Abstract
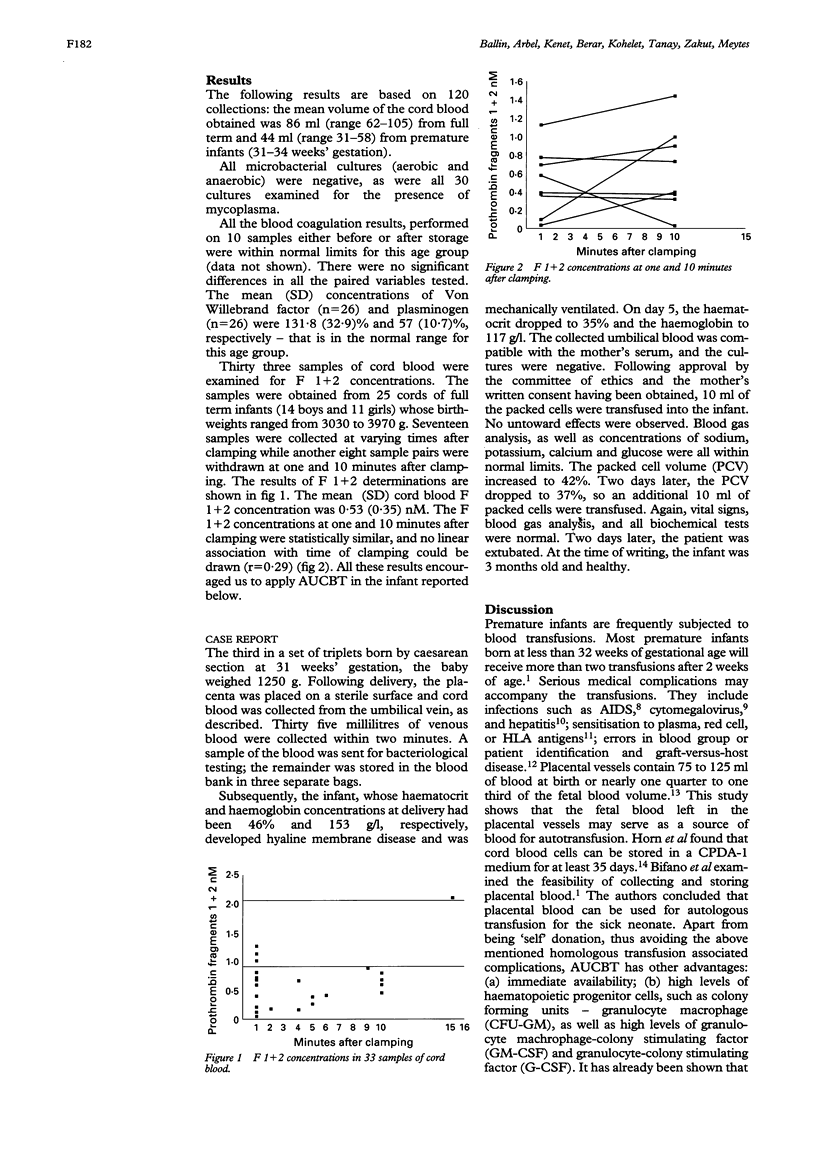
The purpose of this study was to examine some aspects of umbilical cord blood collection for autologous transfusion in premature infants. All 120 microbacterial cultures (aerobic and anaerobic) of cord blood samples as well as 30 cultures of mycoplasma were treated. Cord prothrombin fragment (F 1 + 2) concentrations were quantified at one and 10 minutes after clamping of the cord. F 1 + 2 concentrations assessed on 25 newborn infants were similar and no linear association with time of clamping could be drawn. This means that cord blood thrombosis is not activated for at least 10 minutes following clamping of the cord. As far as is known, the first newborn infant to benefit from this method of transfusion is reported here. The premature infant received two portions of autologous blood (on days 5 and 7). No untoward effects were noted. Blood, collected from the umbilical cord, is a safe source for autotransfusion, provided that bacteriological testing has been carried out.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. C., Weinstein H. J. Transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 2;323(5):315–321. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008023230506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew M., Paes B., Milner R., Johnston M., Mitchell L., Tollefsen D. M., Powers P. Development of the human coagulation system in the full-term infant. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):165–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballin A., Kenet G., Gutman R., Samra Z., Zakut H., Meytes D. Autologous cord blood transfusion. Acta Paediatr. 1994 Jul;83(7):700–703. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1994.tb13122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer K. A., Broekmans A. W., Bertina R. M., Conard J., Horellou M. H., Samama M. M., Rosenberg R. D. Hemostatic enzyme generation in the blood of patients with hereditary protein C deficiency. Blood. 1988 May;71(5):1418–1426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bifano E. M., Dracker R. A., Lorah K., Palit A. Collection and 28-day storage of human placental blood. Pediatr Res. 1994 Jul;36(1 Pt 1):90–94. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199407001-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., Douglas G. W., Hangoc G., Cooper S., Bard J., English D., Arny M., Thomas L., Boyse E. A. Human umbilical cord blood as a potential source of transplantable hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3828–3832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., Kurtzberg J., Gluckman E., Auerbach A. D., Douglas G., Cooper S., Falkenburg J. H., Bard J., Boyse E. A. Umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem and repopulating cells in human clinical transplantation. Blood Cells. 1991;17(2):313–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnielli V., Montini G., Da Riol R., Dall'Amico R., Cantarutti F. Effect of high doses of human recombinant erythropoietin on the need for blood transfusions in preterm infants. J Pediatr. 1992 Jul;121(1):98–102. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82552-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claas F. H., Lagaay E. L., van Rood J. J. Immunological consequences of blood transfusions. Schweiz Med Wochenschr Suppl. 1991;43:70–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban J. I., González A., Hernández J. M., Viladomiu L., Sánchez C., López-Talavera J. C., Lucea D., Martin-Vega C., Vidal X., Esteban R. Evaluation of antibodies to hepatitis C virus in a study of transfusion-associated hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 18;323(16):1107–1112. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010183231605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluckman E., Broxmeyer H. A., Auerbach A. D., Friedman H. S., Douglas G. W., Devergie A., Esperou H., Thierry D., Socie G., Lehn P. Hematopoietic reconstitution in a patient with Fanconi's anemia by means of umbilical-cord blood from an HLA-identical sibling. N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 26;321(17):1174–1178. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910263211707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn S., Mazor D., Zmora E., Meyerstein N. Storage-induced changes in human newborn red cells. Transfusion. 1987 Sep-Oct;27(5):411–414. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1987.27587320535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. C. Red blood cell transfusion in the neonate. Semin Perinatol. 1983 Jul;7(3):159–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver J., Duncan E., Abboud M., Gasparetto C., Sahdev I., Warren D., Bussel J., Auld P., O'Reilly R. J., Moore M. A. High levels of granulocyte and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors in cord blood of normal full-term neonates. J Pediatr. 1990 Apr;116(4):627–632. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81617-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. F., Obladen M., Scigalla P., Linderkamp O., Duc G., Hieronimi G., Halliday H. L., Versmold H. T., Moriette G., Jorch G. The effect of epoetin beta (recombinant human erythropoietin) on the need for transfusion in very-low-birth-weight infants. European Multicentre Erythropoietin Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1994 Apr 28;330(17):1173–1178. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199404283301701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayani H., Lansdorp P. M. Thy-1 expression is linked to functional properties of primitive hematopoietic progenitor cells from human umbilical cord blood. Blood. 1994 May 1;83(9):2410–2417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas S. W., Sondheimer D. L., Willoughby A. D., Yaffe S. J., Katz S. L. Human immunodeficiency virus infection in childhood, adolescence, and pregnancy: a status report and national research agenda. Pediatrics. 1989 Feb;83(2):293–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


