Abstract
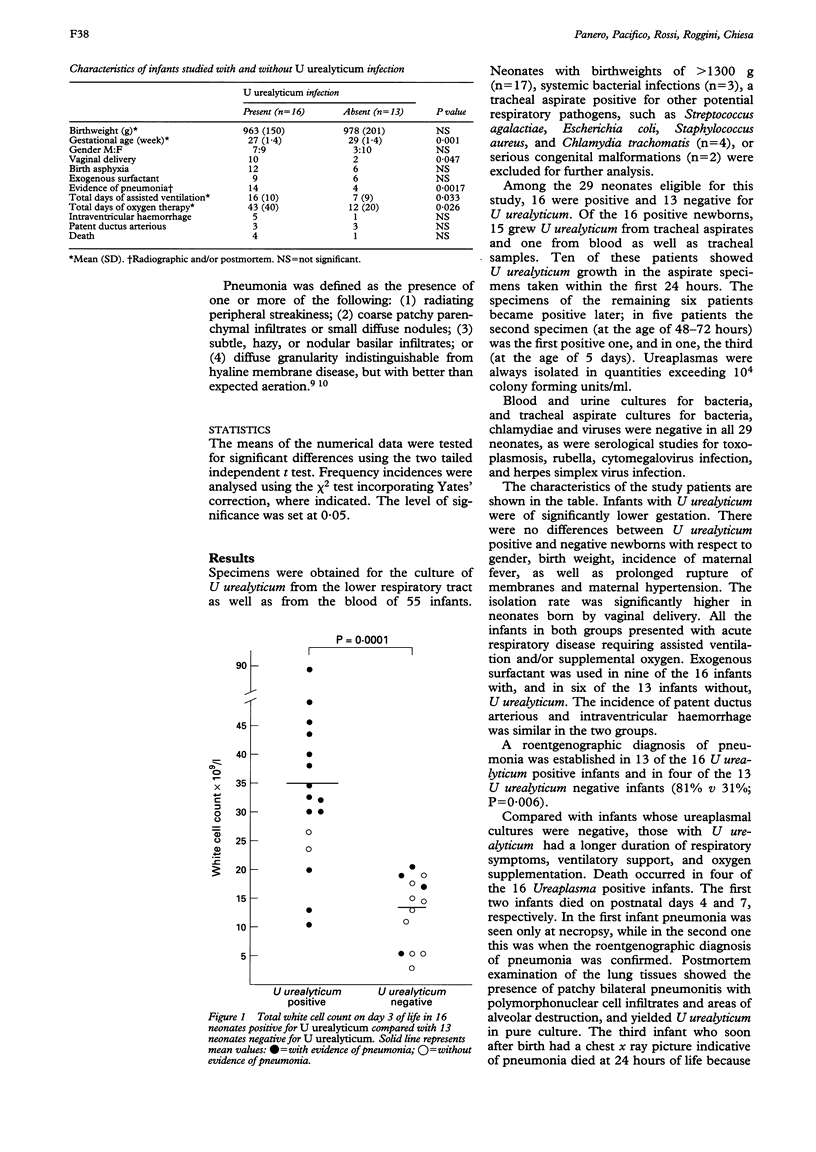
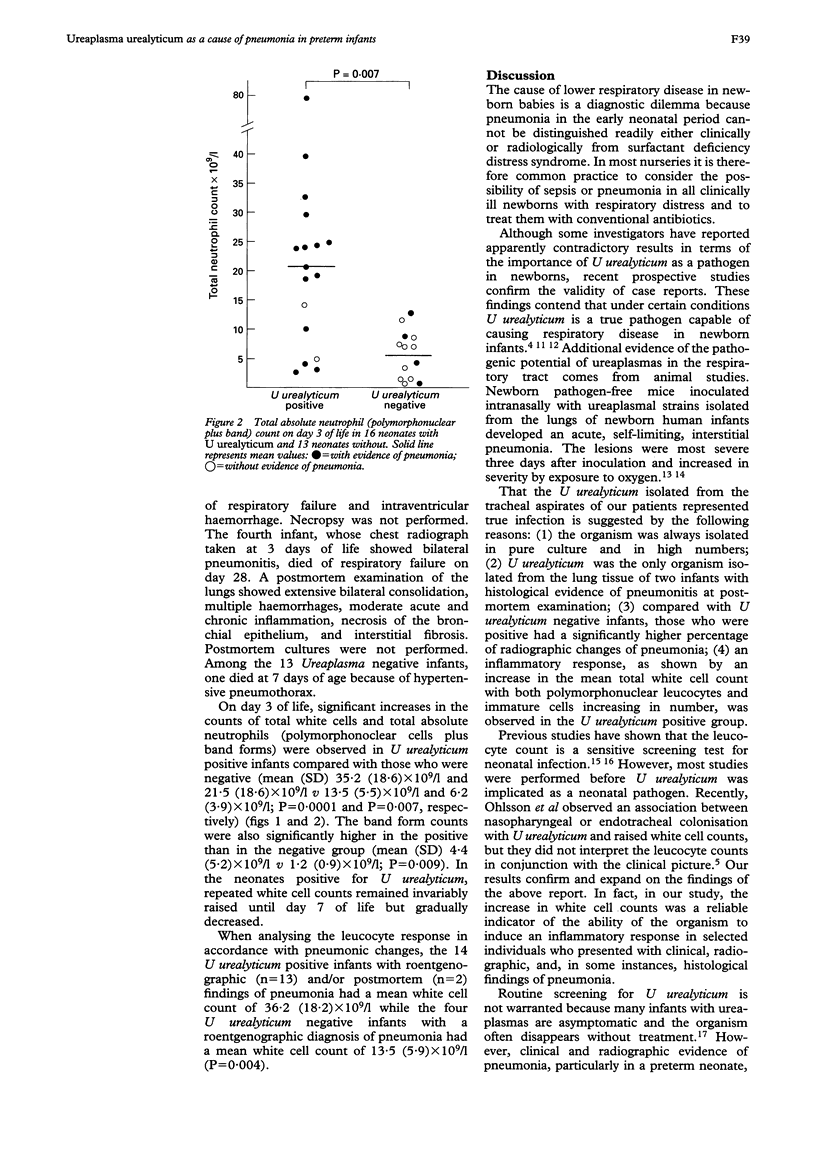
The tracheal isolation of Ureaplasma urealyticum from critically ill infants was investigated to determine if the organism was associated with an inflammatory response. Twenty nine neonates consecutively admitted for acute respiratory disease, with birthweights of < 1301 g and no evidence of viral, chlamydial, or bacterial infections, were identified. Culture results for ureaplasmas were correlated with white cell counts and clinical and radiographic features. Sixteen infants had tracheal aspirates and/or blood specimens positive for U urealyticum. Pneumonia was diagnosed more frequently in the U urealyticum positive infants than in the 13 who were negative for the organism. The mean total white cell count, absolute neutrophil, and band form counts were significantly higher in the U urealyticum positive group than in the negative group. These data suggest that U urealyticum can induce an inflammatory response in selected individuals who present with clinical, radiographic, and, in some instances, histological features of pneumonia.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brus F., van Waarde W. M., Schoots C., Oetomo S. B. Fatal ureaplasmal pneumonia and sepsis in a newborn infant. Eur J Pediatr. 1991 Sep;150(11):782–783. doi: 10.1007/BF02026711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell G. H., Waites K. B., Crouse D. T. Perinatal mycoplasmal infections. Clin Perinatol. 1991 Jun;18(2):241–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell G. H., Waites K. B., Crouse D. T., Rudd P. T., Canupp K. C., Stagno S., Cutter G. R. Association of Ureaplasma urealyticum infection of the lower respiratory tract with chronic lung disease and death in very-low-birth-weight infants. Lancet. 1988 Jul 30;2(8605):240–245. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92536-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse D. T., Cassell G. H., Waites K. B., Foster J. M., Cassady G. Hyperoxia potentiates Ureaplasma urealyticum pneumonia in newborn mice. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3487–3493. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3487-3493.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland S. M., Murton L. J. Neonatal meningitis caused by Ureaplasma urealyticum. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Sep;6(9):868–870. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198709000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manroe B. L., Rosenfeld C. R., Weinberg A. G., Browne R. The differential leukocyte count in the assessment and outcome of early-onset neonatal group B streptococcal disease. J Pediatr. 1977 Oct;91(4):632–637. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80522-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson A., Wang E., Vearncombe M. Leukocyte counts and colonization with Ureaplasma urealyticum in preterm neonates. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Aug;17 (Suppl 1):S144–S147. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.supplement_1.s144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollikainen J., Hiekkaniemi H., Korppi M., Sarkkinen H., Heinonen K. Ureaplasma urealyticum infection associated with acute respiratory insufficiency and death in premature infants. J Pediatr. 1993 May;122(5 Pt 1):756–760. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(06)80022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panero A., Pacifico L., Rossi N., Bucci G., Chiesa C. Elevated white blood cell counts associated with Ureaplasma urealyticum colonization in preterm neonates. Clin Infect Dis. 1994 Nov;19(5):980–981. doi: 10.1093/clinids/19.5.980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. A., Gillan J. E., Markestad T., St John M. A., Daneman A., Lie K. I., Li H. C., Czegledy-Nagy E., Klein A. Intrauterine infection with Ureaplasma urealyticum as a cause of fatal neonatal pneumonia. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1985 Sep-Oct;4(5):538–543. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198509000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd P. T., Carrington D. A prospective study of chlamydial, mycoplasmal, and viral infections in a neonatal intensive care unit. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Feb;59(2):120–125. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.2.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd P. T., Cassell G. H., Waites K. B., Davis J. K., Duffy L. B. Ureaplasma urealyticum pneumonia: experimental production and demonstration of age-related susceptibility. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):918–925. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.918-925.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard M. C., Lunceford C. D. Differential agar medium (A7) for identification of Ureaplasma urealyticum (human T mycoplasmas) in primary cultures of clinical material. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jun;3(6):613–625. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.6.613-625.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tudor J., Young L., Wigglesworth J. S., Steiner R. E. The value of radiology in the idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome: a radiological and pathological correlation study. Clin Radiol. 1976 Jan;27(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(76)80018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waites K. B., Crouse D. T., Cassell G. H. Therapeutic considerations for Ureaplasma urealyticum infections in neonates. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Aug;17 (Suppl 1):S208–S214. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.supplement_1.s208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthou M. Leucocyte blood picture in ill newborn babies. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Oct;47(255):741–746. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.255.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


