Abstract
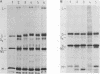
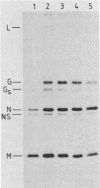
Gs protein is a shorter, soluble form of the viral G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) lacking the membrane-anchoring domain. Production of Gs protein appears to be a general property of VSV because infection of BHK-21 cells by five different isolates of the VSV serotype Indiana led in all cases to the synthesis of Gs protein. Moreover, it is formed in a variety of eucaryotic cell lines after VSV infection. In pulse-chase experiments, we observed a time-dependent change in the ratio of G to Gs protein released into the growth medium, suggesting that Gs is formed intracellularly rather than on the cell surface. Further experiments revealed that Gs protein can be synthesized in vitro in the reticulocyte lysate system after addition of a viral mRNA fraction and in a coupled transcription-translation system with VSV core particles. In the presence of microsomal membranes both G and Gs protein were glycosylated in the reticulocyte lysate, confirming that the authentic Gs protein is synthesized in vitro. The addition of various protease inhibitors to the cell-free system and variation of the incubation conditions did not alter the ratio of G to Gs formation. Taken together, these experiments suggest strongly that Gs protein is not a product of a membrane-associated proteolytic activity but is formed during or shortly after the translation process. Our attempts to detect a specific, shorter mRNA coding for the Gs protein by molecular hybridization procedures did not reveal the existence of such a mRNA species.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Huang A. S., Stampfer M. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus, II. An RNA polymerase in the virion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):572–576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bantle J. A., Maxwell I. H., Hahn W. E. Specificity of oligo (dT)-cellulose chromatography in the isolation of polyadenylated RNA. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:413–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90549-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolognesi D. P., Langlois A. J., Schäfer W. Polypeptides of mammalian oncornaviruses. IV. Structural components of murine leukemia virus released as soluble antigens in cell culture. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):550–555. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90297-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breindl M., Holland J. J. Coupled in vitro transcription and translation of vesicular stomatitis virus messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2545–2549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briley P. A., Sibilli L., Chalvignac M. A., Cossart P., Le Bras G., De Wolf A., Cohen G. N. The primary structure of Escherichia coli K12 aspartokinase I-homoserine dehydrogenase I. Site of limited proteolytic cleavage by subtilisin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8867–8871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Morrison T. G. Characterization of the soluble glycoprotein released from vesicular stomatitis virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):80–90. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.80-90.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Morrison T. G. Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein is anchored to intracellular membranes near its carboxyl end and is proteolytically cleaved at its amino terminus. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):957–963. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.957-963.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzschold B., Wiktor T. J., Wunner W. H., Varrichio A. Chemical and immunological analysis of the rabies soluble glycoprotein. Virology. 1983 Jan 30;124(2):330–337. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90349-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florkiewicz R. Z., Smith A., Bergmann J. E., Rose J. K. Isolation of stable mouse cell lines that express cell surface and secreted forms of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1381–1388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman G. J., Rose J. K., Clinton G. M., Huang A. S. RNA synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. VII. Complete separation of the mRNA's of vesicular stomatitis virus by duplex formation. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1094–1104. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1094-1104.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallione C. J., Rose J. K. A single amino acid substitution in a hydrophobic domain causes temperature-sensitive cell-surface transport of a mutant viral glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):374–382. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.374-382.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garreis-Wabnitz C., Kruppa J. Intracellular appearance of a glycoprotein in VSV-infected BHK cells lacking the membrane-anchoring oligopeptide of the viral G-protein. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1469–1476. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01998.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeve L., Goemann W., Földi P., Kruppa J. Fractionation of biologically active messenger RNAs by HPLC gel filtration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug 31;107(4):1559–1565. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Kuehn M., Delius H., Jaenisch R. Insertion of retrovirus into the first intron of alpha 1(I) collagen gene to embryonic lethal mutation in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1504–1508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. C., Ivatt R. J. Synthesis and processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:555–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving R. A., Ghosh H. P. Shedding of vesicular stomatitis virus soluble glycoprotein by removal of carboxy-terminal peptide. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):322–325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.322-325.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving R. A., Toneguzzo F., Rhee S. H., Hofmann T., Ghosh H. P. Synthesis and assembly of membrane glycoproteins: presence of leader peptide in nonglycosylated precursor of membrane glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):570–574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Prevec L. Proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. II. Immunological comparisons of viral antigens. J Virol. 1970 Jul;6(1):20–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.1.20-27.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Choppin P. W. Glycolipid content of vesicular stomatitis virus grown in baby hamster kidney cells. J Virol. 1971 Mar;7(3):416–417. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.3.416-417.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruppa J. Transfer of carbohydrates on to nascent glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 1;181(2):295–300. doi: 10.1042/bj1810295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. P., Huang A. S. Shedding of the glycoprotein from vesicular stomatitis virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):330–339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.330-339.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. P., Huang A. S. Synthesis and distribution of vesicular stomatitis virus-specific polypeptides in the absence of progeny production. Virology. 1977 Aug;81(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J. J., Wagner R. R. Lipid composition of purified vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):59–70. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.59-70.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd J. A., Summers D. F. Protein synthesis in vesicular stomatitis virus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1970 Oct;42(2):328–340. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racevskis J., Sarkar N. H. Synthesis and processing of precursor polypeptides to murine mammary tumor virus structural proteins. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):374–383. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.374-383.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Bergmann J. E. Altered cytoplasmic domains affect intracellular transport of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):513–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Bergmann J. E. Expression from cloned cDNA of cell-surface secreted forms of the glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus in eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):753–762. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Gallione C. J. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus G and M proteins determined from cDNA clones containing the complete coding regions. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.519-528.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Welch W. J., Sefton B. M., Esch F. S., Ling N. C. Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein is anchored in the viral membrane by a hydrophobic domain near the COOH terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3884–3888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Lodish H. F. Synchronised transmembrane insertion and glycosylation of a nascent membrane protein. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):775–780. doi: 10.1038/269775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert M., Harmison G. G., Meier E. Primary structure of the vesicular stomatitis virus polymerase (L) gene: evidence for a high frequency of mutations. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):505–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.505-514.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toneguzzo F., Ghosh H. P. In vitro synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus membrane glycoprotein and insertion into membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):715–719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G., Dobberstein B. Protein transfer across microsomal membranes reassembled from separated membrane components. Nature. 1978 Jun 15;273(5663):569–571. doi: 10.1038/273569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]