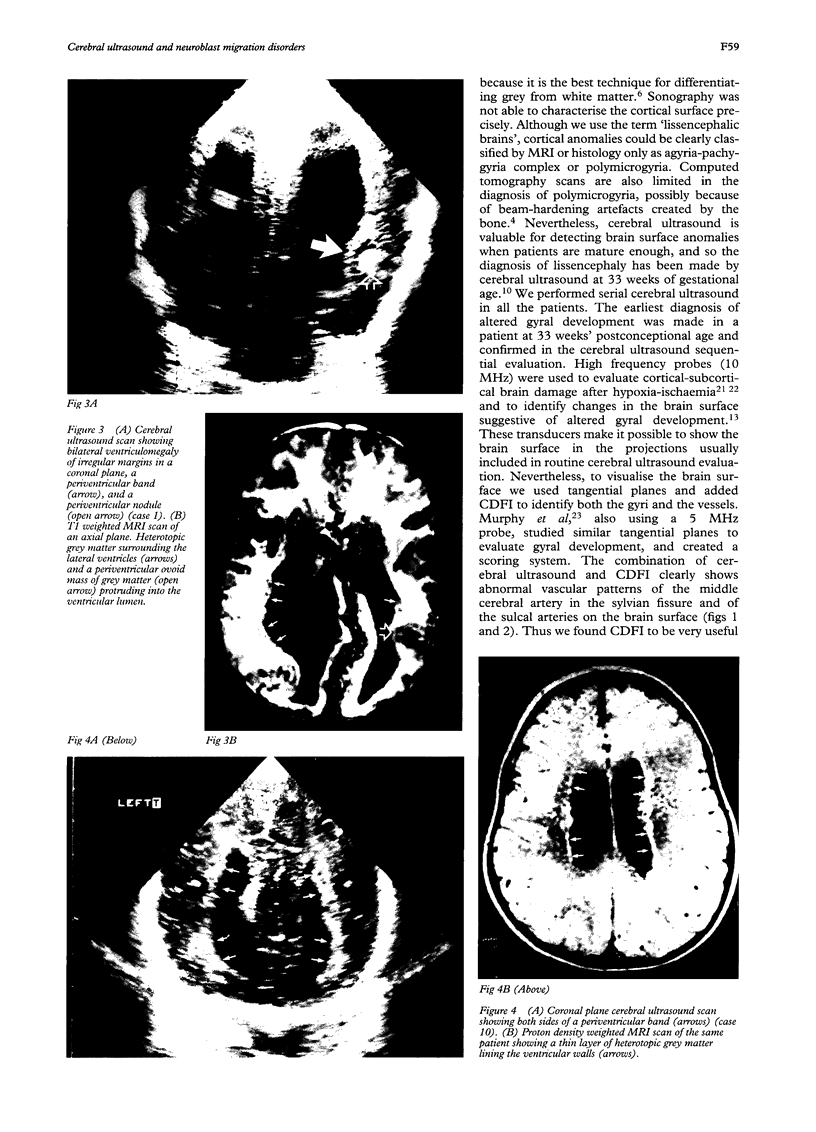
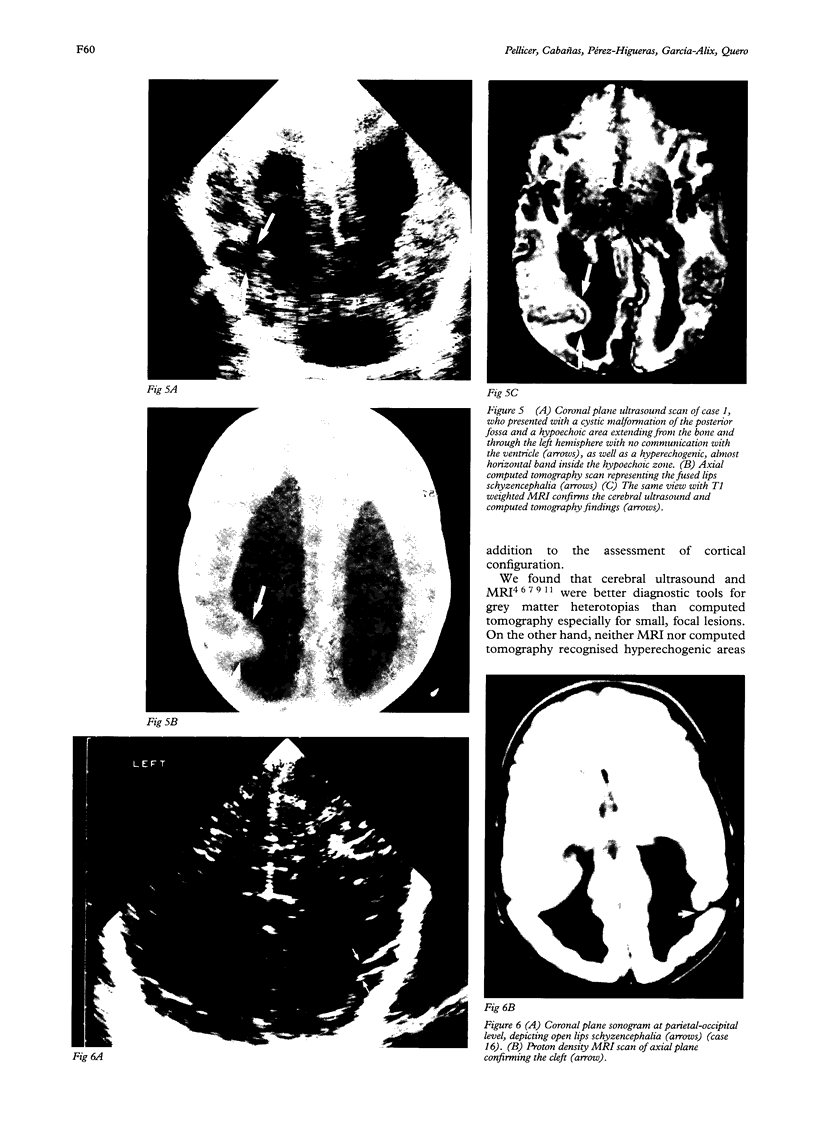
Abstract
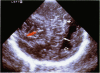
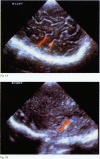
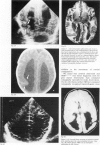
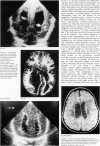
Cerebral ultrasound and colour Doppler flow imaging (CDFI) were used to diagnose a wide spectrum of anomalies of cell migration (17 patients): presumed lissencephaly (n = 12); schizencephaly of both fused (n = 2) and open lips (n = 2); hemimegalencephaly (n = 1); and subependymal type grey matter heterotopia (n = 12). The patients with grey matter heterotopia had irregular ventricular margins (n = 10), periventricular hyperechogenic bands (n = 12), and/or periventricular hyperechogenic nodules (n = 7). Some patients had more than one type of migration disorder as well as other central nervous system malformations. Cerebral ultrasound diagnoses were confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or necropsy. It is concluded that colour Doppler flow imaging is a worthwhile addition to the assessment of brain surface anomalies.
Full text
PDF
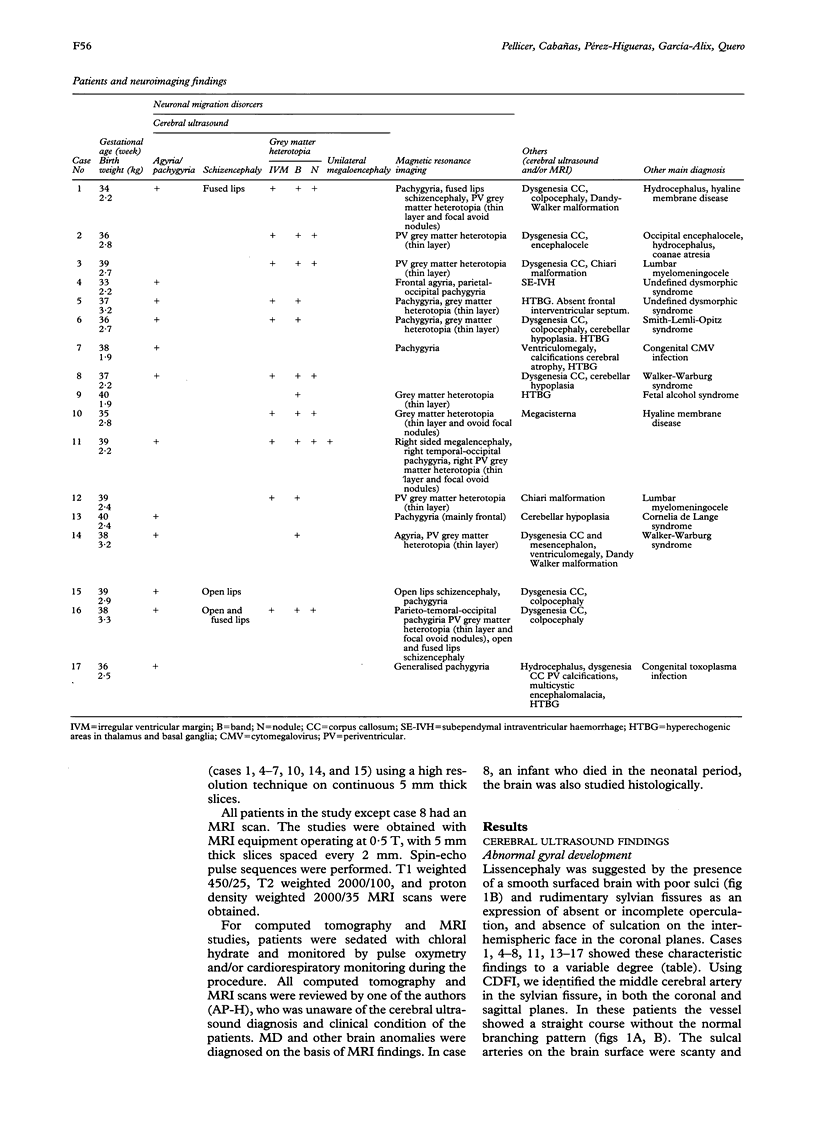
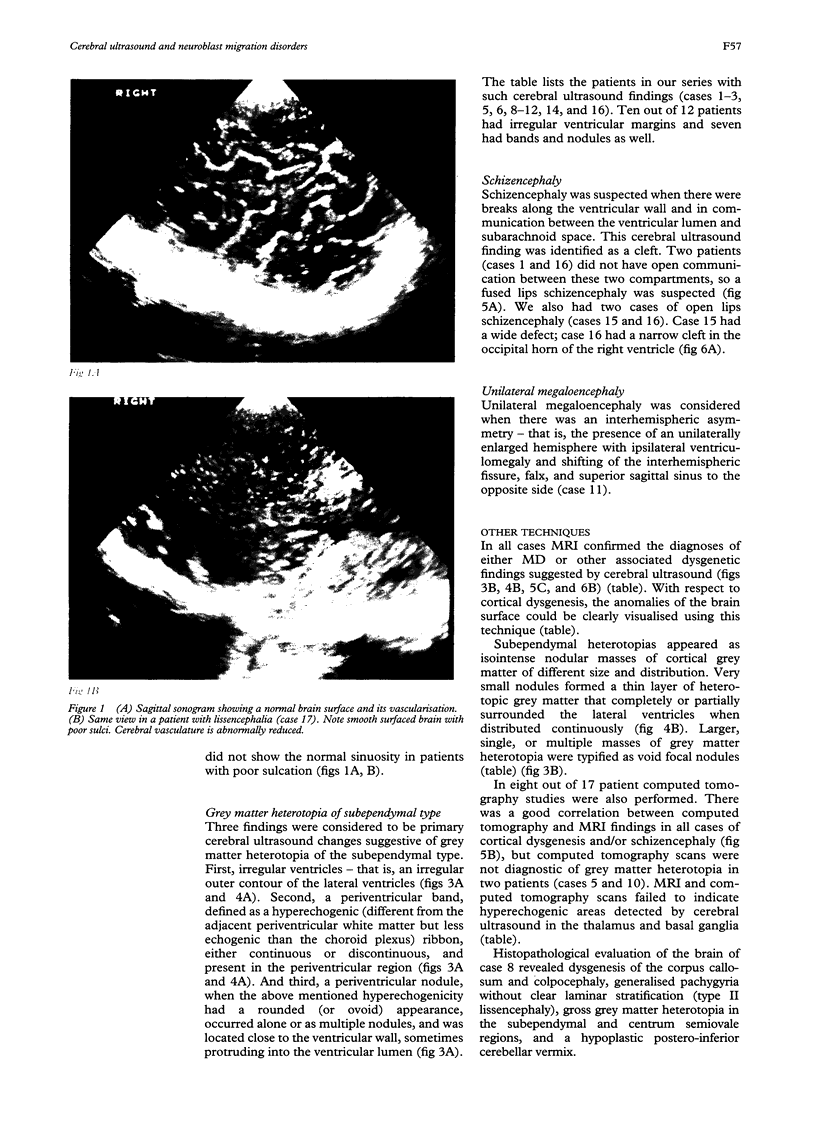
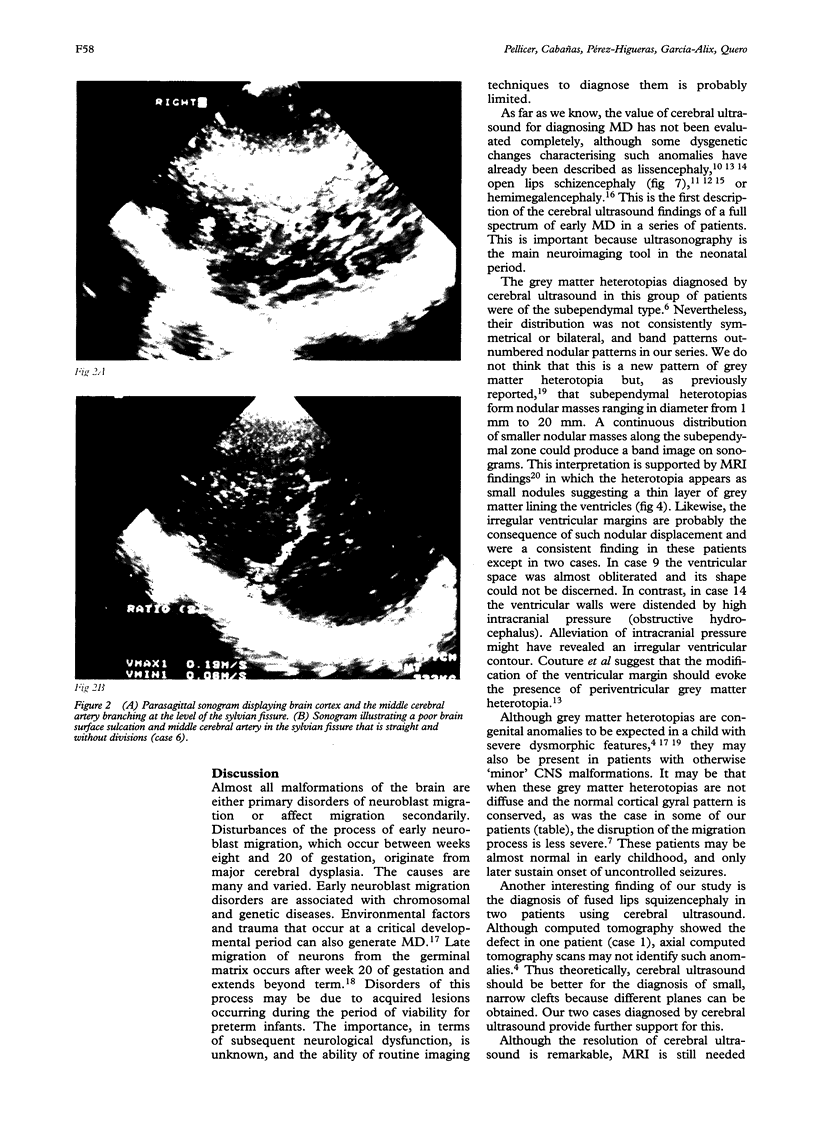

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barkovich A. J., Chuang S. H., Norman D. MR of neuronal migration anomalies. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988 Jan;150(1):179–187. doi: 10.2214/ajr.150.1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkovich A. J., Gressens P., Evrard P. Formation, maturation, and disorders of brain neocortex. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1992 Mar-Apr;13(2):423–446. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkovich A. J., Kjos B. O. Gray matter heterotopias: MR characteristics and correlation with developmental and neurologic manifestations. Radiology. 1992 Feb;182(2):493–499. doi: 10.1148/radiology.182.2.1732969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkovich A. J., Norman D. Anomalies of the corpus callosum: correlation with further anomalies of the brain. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988 Jul;151(1):171–179. doi: 10.2214/ajr.151.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd S. E., Bohan T. P., Osborn R. E., Naidich T. P. The CT and MR evaluation of lissencephaly. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1988 Sep;9(5):923–927. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabañas F., Pellicer A., Morales C., García-Alix A., Stiris T. A., Quero J. New pattern of hyperechogenicity in thalamus and basal ganglia studied by color Doppler flow imaging. Pediatr Neurol. 1994 Mar;10(2):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0887-8994(94)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canapicchi R., Padolecchia R., Puglioli M., Collavoli P., Marcella F., Valleriani A. M. Heterotopic gray matter. Neuroradiological aspects and clinical correlations. J Neuroradiol. 1990;17(4):277–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain M. C., Press G. A., Bejar R. F. Neonatal schizencephaly: comparison of brain imaging. Pediatr Neurol. 1990 Nov-Dec;6(6):382–387. doi: 10.1016/0887-8994(90)90005-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couture A., Veyrac C., Baud C., Leboucq N., Montoya F. New imaging of cerebral ischaemic lesions. High frequency probes and pulsed Doppler. Ann Radiol (Paris) 1987;30(7):452–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPietro M. A., Brody B. A., Kuban K., Cole F. S. Schizencephaly: rare cerebral malformation demonstrated by sonography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1984 Mar-Apr;5(2):196–198. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobyns W. B., Kirkpatrick J. B., Hittner H. M., Roberts R. M., Kretzer F. L. Syndromes with lissencephaly. II: Walker-Warburg and cerebro-oculo-muscular syndromes and a new syndrome with type II lissencephaly. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Sep;22(1):157–195. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320220118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobyns W. B., Stratton R. F., Greenberg F. Syndromes with lissencephaly. I: Miller-Dieker and Norman-Roberts syndromes and isolated lissencephaly. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Jul;18(3):509–526. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320180320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eken P., Jansen G. H., Groenendaal F., Rademaker K. J., de Vries L. S. Intracranial lesions in the fullterm infant with hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy: ultrasound and autopsy correlation. Neuropediatrics. 1994 Dec;25(6):301–307. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1073044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fariello G., Malena S., Lucigrai G., Tomà P. Hemimegalencephaly: early sonographic pattern. Pediatr Radiol. 1993;23(2):151–152. doi: 10.1007/BF02012414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo W. W., Shelton C., Waluch V., Solti-Bohman L. G., Carberry J. N., Brackmann D. E., Wade C. T. Intratemporal vascular tumors: detection with CT and MR imaging. Radiology. 1989 May;171(2):445–448. doi: 10.1148/radiology.171.2.2704809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. M., Stears J. C., Guggenheim M. A., Wilkening G. N. Schizencephaly: a clinical and CT study. Neurology. 1984 Aug;34(8):997–1001. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.8.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motte J., Gomes H., Morville P., Cymbalista M. Sonographic diagnosis of lissencephaly. Pediatr Radiol. 1987;17(5):362–364. doi: 10.1007/BF02396608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy N. P., Rennie J., Cooke R. W. Cranial ultrasound assessment of gestational age in low birthweight infants. Arch Dis Child. 1989 Apr;64(4):569–572. doi: 10.1136/adc.64.4.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmini A., Andermann F., de Grissac H., Tampieri D., Robitaille Y., Langevin P., Desbiens R., Andermann E. Stages and patterns of centrifugal arrest of diffuse neuronal migration disorders. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1993 Apr;35(4):331–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1993.tb11645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnat H. B. Disturbances of late neuronal migrations in the perinatal period. Am J Dis Child. 1987 Sep;141(9):969–980. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1987.04460090046022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trounce J. Q., Fagan D. G., Young I. D., Levene M. I. Disorders of neuronal migration: sonographic features. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1986 Aug;28(4):467–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1986.tb14284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman R. A., Bilaniuk L. T., Grossman R. I. Computed tomography in migratory disorders of human brain development. Neuroradiology. 1983;25(4):257–263. doi: 10.1007/BF00540237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]