Abstract
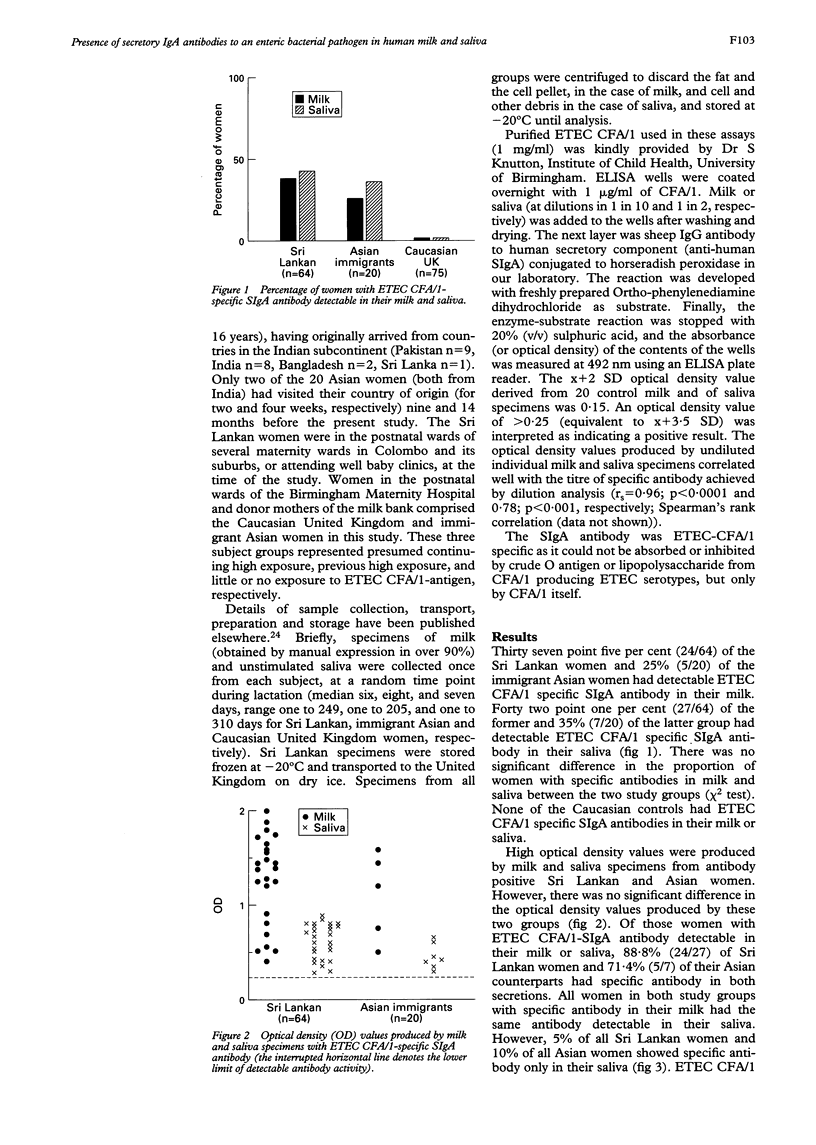
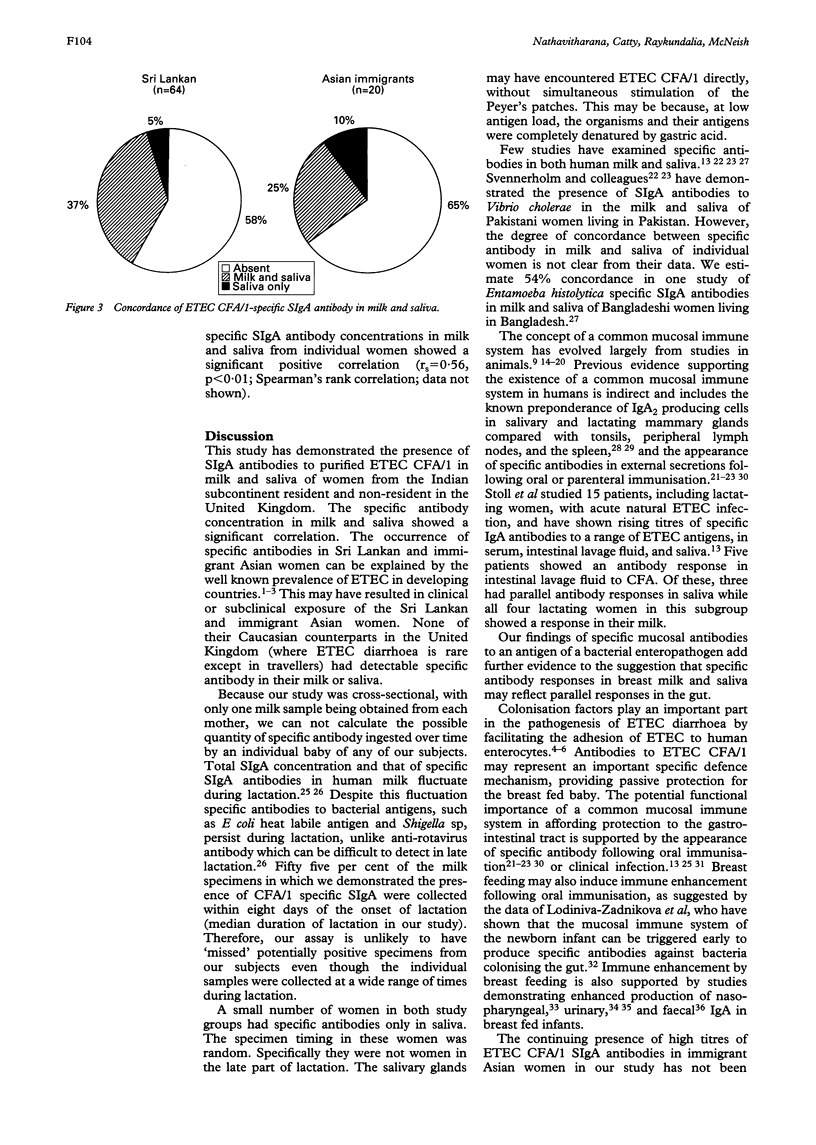
The concept of a common mucosal immune system in man was tested by examining the concurrent presence of specific-secretory IgA (SIgA) antibodies in human milk and saliva from three groups of subjects: 64 Sri Lankan women living in Sri Lanka; 20 immigrant Asian women living in Birmingham (median duration of residence in the United Kingdom five years); and 75 Caucasian women living in Birmingham (controls). Enzyme linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) were developed to detect enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) colonisation factor/1 (CFA/1) specific SIgA antibodies in milk and saliva. ETEC CFA/1 specific SIgA antibody activity was detectable in milk (37.5% and 25%) and saliva (42.1% and 35%) of Sri Lankan and immigrant Asian women, respectively, but not in any of the Caucasian controls. Eighty five point two per cent of subjects who were positive had specific antibodies detectable in both milk and saliva; 5% of all Sri Lankan women and 10% of all immigrant Asian women had detectable antibody only in saliva. These observations lend further strong support to the idea that a common mucosal immune system exists in man. The continuing presence of specific SIgA antibodies in Asian immigrants to previously encountered antigens suggests that there may be an 'immunological memory' in the human secretory immune system.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allardyce R. A., Shearman D. J., McClelland D. B., Marwick K., Simpson A. J., Laidlaw R. B. Appearance of specific colostrum antibodies after clinical infection with Salmonella typhimurium. Br Med J. 1974 Aug 3;3(5926):307–309. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5926.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertotto A., Gerli R., Fabietti G., Crupi S., Arcangeli C., Scalise F., Vaccaro R. Human breast milk T lymphocytes display the phenotype and functional characteristics of memory T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Aug;20(8):1877–1880. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienenstock J., Befus A. D. Mucosal immunology. Immunology. 1980 Oct;41(2):249–270. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienenstock J., Befus A. D. Some thoughts on the biologic role of immunoglobulin A. Gastroenterology. 1983 Jan;84(1):178–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. The secretory immune system of lactating human mammary glands compared with other exocrine organs. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 30;409:353–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb26883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butte N. F., Goldblum R. M., Fehl L. M., Loftin K., Smith E. O., Garza C., Goldman A. S. Daily ingestion of immunologic components in human milk during the first four months of life. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984 May;73(3):296–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1994.tb17738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz J. R., Arévalo C. Fluctuation of specific IgA antibodies in human milk. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1985 Nov;74(6):897–903. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1985.tb10055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Silver R. P., Evans D. J., Jr, Chase D. G., Gorbach S. L. Plasmid-controlled colonization factor associated with virulence in Esherichia coli enterotoxigenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):656–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.656-667.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum R. M., Ahlstedt S., Carlsson B., Hanson L. A., Jodal U., Lidin-Janson G., Sohl-Akerlund A. Antibody-forming cells in human colostrum after oral immunisation. Nature. 1975 Oct 30;257(5529):797–798. doi: 10.1038/257797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum R. M., Schanler R. J., Garza C., Goldman A. S. Human milk feeding enhances the urinary excretion of immunologic factors in low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res. 1989 Feb;25(2):184–188. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198902000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Hanson L. A., Carlson B., Lindblad B. S., Rahimtoola J. Neutralizing antibodies against Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae enterotoxins in human milk from a developing country. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(6-7):867–871. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb03036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam A., Stoll B. J., Ljungstrom I., Biswas J., Nazrul H., Huldt G. The prevalence of Entamoeba histolytica in lactating women and in their infants in Bangladesh. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1988;82(1):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(88)90276-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kett K., Brandtzaeg P., Radl J., Haaijman J. J. Different subclass distribution of IgA-producing cells in human lymphoid organs and various secretory tissues. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3631–3635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Lloyd D. R., Candy D. C., McNeish A. S. Adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to human small intestinal enterocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):824–831. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.824-831.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koutras A. K., Vigorita V. J. Fecal secretory immunoglobulin A in breast milk versus formula feeding in early infancy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1989 Jul;9(1):58–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Edelman R. Acute diarrheal infections in infants. I. Epidemiology, Treatment, and prospects for immunoprophylaxis. Hosp Pract. 1979 Dec;14(12):89–100. doi: 10.1080/21548331.1979.11707662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodinová-Zádníková R., Slavíková M., Tlaskalová-Hogenová H., Adlerberth I., Hanson L. A., Wold A., Carlsson B., Svanborg C., Mellander L. The antibody response in breast-fed and non-breast-fed infants after artificial colonization of the intestine with Escherichia coli O83. Pediatr Res. 1991 Apr;29(4 Pt 1):396–399. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199104000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R. Immunological memory. Adv Immunol. 1993;53:217–265. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60501-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott M. R., Bienenstock J. Evidence for a common mucosal immunologic system. I. Migration of B immunoblasts into intestinal, respiratory, and genital tissues. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1892–1898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., McGhee J. R., Arnold R. R., Michalek S. M., Prince S. J., Babb J. L. Selective induction of an immune response in human external secretions by ingestion of bacterial antigen. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):731–737. doi: 10.1172/JCI108986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., McGhee J. R. Immunoglobulin A (IgA): molecular and cellular interactions involved in IgA biosynthesis and immune response. Adv Immunol. 1987;40:153–245. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentice A. Breast feeding increases concentrations of IgA in infants' urine. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Aug;62(8):792–795. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.8.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudzik R., Clancy R. L., Perey D. Y., Day R. P., Bienenstock J. Repopulation with IgA-containing cells of bronchial and intestinal lamina propria after transfer of homologous Peyer's patch and bronchial lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1975 May;114(5):1599–1604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satterwhite T. K., Evans D. G., DuPont H. L., Evans D. J., Jr Role of Escherichia coli colonisation factor antigen in acute diarrhoea. Lancet. 1978 Jul 22;2(8082):181–184. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91921-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. E., Martin A. F., Ford W. L. Migration of lymphoblasts in the rat. Preferential localization of DNA-synthesizing lymphocytes in particular lymph nodes and other sties. Monogr Allergy. 1980;16:203–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens S. Development of secretory immunity in breast fed and bottle fed infants. Arch Dis Child. 1986 Mar;61(3):263–269. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.3.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoliar O. A., Pelley R. P., Kaniecki-Green E., Kkaus M. H., Carpenter C. C. Secretory IgA against enterotoxins in breast-milk. Lancet. 1976 Jun 12;1(7972):1258–1261. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91735-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll B. J., Glass R. I., Huq M. I., Khan M. U., Holt J. E., Banu H. Surveillance of patients attending a diarrhoeal disease hospital in Bangladesh. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Oct 23;285(6349):1185–1188. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6349.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll B. J., Svennerholm A. M., Gothefors L., Barua D., Huda S., Holmgren J. Local and systemic antibody responses to naturally acquired enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhea in an endemic area. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):527–534. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Holmgren J., Hanson L. A., Lindblad B. S., Quereshi F., Rahimtoola R. J. Boosting of secretory IgA antibody responses in man by parenteral cholera vaccination. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(12):1345–1349. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Jertborn M., Gothefors L., Karim A. M., Sack D. A., Holmgren J. Mucosal antitoxic and antibacterial immunity after cholera disease and after immunization with a combined B subunit-whole cell vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jun;149(6):884–893. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.6.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMASI T. B., Jr, TAN E. M., SOLOMON A., PRENDERGAST R. A. CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IMMUNE SYSTEM COMMON TO CERTAIN EXTERNAL SECRETIONS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:101–124. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Grey H. M. Structure and function of immunoglobulin A. Prog Allergy. 1972;16:81–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisz-Carrington P., Grimes S. R., Jr, Lamm M. E. Gut-associated lymphoid tissue as source of an IgA immune response in respiratory tissues after oral immunization and intrabronchial challenge. Cell Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;106(1):132–138. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90156-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisz-Carrington P., Roux M. E., McWilliams M., PHILLIPS-Quagliata J. M., Lamm M. E. Organ and isotype distribution of plasma cells producing specific antibody after oral immunization: evidence for a generalized secretory immune system. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1705–1708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Garcia B., Cáceres A., Mata L. J. Immunoglobulins and antibodies in colostrum and milk of Guatemalan mayan women. Arch Latinoam Nutr. 1972 Dec;22(4):629–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


