Abstract
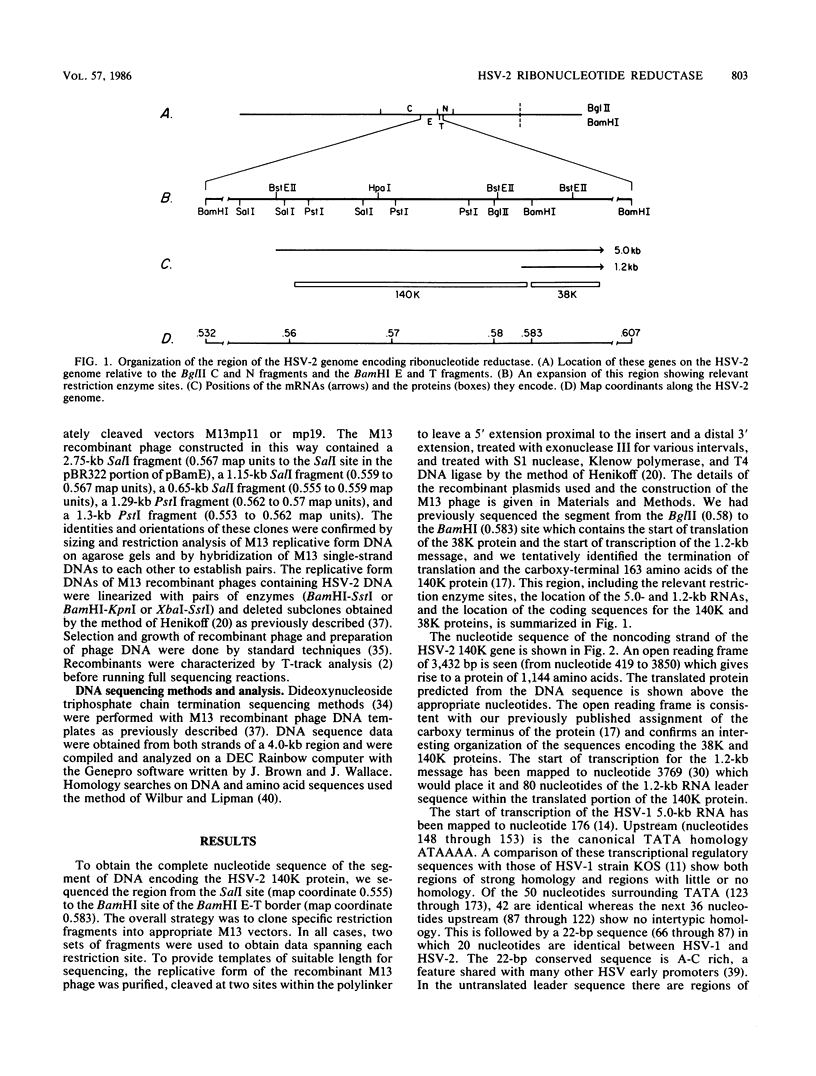
We have previously described a transcription unit located between map coordinates 0.558 and 0.595 on the herpes simplex virus type 2 strain 333 genome which encodes two mRNAs of 5.0 and 1.2 kilobases that share a common 3' terminus, and we have determined the nucleotide sequence of a 38,000-dalton protein specified by the smaller RNA (D. A. Galloway and M. A. Swain, J. Virol. 49:724-730, 1984). The entire nucleotide sequence of the 140,000-dalton protein specified by a 3,432-base-pair open reading frame within the large mRNA is presented, as are transcriptional regulatory sequences upstream of the RNA. The 140,000-dalton protein shows strong homology with the large subunit of well-characterized ribonucleotide reductase enzymes from the mouse and from Escherichia coli and with an Epstein-Barr virus gene. The 38,000-dalton protein has been shown previously to have homology with the small subunit of these enzymes (B.-M. Sjoberg, H. Eklund, J. A. Fuchs, J. Carlson, N. M. Standart, J. V. Ruderman, S. J. Bray, and T. Hunt, FEBS Lett. 183:99-102, 1985). This is the first example of a herpesvirus transcriptional unit that encodes functionally related proteins.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. P., Frink R. J., Devi G. B., Gaylord B. H., Costa R. H., Wagner E. K. Detailed characterization of the mRNA mapping in the HindIII fragment K region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):1011–1027. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.1011-1027.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. Shotgun DNA sequencing using cloned DNase I-generated fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3015–3027. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aurelian L., Kessler I. I., Rosenshein N. B., Barbour G. Viruses and gynecologic cancers: herpesvirus protein (ICP 10/AG-4), a cervical tumor antigen that fulfills the criteria for a marker of carcinogenicity. Cancer. 1981 Jul 15;48(2 Suppl):455–471. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810715)48:1+<455::aid-cncr2820481306>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacchetti S., Evelegh M. J., Muirhead B., Sartori C. S., Huszar D. Immunological characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2 polypeptide(s) involved in viral ribonucleotide reductase activity. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):591–593. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.591-593.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caras I. W., Levinson B. B., Fabry M., Williams S. R., Martin D. W., Jr Cloned mouse ribonucleotide reductase subunit M1 cDNA reveals amino acid sequence homology with Escherichia coli and herpesvirus ribonucleotide reductases. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7015–7022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson J., Fuchs J. A., Messing J. Primary structure of the Escherichia coli ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4294–4297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Factor M. N., Ponce de Leon M. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 2 replication by thymidine. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):20–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.20-25.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H. Ribonucleotide reductase activity of synchronized KB cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1972 Mar;9(3):408–418. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.3.408-418.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. C., Henry B. E., Randall C. C., O'Callaghan D. J. Ribonucleotide reductase activity in hydroxyurea-resistant herpesvirus replication. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Jul;155(3):395–399. doi: 10.3181/00379727-155-39815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper K. G., Frink R. J., Wagner E. K. Detailed characterization of an apparently unspliced beta herpes simplex virus type 1 gene mapping in the interior of another. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1123–1128. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1123-1128.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutia B. M. Ribonucleotide reductase induced by herpes simplex virus has a virus-specified constituent. J Gen Virol. 1983 Mar;64(Pt 3):513–521. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-3-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame M. C., Marsden H. S., Dutia B. M. The ribonucleotide reductase induced by herpes simplex virus type 1 involves minimally a complex of two polypeptides (136K and 38K). J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1581–1587. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Draper K. G., Wagner E. K. Uninfected cell polymerase efficiently transcribes early but not late herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6139–6143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., Goldstein L. C., Lewis J. B. Identification of proteins encoded by a fragment of herpes simplex virus type 2 DNA that has transforming activity. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):530–537. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.530-537.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., Nelson J. A., McDougall J. K. Small fragments of herpesvirus DNA with transforming activity contain insertion sequence-like structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4736–4740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., Swain M. A. Organization of the left-hand end of the herpes simplex virus type 2 BglII N fragment. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):724–730. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.724-730.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T., Stockwell P., Ginsburg M., Barrell B. Homology between two EBV early genes and HSV ribonucleotide reductase and 38K genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):5087–5099. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.5087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. C., Corey L., McDougall J. K., Tolentino E., Nowinski R. C. Monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex viruses: use in antigenic typing and rapid diagnosis. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):829–837. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry B. E., Glaser R., Hewetson J., O'Callaghan D. J. Expression of altered ribonucleotide reductase activity associated with the replication of the Epstein-Barr virus. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):262–271. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XI. Identification and relative molar rates of synthesis of structural and nonstructural herpes virus polypeptides in the infected cell. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1347–1365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1347-1365.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huszar D., Bacchetti S. Is ribonucleotide reductase the transforming function of herpes simplex virus 2? Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):76–79. doi: 10.1038/302076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huszar D., Beharry S., Bacchetti S. Herpes simplex virus-induced ribonucleotide reductase: development of antibodies specific for the enzyme. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jun;64(Pt 6):1327–1335. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-6-1327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jariwalla R. J., Aurelian L., Ts'o P. O. Tumorigenic transformation induced by a specific fragment of DNA from herpes simplex virus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2279–2283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lankinen H., Gräslund A., Thelander L. Induction of a new ribonucleotide reductase after infection of mouse L cells with pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):893–900. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.893-900.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougall J. K., Crum C. P., Fenoglio C. M., Goldstein L. C., Galloway D. A. Herpesvirus-specific RNA and protein in carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3853–3857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Clements J. B. A 3' co-terminus of two early herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):501–512. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Clements J. B. DNA sequence homology between two co-linear loci on the HSV genome which have different transforming abilities. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1953–1961. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01684.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Clements J. B. Organization of the herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription unit encoding two early proteins with molecular weights of 140000 and 40000. J Gen Virol. 1983 May;64(Pt 5):997–1006. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-5-997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Courtney R. J. Polypeptide synthesized in herpes simplex virus type 2-infected HEp-2 cells. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G., Palfreyman J. W., Dutia B. M. Identification of a herpes simplex virus type 1 polypeptide which is a component of the virus-induced ribonucleotide reductase. J Gen Virol. 1984 Sep;65(Pt 9):1457–1466. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-9-1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichard P., Ehrenberg A. Ribonucleotide reductase--a radical enzyme. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):514–519. doi: 10.1126/science.6306767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier P. H., Cortese R. A fast and simple method for sequencing DNA cloned in the single-stranded bacteriophage M13. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 25;129(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöberg B. M., Eklund H., Fuchs J. A., Carlson J., Standart N. M., Ruderman J. V., Bray S. J., Hunt T. Identification of the stable free radical tyrosine residue in ribonucleotide reductase. A sequence comparison. FEBS Lett. 1985 Apr 8;183(1):99–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80962-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain M. A., Peet R. W., Galloway D. A. Characterization of the gene encoding herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoprotein C and comparison with the type 1 counterpart. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):561–569. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.561-569.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelander L., Reichard P. Reduction of ribonucleotides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:133–158. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



