Abstract
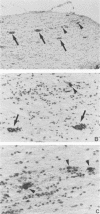
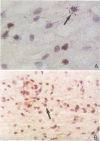
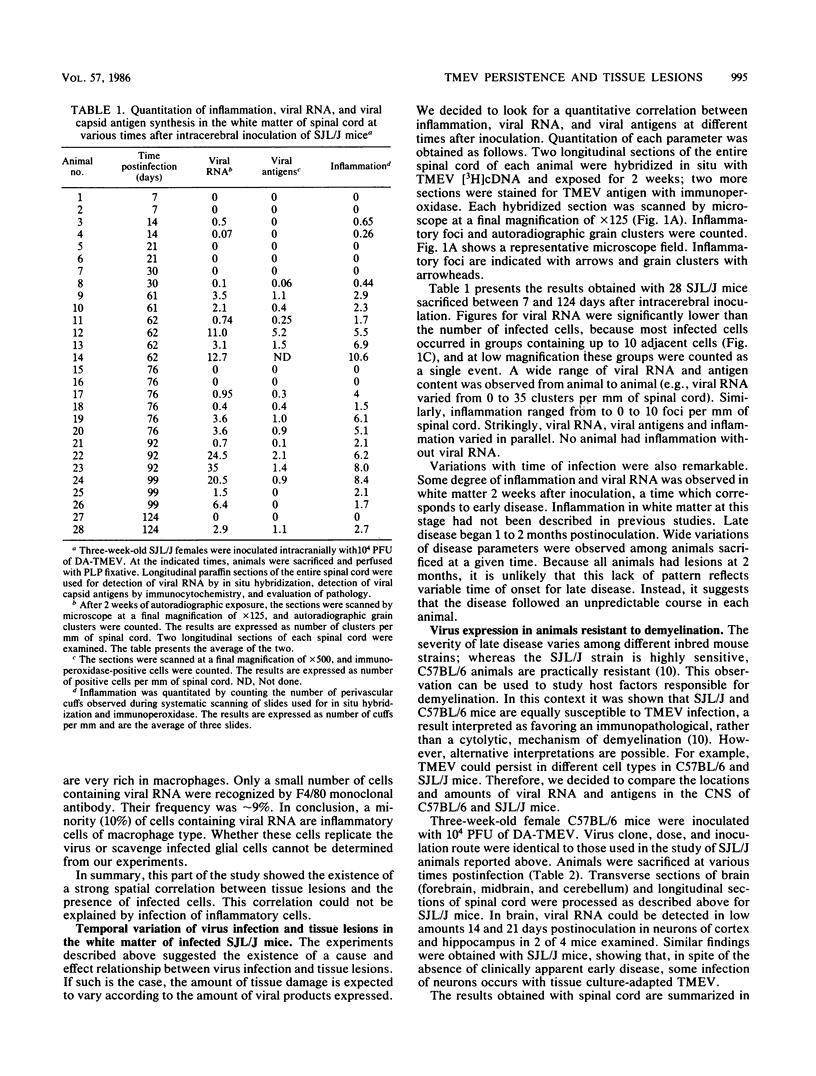
We used in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry to look for a correlation between virus expression and white matter lesions during late demyelinating disease due to persistent Theiler's virus infection. We found the following. (i) Tissue lesions developed at the site of virus infection. This correlation was not explained by infection of lymphocytes and macrophages. (ii) Large differences in the extent of pathology existed between mice. The amount of inflammation paralleled the number of cells containing viral RNA or viral capsid antigens. (iii) C57BL/6 mice, which are resistant to demyelination, were able to eradicate the infection. Our results are strongly in favor of a mechanism of demyelination in which viral gene products play a central role.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brahic M., Haase A. T., Cash E. Simultaneous in situ detection of viral RNA and antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5445–5448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahic M., Stroop W. G., Baringer J. R. Theiler's virus persists in glial cells during demyelinating disease. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash E., Chamorro M., Brahic M. Theiler's virus RNA and protein synthesis in the central nervous system of demyelinating mice. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):290–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90327-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dal Canto M. C., Lipton H. L. Primary demyelination in Theiler's virus infection. An ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1975 Dec;33(6):626–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dal Canto M. C., Lipton H. L. Ultrastructural immunohistochemical localization of virus in acute and chronic demyelinating Theiler's virus infection. Am J Pathol. 1982 Jan;106(1):20–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume D. A., Gordon S. Mononuclear phagocyte system of the mouse defined by immunohistochemical localization of antigen F4/80. Identification of resident macrophages in renal medullary and cortical interstitium and the juxtaglomerular complex. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1704–1709. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L., Dal Canto M. C. Susceptibility of inbred mice to chronic central nervous system infection by Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):369–374. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.369-374.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L., Dal Canto M. C. Theiler's virus-induced demyelination: prevention by immunosuppression. Science. 1976 Apr 2;192(4234):62–64. doi: 10.1126/science.176726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L. Theiler's virus infection in mice: an unusual biphasic disease process leading to demyelination. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1147–1155. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1147-1155.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez M., Leibowitz J. L., Lampert P. W. Persistent infection of oligodendrocytes in Theiler's virus-induced encephalomyelitis. Ann Neurol. 1983 Apr;13(4):426–433. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos R. P., Firestone S., Wollmann R., Variakojis D., Arnason B. G. The effect of short-term and chronic immunosuppression on Theiler's virus demyelination. J Neuroimmunol. 1982 Jun;2(3-4):223–234. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(82)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]