Abstract
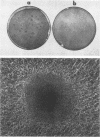
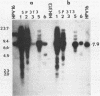
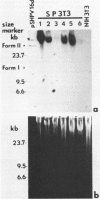
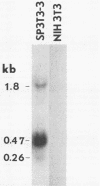
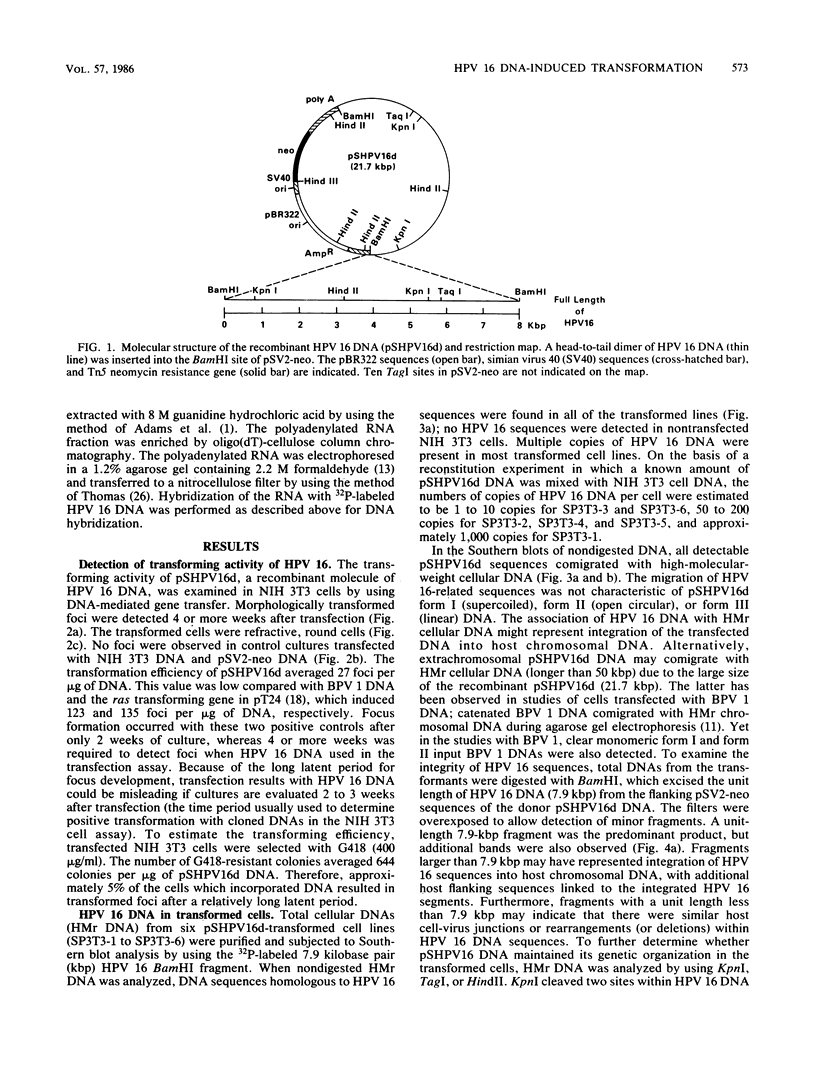
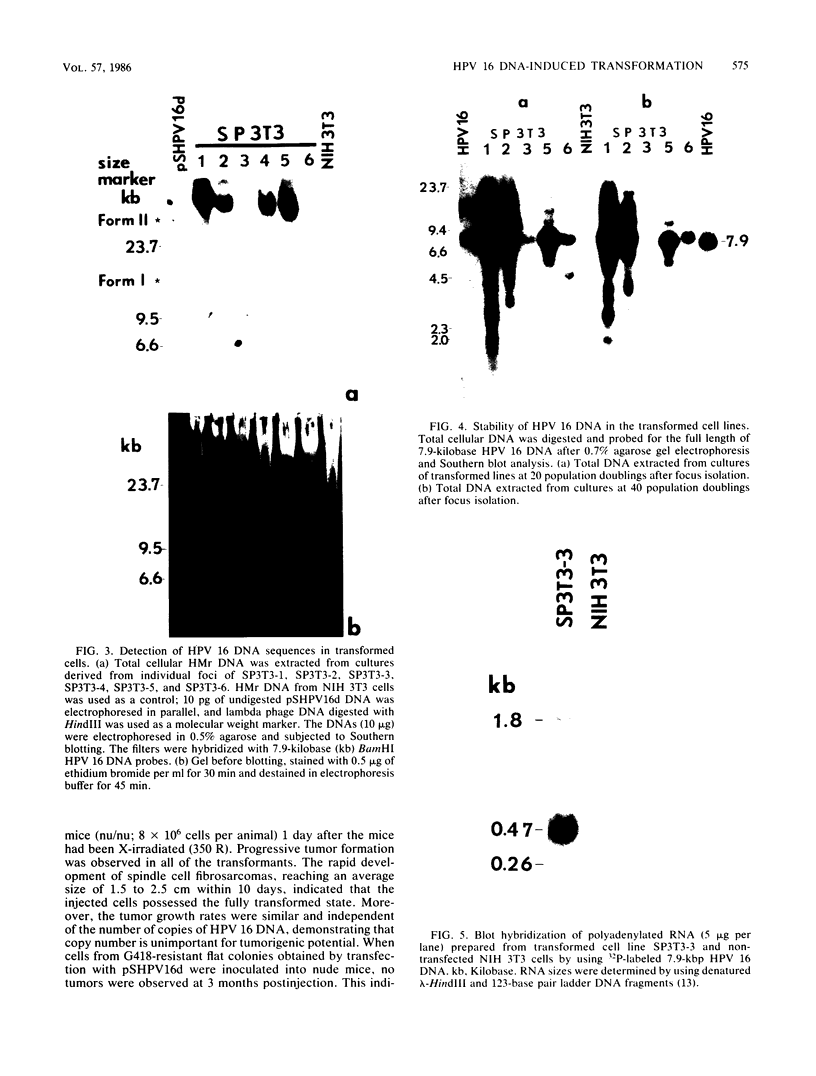
A biological function for human papillomavirus 16 (HPV 16) DNA was demonstrated by transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. HPV 16 DNA has been found frequently in genital cancer and has been classified as a papillomavirus on the basis of DNA homology. A recombinant HPV 16 DNA (pSHPV16d), which contains a head-to-tail dimer of the full-length HPV 16 genome, induced morphologic transformation; the transformed cells were tumorigenic in nude mice. Expression of transforming activity was unique because of the long latency period (more than 4 weeks) required for induction of morphologic transformation and because the transfected DNA existed primarily in a multimeric form with some rearrangements. Furthermore, virus-specific RNAs were expressed in the transformants. The transformation of NIH 3T3 cells provides a model for analyzing the functions of HPV 16, which is associated with cervical carcinomas.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. L., Sobel M. E., Howard B. H., Olden K., Yamada K. M., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Levels of translatable mRNAs for cell surface protein, collagen precursors, and two membrane proteins are altered in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3399–3403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., Kleinheinz A., Scheurlen W., zur Hausen H. A new type of papillomavirus DNA, its presence in genital cancer biopsies and in cell lines derived from cervical cancer. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campo M. S., Spandidos D. A. Molecularly cloned bovine papillomavirus DNA transforms mouse fibroblasts in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1983 Mar;64(Pt 3):549–557. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-3-549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Corbin V., Sibley E., Maniatis T. High-level expression of a cloned HLA heavy chain gene introduced into mouse cells on a bovine papillomavirus vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):340–350. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Treisman R., Maniatis T. Bovine papillomavirus vector that propagates as a plasmid in both mouse and bacterial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4030–4034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., zur Hausen H. A papillomavirus DNA from a cervical carcinoma and its prevalence in cancer biopsy samples from different geographic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3812–3815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gissmann L., Boshart M., Dürst M., Ikenberg H., Wagner D., zur Hausen H. Presence of human papillomavirus in genital tumors. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Jul;83(1 Suppl):26s–28s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12281143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groff D. E., Sundberg J. P., Lancaster W. D. Extrachromosomal deer fibromavirus DNA in deer fibromas and virus-transformed mouse cells. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):546–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90519-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. F., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. A stable bovine papillomavirus hybrid plasmid that expresses a dominant selective trait. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2110–2115. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. F., Lowy D. R., Dvoretzky I., Howley P. M. Mouse cells transformed by bovine papillomavirus contain only extrachromosomal viral DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2727–2731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehn H., Sauer G. The physical state of hybrid genomes containing simian virus 40 and bovine papilloma virus DNA sequences in transformed clonal cell lines. J Gen Virol. 1984 Aug;65(Pt 8):1413–1418. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-8-1413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. R. Genetic analysis of bovine papillomavirus type 1 trans-acting replication factors. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):955–965. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.955-965.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi Y., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R. The transforming function of bovine papillomavirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5832–5836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister H. Biology and biochemistry of papillomaviruses. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1984;99:111–181. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulciani S., Santos E., Lauver A. V., Long L. K., Barbacid M. Transforming genes in human tumors. J Cell Biochem. 1982;20(1):51–61. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240200106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. Transformation and replication in mouse cells of a bovine papillomavirus--pML2 plasmid vector that can be rescued in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7147–7151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Rabson M. S., Yang Y. C., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. Localization and analysis of bovine papillomavirus type 1 transforming functions. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):377–388. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.377-388.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Freese U. K., Gissmann L., Mayer W., Roggenbuck B., Stremlau A., zur Hausen H. Structure and transcription of human papillomavirus sequences in cervical carcinoma cells. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):111–114. doi: 10.1038/314111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Krämmer G., Dürst M., Suhai S., Röwekamp W. G. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA sequence. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90214-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts S. L., Ostrow R. S., Phelps W. C., Prince J. T., Faras A. J. Free cottontail rabbit papillomavirus DNA persists in warts and carcinomas of infected rabbits and in cells in culture transformed with virus or viral DNA. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts S. L., Phelps W. C., Ostrow R. S., Zachow K. R., Faras A. J. Cellular transformation by human papillomavirus DNA in vitro. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):634–636. doi: 10.1126/science.6330900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee C., Krishnan-Hewlett I., Baker C. C., Schlegel R., Howley P. M. Presence and expression of human papillomavirus sequences in human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jun;119(3):361–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Human papillomaviruses and their possible role in squamous cell carcinomas. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1977;78:1–30. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66800-5_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]