Abstract
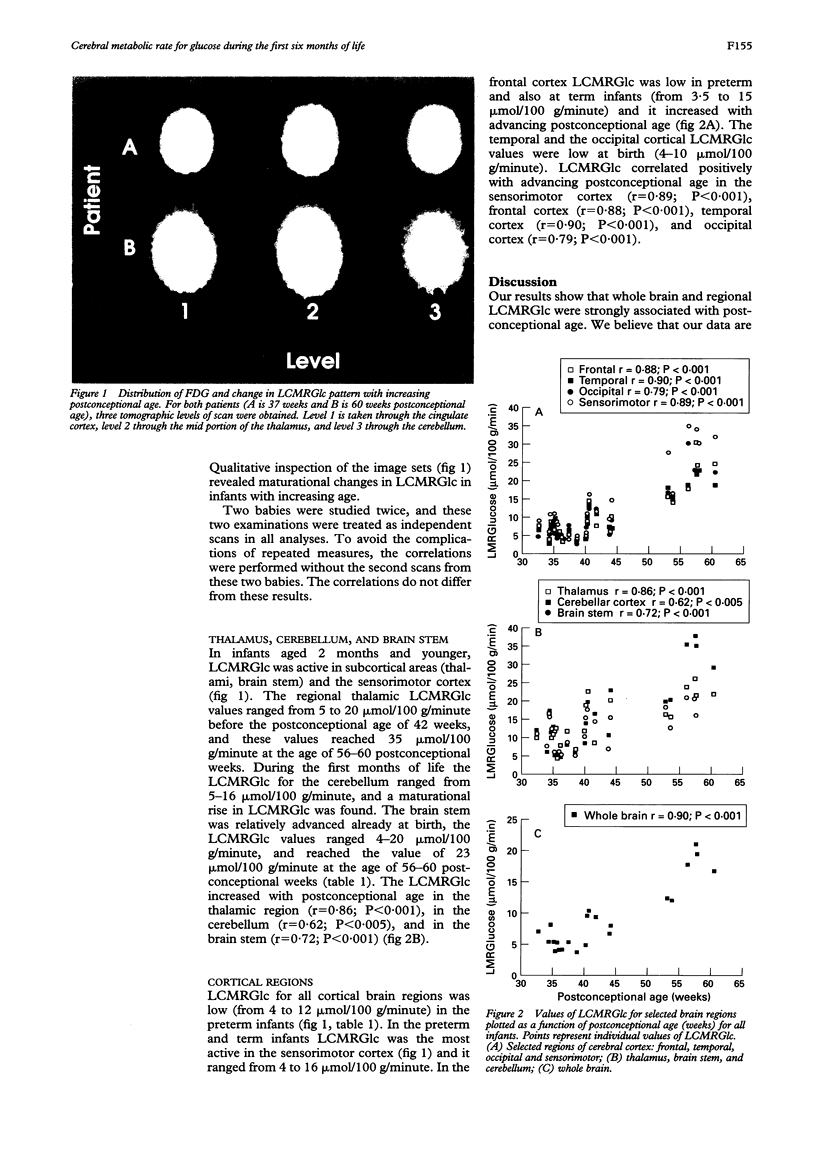
AIM: To measure the local cerebral metabolic rate for glucose (LCMRGlc) in neonatal brains during maturation using positron emission tomography (PET) and 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose (FDG). METHODS: Twenty infants were studied using PET during the neonatal period. The postconceptional age ranged from 32.7 to 60.3 weeks. All infants had normal neurodevelopment and were normoglycaemic. The development of the infants was carefully evaluated (follow up 12-36 months) clinically, and by using a method based on Gesell Amatruda's developmental diagnosis. LCMRGlc was quantitated using PET derived from FDG kinetics and calculated in the whole brain and for regional brain structures. RESULTS: LCMRGlc for various cortical brain regions and the basal ganglia was low at birth (from 4 to 16 mumol/100 g/minute). In infants 2 months of age and younger LCMRGlc was highest in the sensorimotor cortex, thalamus, and brain stem. By 5 months, LCMRGlc had increased in the frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital and cerebellar cortical regions. In general, the whole brain LCMRGlc correlated with postconceptional age (r = 0.90; P < 0.001). The change in the glucose metabolic pattern observed in the neonatal brain reflects the functional maturation of these brain regions. CONCLUSION: These findings show that LCMRGlc in infants increases with maturation. Accordingly, when LCMRGlc is measured during infancy, the postconceptional age has to be taken into account when interpretating the results.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chugani H. T., Hovda D. A., Villablanca J. R., Phelps M. E., Xu W. F. Metabolic maturation of the brain: a study of local cerebral glucose utilization in the developing cat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1991 Jan;11(1):35–47. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1991.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chugani H. T., Phelps M. E. Maturational changes in cerebral function in infants determined by 18FDG positron emission tomography. Science. 1986 Feb 21;231(4740):840–843. doi: 10.1126/science.3945811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chugani H. T., Phelps M. E., Mazziotta J. C. Positron emission tomography study of human brain functional development. Ann Neurol. 1987 Oct;22(4):487–497. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamacher K., Coenen H. H., Stöcklin G. Efficient stereospecific synthesis of no-carrier-added 2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose using aminopolyether supported nucleophilic substitution. J Nucl Med. 1986 Feb;27(2):235–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. C., Phelps M. E., Hoffman E. J., Sideris K., Selin C. J., Kuhl D. E. Noninvasive determination of local cerebral metabolic rate of glucose in man. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jan;238(1):E69–E82. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.1.E69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C., Sakurada O., Shinohara M., Miyaoka M. Local cerebral glucose utilization in the newborn macaque monkey. Ann Neurol. 1982 Oct;12(4):333–340. doi: 10.1002/ana.410120404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak C. S., Blasberg R. G. Graphical evaluation of blood-to-brain transfer constants from multiple-time uptake data. Generalizations. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1985 Dec;5(4):584–590. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1985.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira de Vasconcelos A., Colin C., Desor D., Divry M., Nehlig A. Influence of early neonatal phenobarbital exposure on cerebral energy metabolism and behavior. Exp Neurol. 1990 May;108(2):176–187. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(90)90025-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps M. E., Huang S. C., Hoffman E. J., Selin C., Sokoloff L., Kuhl D. E. Tomographic measurement of local cerebral glucose metabolic rate in humans with (F-18)2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose: validation of method. Ann Neurol. 1979 Nov;6(5):371–388. doi: 10.1002/ana.410060502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff L., Reivich M., Kennedy C., Des Rosiers M. H., Patlak C. S., Pettigrew K. D., Sakurada O., Shinohara M. The [14C]deoxyglucose method for the measurement of local cerebral glucose utilization: theory, procedure, and normal values in the conscious and anesthetized albino rat. J Neurochem. 1977 May;28(5):897–916. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suhonen-Polvi H., Kero P., Korvenranta H., Ruotsalainen U., Haaparanta M., Bergman J., Simell O., Wegelius U. Repeated fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography of the brain in infants with suspected hypoxic-ischaemic brain injury. Eur J Nucl Med. 1993 Sep;20(9):759–765. doi: 10.1007/BF00180905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suhonen-Polvi H., Ruotsalainen U., Kinnala A., Bergman J., Haaparanta M., Teräs M., M akel a P., Solin O., Wegelius U. FDG-PET in early infancy: simplified quantification methods to measure cerebral glucose utilization. J Nucl Med. 1995 Jul;36(7):1249–1254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodore W. H. Antiepileptic drugs and cerebral glucose metabolism. Epilepsia. 1988;29 (Suppl 2):S48–S55. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1988.tb05797.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannucci S. J., Seaman L. B., Brucklacher R. M., Vannucci R. C. Glucose transport in developing rat brain: glucose transporter proteins, rate constants and cerebral glucose utilization. Mol Cell Biochem. 1994 Nov 23;140(2):177–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00926756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. J., Volkow N. D., Wolf A. P., Brodie J. D., Hitzemann R. J. Intersubject variability of brain glucose metabolic measurements in young normal males. J Nucl Med. 1994 Sep;35(9):1457–1466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]