Abstract
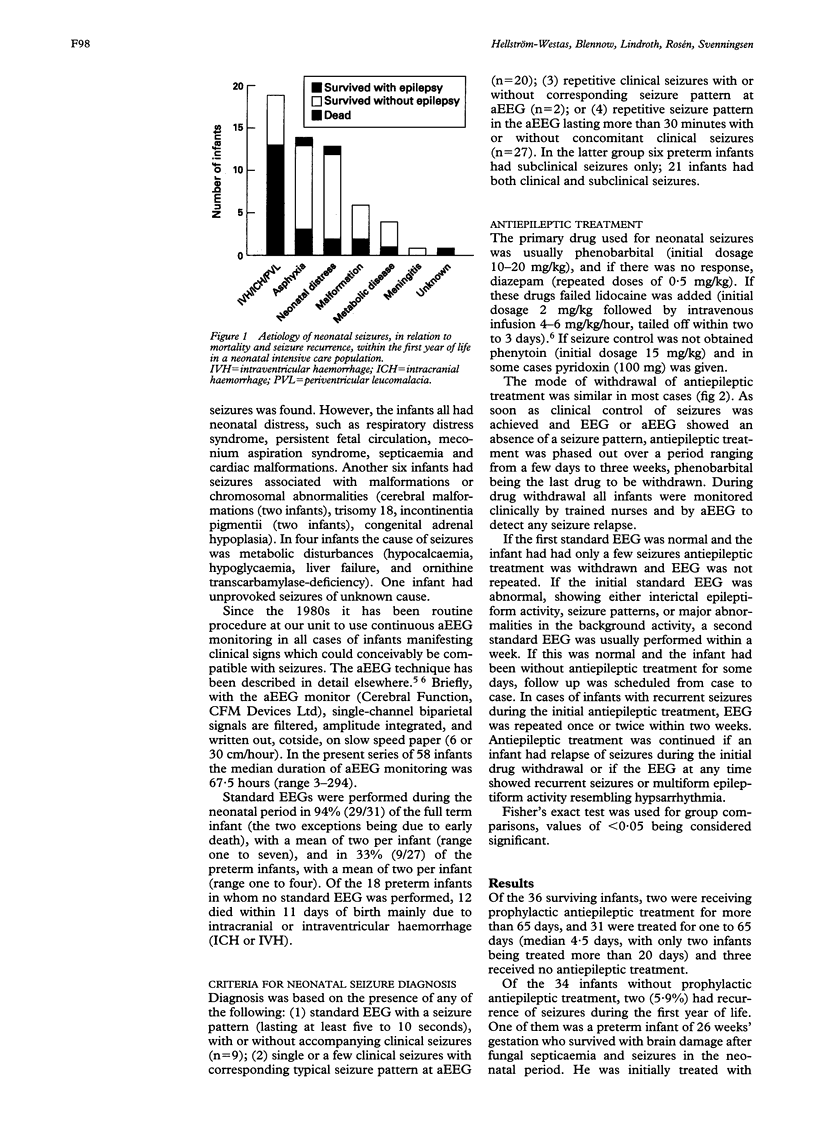
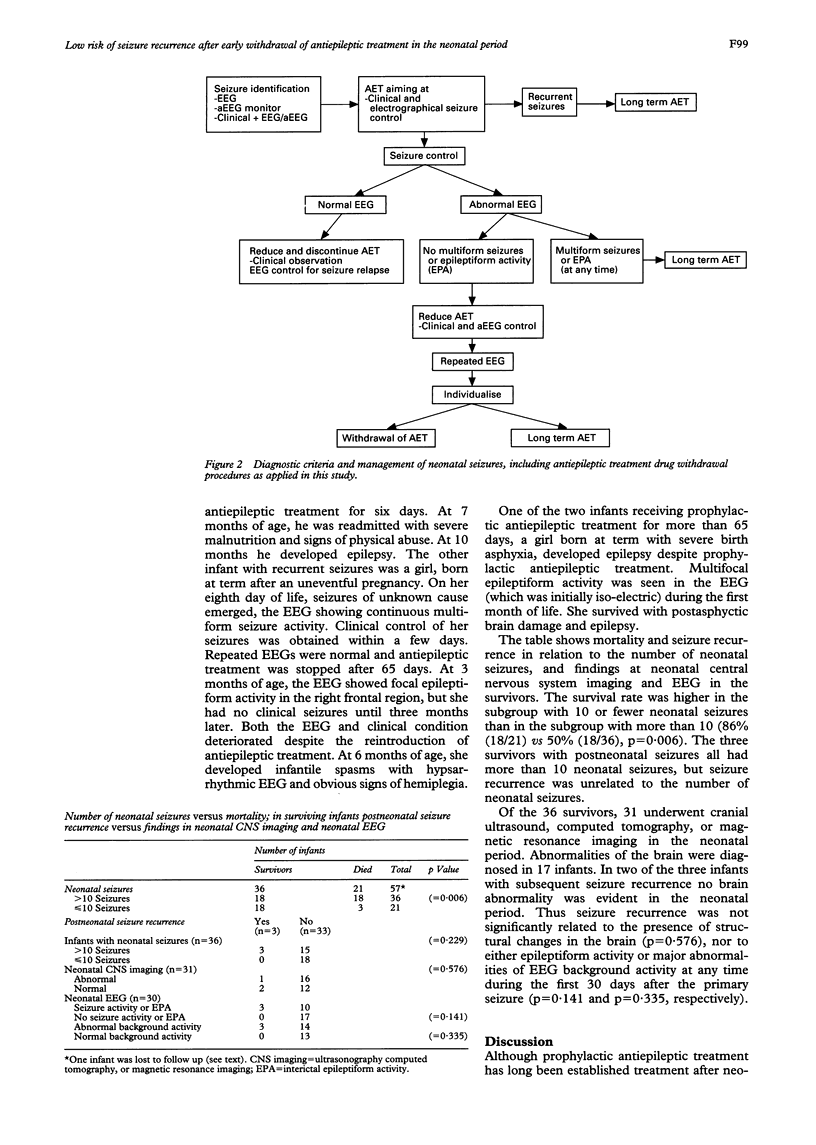
The risk of seizure recurrence within the first year of life was evaluated in infants with neonatal seizures diagnosed with a combination of clinical signs, amplitude-integrated electroencephalogram (EEG) monitoring, and standard EEG. Fifty eight of 283 (4.5%) neonates in tertiary level neonatal intensive care had seizures. The mortality in the infants with neonatal seizures was 36.2%. In 31 surviving infants antiepileptic treatment was discontinued after one to 65 days (median 4.5 days). Three infants received no antiepileptic treatment, two continued with prophylactic antiepileptic treatment. Seizure recurrence was present in only three cases (8.3%)--one infant receiving prophylaxis, one treated for 65 days, and in one infant treated for six days. Owing to the small number of infants with seizure recurrence, no clinical features could be specifically related to an increased risk of subsequent seizures. When administering antiepileptic treatment, one aim was to abolish both clinical and electrographical seizures. Another goal was to minimise the duration of treatment and to keep the treatment as short as possible. It is suggested that treating neonatal seizures in this way may not only reduce the risk of subsequent seizure recurrence, but may also minimise unnecessary non-specific prophylactic treatment for epilepsy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brod S. A., Ment L. R., Ehrenkranz R. A., Bridgers S. Predictors of success for drug discontinuation following neonatal seizures. Pediatr Neurol. 1988 Jan-Feb;4(1):13–17. doi: 10.1016/0887-8994(88)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy R. R., Legido A., Lewis D. Occult neonatal seizures. Epilepsia. 1988 May-Jun;29(3):256–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1988.tb03715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy R. R., Legido A. Postnatal epilepsy after EEG-confirmed neonatal seizures. Epilepsia. 1991 Jan-Feb;32(1):69–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1991.tb05614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell J., Oozeer R., de Vries L., Dubowitz L. M., Dubowitz V. Continuous EEG monitoring of neonatal seizures: diagnostic and prognostic considerations. Arch Dis Child. 1989 Apr;64(4 Spec No):452–458. doi: 10.1136/adc.64.4_spec_no.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz J., Schain R. J. Phenobarbital: effects of long-term administration on behavior and brain of artificially reared rats. Science. 1978 Jan 6;199(4324):90–91. doi: 10.1126/science.199.4324.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson M., Zetterström R. Neonatal convulsions. Incidence and causes in the Stockholm area. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 Nov;68(6):807–811. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb08216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre J. A., Oozeer R. C., Wilkinson A. R. Diagnosis of neonatal seizure by continuous recording and rapid analysis of the electroencephalogram. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Oct;58(10):785–790. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.10.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farwell J. R., Lee Y. J., Hirtz D. G., Sulzbacher S. I., Ellenberg J. H., Nelson K. B. Phenobarbital for febrile seizures--effects on intelligence and on seizure recurrence. N Engl J Med. 1990 Feb 8;322(6):364–369. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199002083220604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakeem V. F., Wallace S. J. EEG monitoring of therapy for neonatal seizures. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1990 Oct;32(10):858–864. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1990.tb08097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström-Westas L. Comparison between tape-recorded and amplitude-integrated EEG monitoring in sick newborn infants. Acta Paediatr. 1992 Oct;81(10):812–819. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1992.tb12109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström-Westas L., Rosén I., Swenningsen N. W. Silent seizures in sick infants in early life. Diagnosis by continuous cerebral function monitoring. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1985 Sep;74(5):741–748. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1985.tb10024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström-Westas L., Westgren U., Rosén I., Svenningsen N. W. Lidocaine for treatment of severe seizures in newborn infants. I. Clinical effects and cerebral electrical activity monitoring. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1988 Jan;77(1):79–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1988.tb10602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden K. R., Mellits E. D., Freeman J. M. Neonatal seizures. I. Correlation of prenatal and perinatal events with outcomes. Pediatrics. 1982 Aug;70(2):165–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi E. M., Kellaway P. Characterization and classification of neonatal seizures. Neurology. 1987 Dec;37(12):1837–1844. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.12.1837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moshé S. L. Epileptogenesis and the immature brain. Epilepsia. 1987;28 (Suppl 1):S3–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1987.tb05753.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe J. C., Holmes G. L., Hafford J., Baboval D., Robinson S., Philipps A., Rosenkrantz T., Raye J. Prognostic value of the electroencephalogram in term and preterm infants following neonatal seizures. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1985 Mar;60(3):183–196. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(85)90030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher M. S., Aso K., Beggarly M. E., Hamid M. Y., Steppe D. A., Painter M. J. Electrographic seizures in preterm and full-term neonates: clinical correlates, associated brain lesions, and risk for neurologic sequelae. Pediatrics. 1993 Jan;91(1):128–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrard W. J. Neonatal diagnosis of congenital dislocation of hip. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1978 Jun;20(3):389–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1978.tb15232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J. Neonatal seizures: current concepts and revised classification. Pediatrics. 1989 Sep;84(3):422–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


