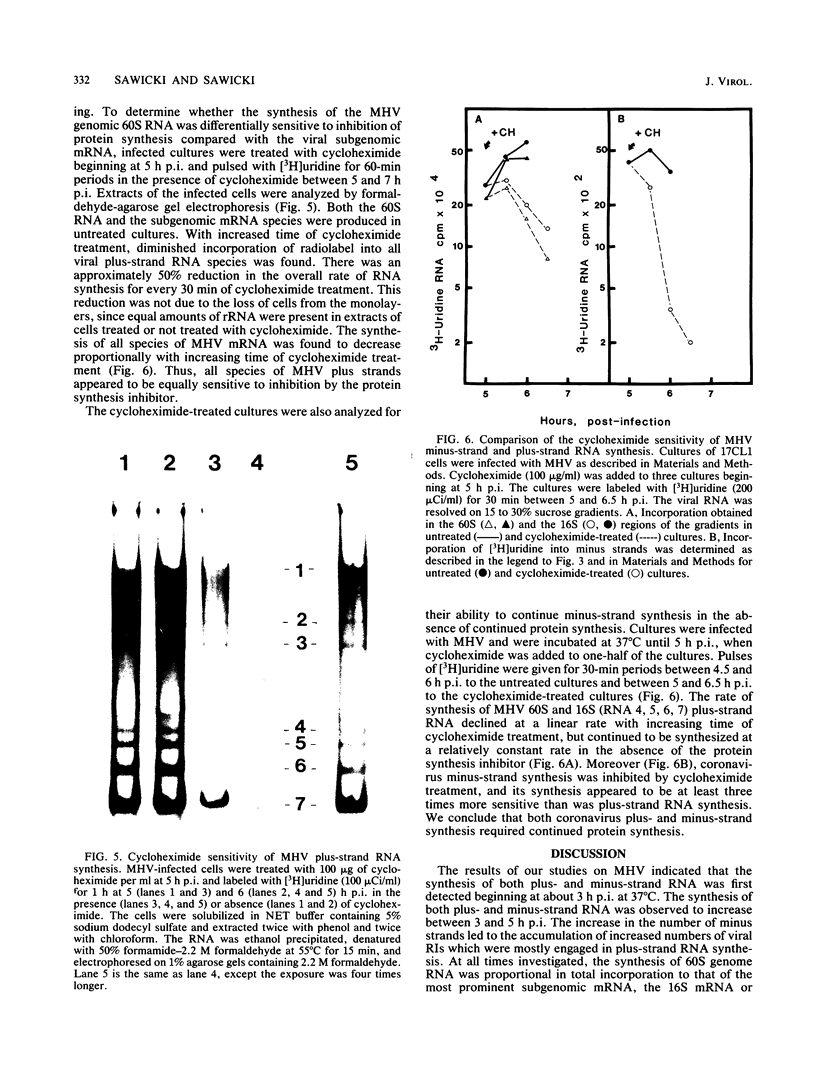
The temporal sequence of coronavirus plus-strand and minus-strand RNA synthesis was determined in 17CL1 cells infected with the A59 strain of mouse hepatitis virus (MHV). MHV-induced fusion was prevented by keeping the pH of the medium below pH 6.8. This had no effect on the MHV replication cycle, but gave 5- to 10-fold-greater titers of infectious virus and delayed the detachment of cells from the monolayer which permitted viral RNA synthesis to be studied conveniently until at least 10 h postinfection. Seven species of poly(A)-containing viral RNAs were synthesized at early and late times after infection, in nonequal but constant ratios. MHV minus-strand RNA synthesis was first detected at about 3 h after infection and was found exclusively in the viral replicative intermediates and was not detected in 60S single-stranded form in infected cells. Early in the replication cycle, from 45 to 65% of the [3H]uridine pulse-labeled RF core of purified MHV replicative intermediates was in minus-strand RNA. The rate of minus-strand synthesis peaked at 5 to 6 h postinfection and then declined to about 20% of the maximum rate. The addition of cycloheximide before 3 h postinfection prevented viral RNA synthesis, whereas the addition of cycloheximide after viral RNA synthesis had begun resulted in the inhibition of viral RNA synthesis. The synthesis of both genome and subgenomic mRNAs and of viral minus strands required continued protein synthesis, and minus-strand RNA synthesis was three- to fourfold more sensitive to inhibition by cycloheximide than was plus-strand synthesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander D. J., Collins M. S. Effect of pH on the growth and cytopathogenicity of avian infectious bronchitis virus in chick kidney cells. Arch Virol. 1975;49(4):339–348. doi: 10.1007/BF01318243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B. M., Giorgi C., Kolakofsky D. N protein of vesicular stomatitis virus selectively encapsidates leader RNA in vitro. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90475-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B. M., Leppert M., Kolakofsky D. Interaction of VSV leader RNA and nucleocapsid protein may control VSV genome replication. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90448-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brayton P. R., Lai M. M., Patton C. D., Stohlman S. A. Characterization of two RNA polymerase activities induced by mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):847–853. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.847-853.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheley S., Anderson R., Cupples M. J., Chan E. C., Morris V. L. Intracellular murine hepatitis virus-specific RNAs contain common sequences. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):596–604. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90305-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis D. E., Brian D. A. Coronavirus cell-associated RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;142:155–170. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0456-3_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis D. E., Brian D. A. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity in coronavirus- infected cells. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):153–164. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.153-164.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs L., Spaan W. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Synthesis of subgenomic mRNA's of mouse hepatitis virus is initiated independently: evidence from UV transcription mapping. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):401–406. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.401-406.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Patton C. D., Baric R. S., Stohlman S. A. Presence of leader sequences in the mRNA of mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):1027–1033. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.1027-1033.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Patton C. D., Stohlman S. A. Replication of mouse hepatitis virus: negative-stranded RNA and replicative form RNA are of genome length. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):487–492. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.487-492.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Stohlman S. A. RNA of mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):236–242. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.236-242.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz J. L., Wilhelmsen K. C., Bond C. W. The virus-specific intracellular RNA species of two murine coronaviruses: MHV-a59 and MHV-JHM. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):39–51. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90250-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman S. M., Huang A. S. RNA synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. V. Interactions between transcription and replication. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1395–1400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1395-1400.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocock D. H., Garwes D. J. The influence of pH on the growth and stability of transmissible gastroenteritis virus in vitro. Arch Virol. 1975;49(2-3):239–247. doi: 10.1007/BF01317542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki D. L., Gomatos P. J. Replication of semliki forest virus: polyadenylate in plus-strand RNA and polyuridylate in minus-strand RNA. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):446–464. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.446-464.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki D. L., Sawicki S. G. Short-lived minus-strand polymerase for Semliki Forest virus. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):108–118. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.108-118.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki S. G., Sawicki D. L., Käriäinen L., Keränen S. A Sindbis virus mutant temperature-sensitive in the regulation of minus-strand RNA synthesis. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S., Wege H., Ter Meulen V. The biology of coronaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1983 Apr;64(Pt 4):761–776. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-4-761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S., Wege H., ter Meulen V. The structure and replication of coronaviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;99:131–163. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68528-6_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W. J., Rottier P. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Isolation and identification of virus-specific mRNAs in cells infected with mouse hepatitis virus (MHV-A59). Virology. 1981 Jan 30;108(2):424–434. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90449-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W. J., Rottier P. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Sequence relationships between the genome and the intracellular RNA species 1, 3, 6, and 7 of mouse hepatitis virus strain A59. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):432–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.432-439.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W., Delius H., Skinner M. A., Armstrong J., Rottier P., Smeekens S., Siddell S. G., van der Zeijst B. Transcription strategy of coronaviruses: fusion of non-contiguous sequences during mRNA synthesis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;173:173–186. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9373-7_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Kennedy S. I. Coronavirus multiplication strategy. II. Mapping the avian infectious bronchitis virus intracellular RNA species to the genome. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):440–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.440-449.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Takemoto K. K. Enhanced growth of a murine coronavirus in transformed mouse cells. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):501–507. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.501-507.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegami T., Kuhn R. J., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Membrane-dependent uridylylation of the genome-linked protein VPg of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7447–7451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Siddell S., Sturm M., Ter Meulen V. Coronavirus JHM: characterization of intracellular viral RNA. J Gen Virol. 1981 May;54(Pt 1):213–217. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-1-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. R., Leibowitz J. L. Characterization of murine coronavirus RNA by hybridization with virus-specific cDNA probes. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jan;64(Pt 1):127–133. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Levine M. RNA synthesis by vesicular stomatitis virus and a small plaque mutant: effects of cycloheximide. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):253–264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.253-264.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W. Replication of vesicular stomatitis virus defective interfering particle RNA in vitro: transition from synthesis of defective interfering leader RNA to synthesis of full-length defective interfering RNA. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):513–522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.513-522.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]