Abstract
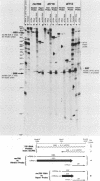
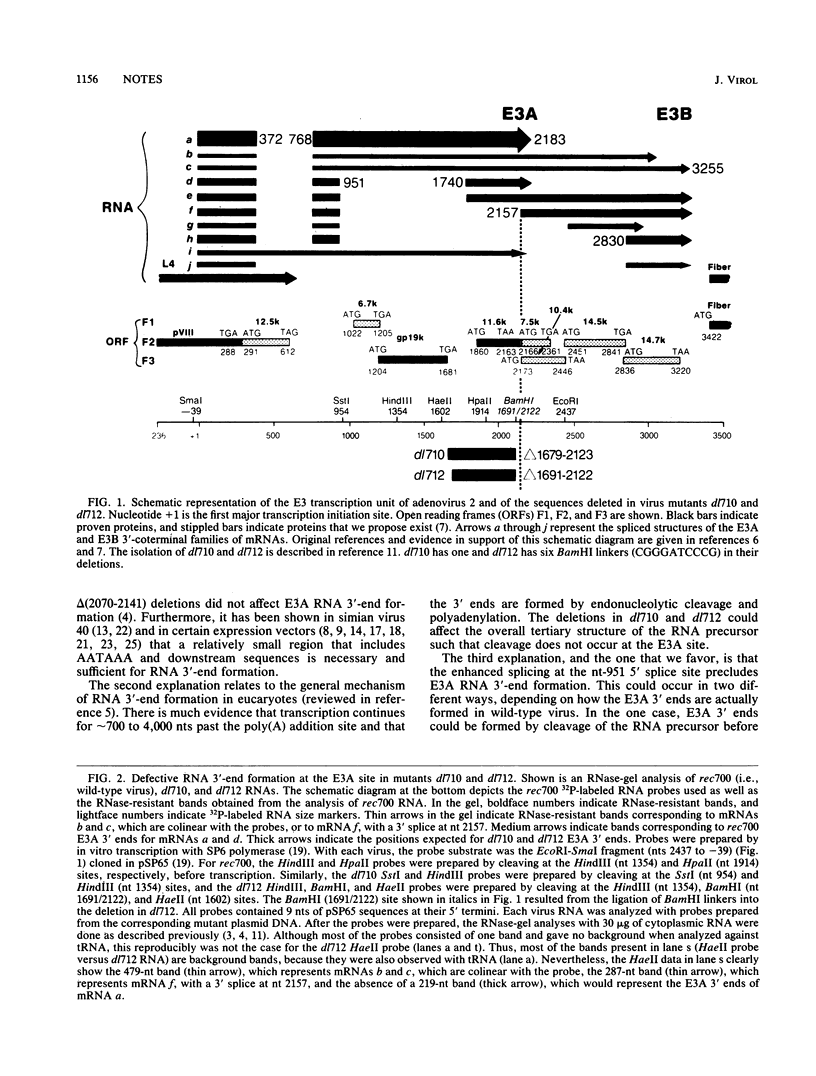
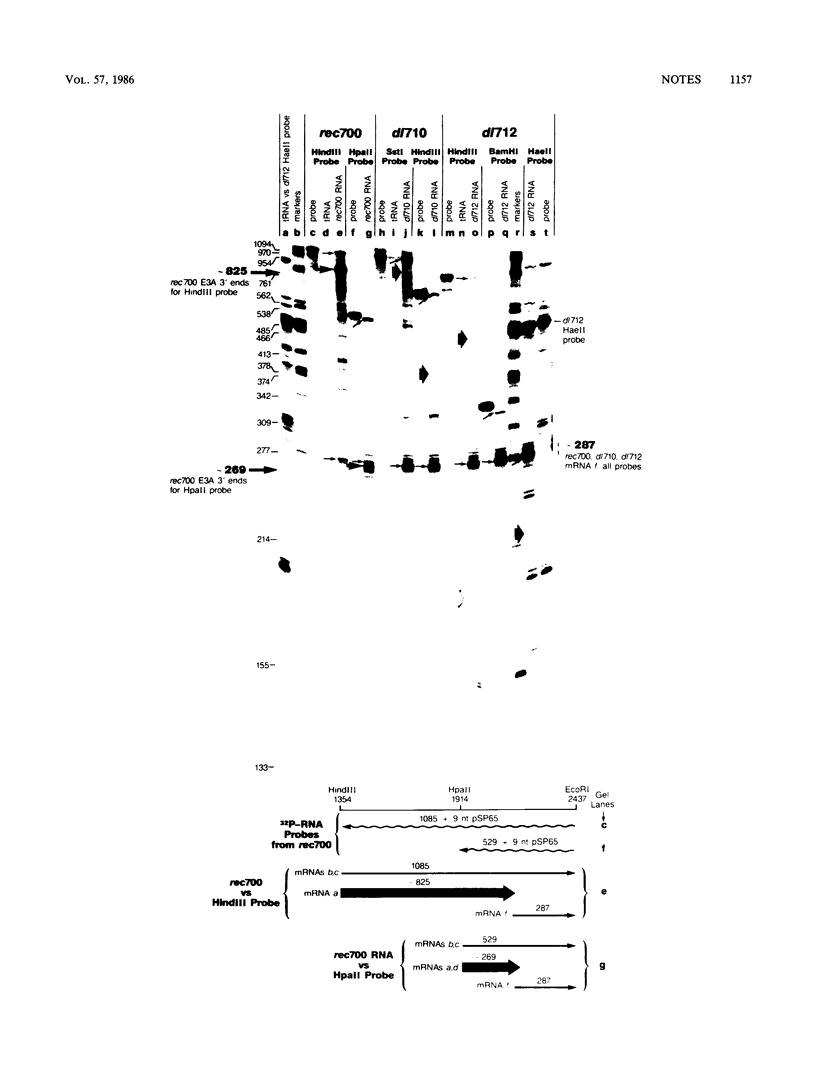
Region E3 of adenovirus encodes about 10 overlapping mRNAs with different spliced structures. The mRNAs are 5' coterminal and form two major 3'-coterminal families termed E3A and E3B. As a group, the mRNAs have two 5' splice sites and four or five 3' splice sites. We previously described a novel class of virus mutants with deletions that enhance distant upstream and downstream 5' and 3' splice sites in region E3 (S. L. Deutscher, B. M. Bhat, M. H. Pursley, C. Cladaras, and W. S. M. Wold, Nucleic Acids Res. 13:5771-5788, 1985). We now report that two of these mutants, dl710 and dl712, are defective in RNA 3'-end formation at the E3A site. This result was surprising because the deletions in dl710 and dl712 are upstream of the putative signal for E3A RNA 3'-end formation. The explanation that we favor for this result is that the enhanced splicing activity in these mutants results in the splicing out of the E3A 3'-end site from the RNA precursor before the E3A 3' ends have a chance to form.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amara S. G., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide transcription unit: tissue-specific expression involves selective use of alternative polyadenylation sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2151–2160. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat B. M., Brady H. A., Wold W. S. Virus deletion mutants that affect a 3' splice site in the E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 2. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2405–2413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat B. M., Wold W. S. ATTAAA as well as downstream sequences are required for RNA 3'-end formation in the E3 complex transcription unit of adenovirus. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3183–3193. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cladaras C., Bhat B., Wold W. S. Mapping the 5' ends, 3' ends, and splice sites of mRNAs from the early E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 5. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):44–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90444-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cladaras C., Wold W. S. DNA sequence of the early E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 5. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):28–43. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Santangelo G. M. Analysis in Cos-1 cells of processing and polyadenylation signals by using derivatives of the herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):267–279. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway L., Wickens M. A sequence downstream of A-A-U-A-A-A is required for formation of simian virus 40 late mRNA 3' termini in frog oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3949–3953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Variety in the level of gene control in eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):365–371. doi: 10.1038/297365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher S. L., Bhat B. M., Pursley M. H., Cladaras C., Wold W. S. Novel deletion mutants that enhance a distant upstream 5' splice in the E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 26;13(16):5771–5788. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.16.5771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edbrooke M. R., Parker D., McVey J. H., Riley J. H., Sorenson G. D., Pettengill O. S., Craig R. K. Expression of the human calcitonin/CGRP gene in lung and thyroid carcinoma. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):715–724. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03688.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. A sequence downstream of AAUAAA is required for rabbit beta-globin mRNA 3'-end formation. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):473–474. doi: 10.1038/312473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Morahan G., Cowman A. F., Harris A. W. Production of RNA for secreted immunoglobulin mu chains does not require transcriptional termination 5' to the microM exons. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):84–86. doi: 10.1038/301084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Imperiale M. J., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Requirement of a downstream sequence for generation of a poly(A) addition site. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. The pathway of eukaryotic mRNA formation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:441–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., Vuocolo G. A. Synthesis of two mRNAs by utilization of alternate polyadenylation sites: expression of SV40-mouse immunoglobulin mu chain gene recombinants in Cos monkey cells. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):689–699. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadofsky M., Alwine J. C. Sequences on the 3' side of hexanucleotide AAUAAA affect efficiency of cleavage at the polyadenylation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1460–1468. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M., Stephenson P. Role of the conserved AAUAAA sequence: four AAUAAA point mutants prevent messenger RNA 3' end formation. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1045–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.6208611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold W. S., Cladaras C., Magie S. C., Yacoub N. Mapping a new gene that encodes an 11,600-molecular-weight protein in the E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 2. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):307–313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.307-313.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik R. P., Lyons R. H., Post L., Rottman F. M. Requirement for the 3' flanking region of the bovine growth hormone gene for accurate polyadenylylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3944–3948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeevi M., Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Nuclear RNA is spliced in the absence of poly(A) addition. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]