Abstract
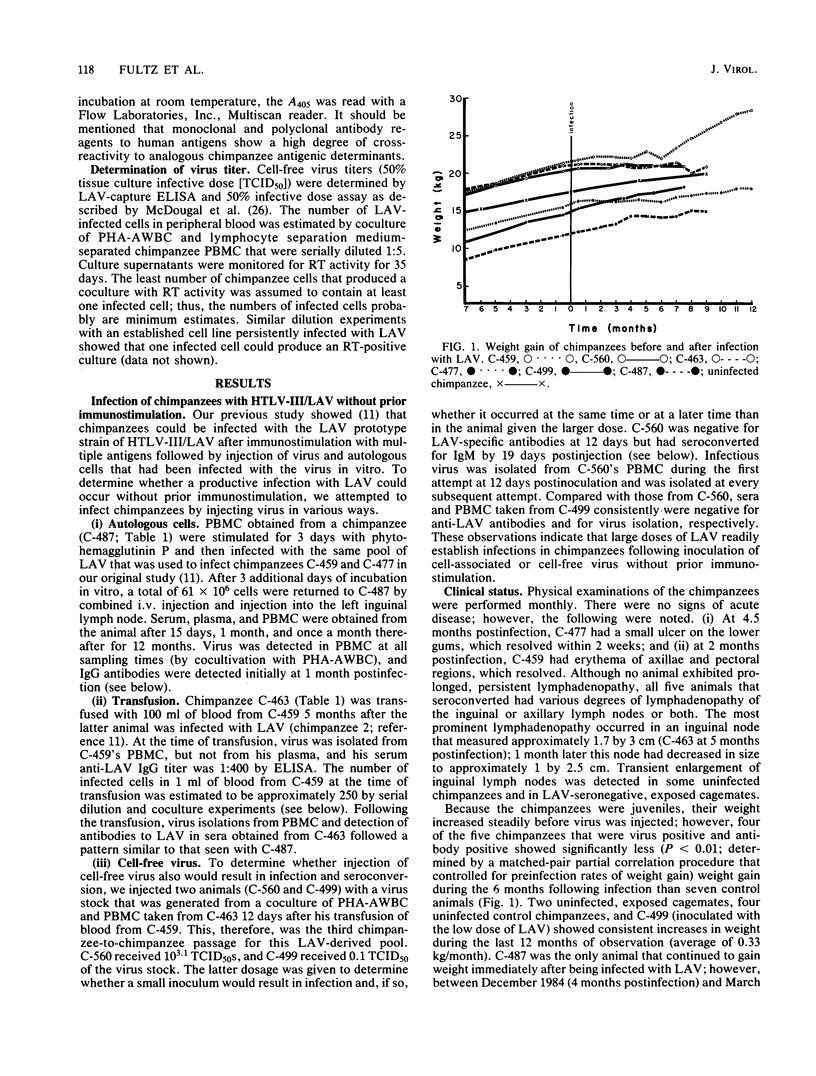
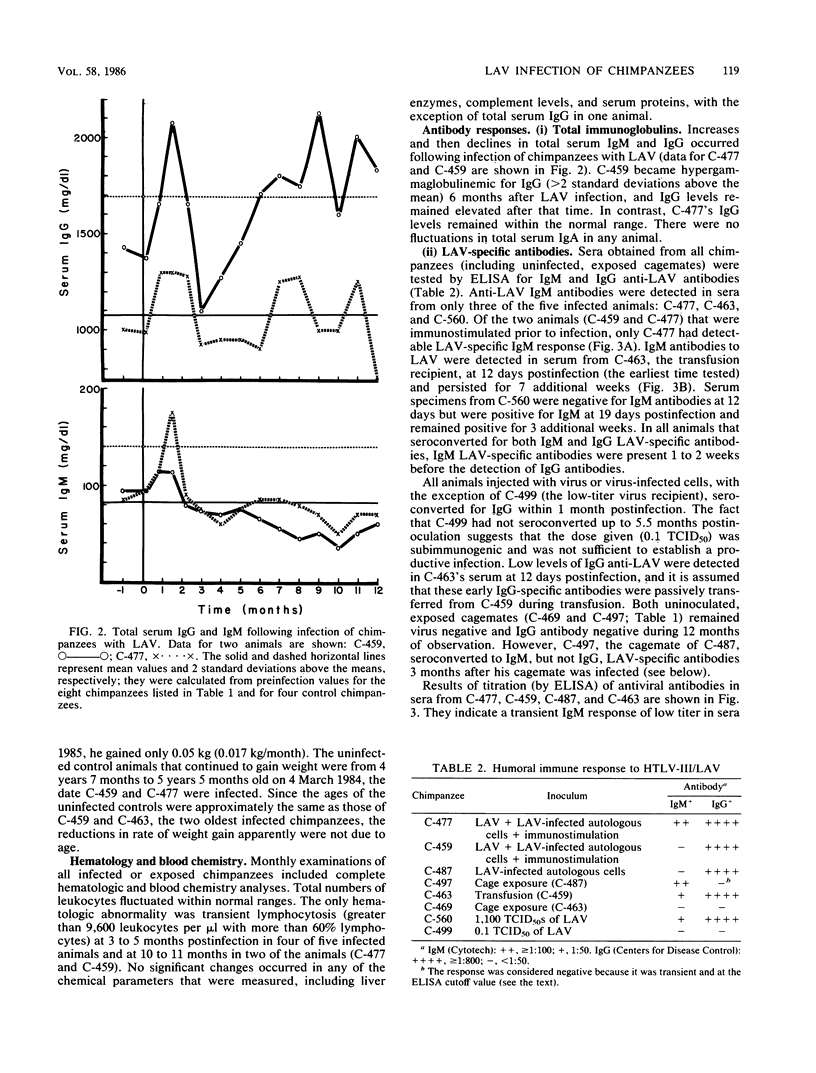
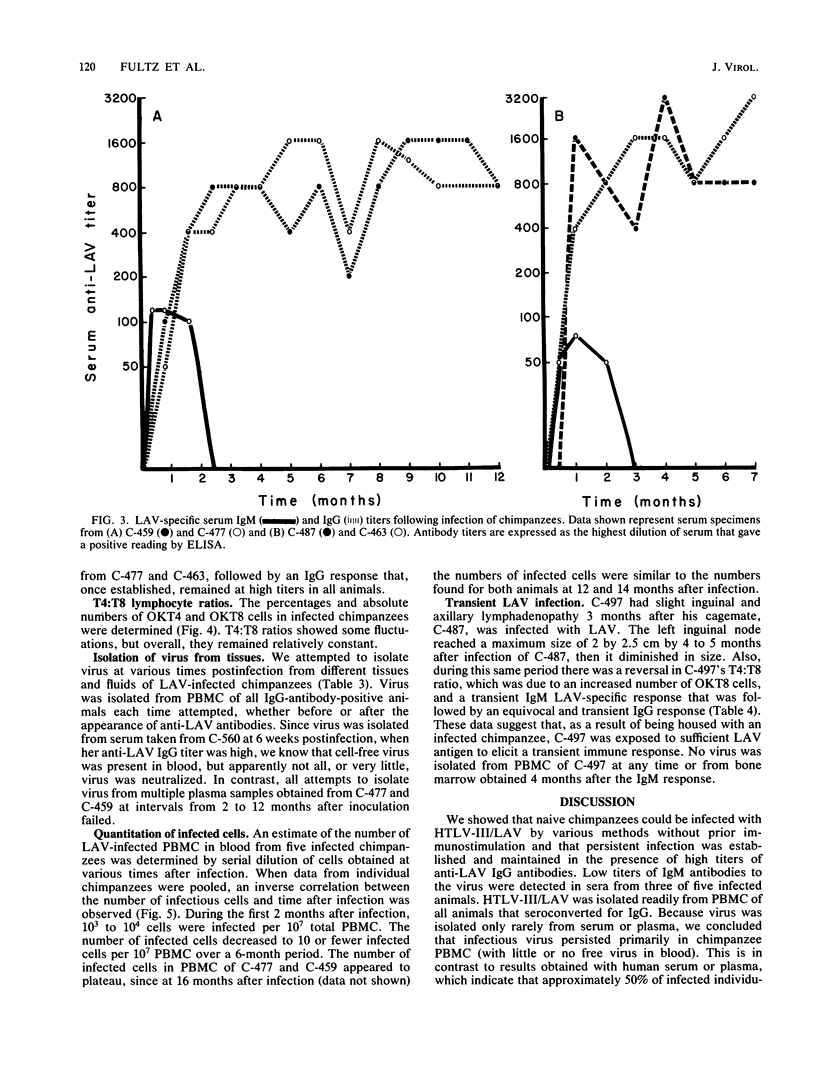
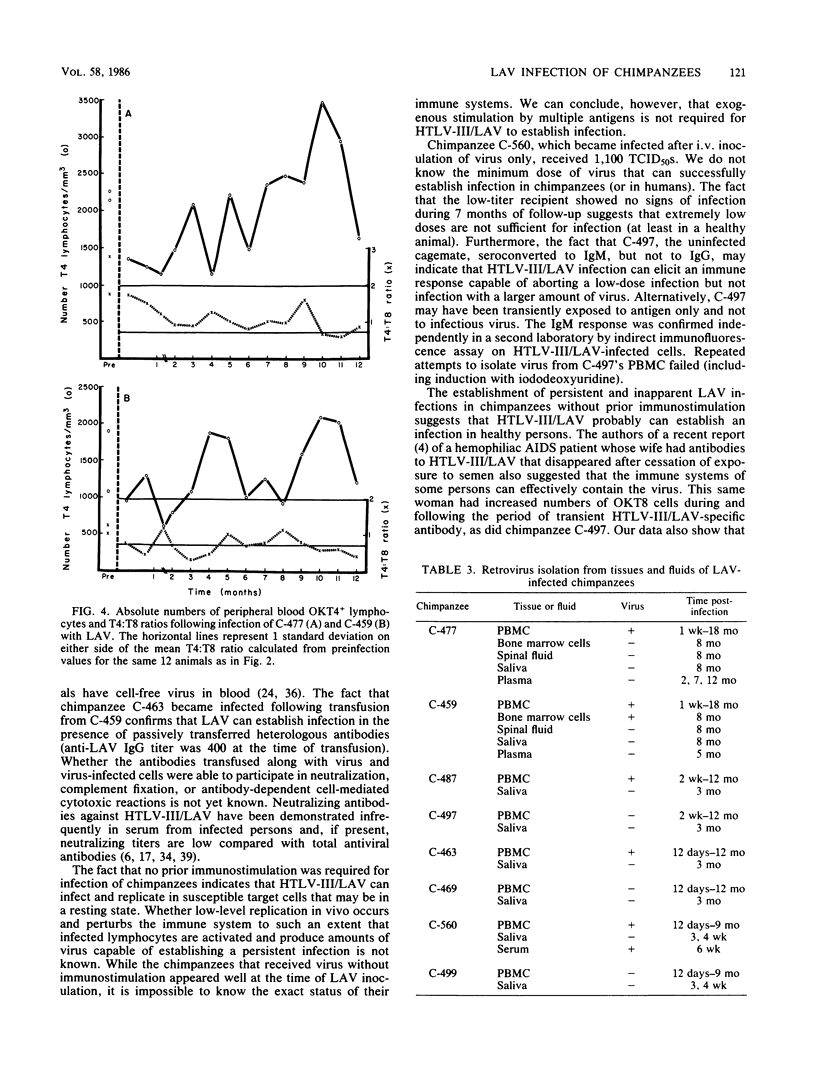
The lymphadenopathy-associated virus (LAV) prototype strain of human T-lymphotropic virus type III/LAV was transmitted to juvenile chimpanzees with no prior immunostimulation by (i) intravenous injection of autologous cells infected in vitro, (ii) intravenous injection of cell-free virus, and (iii) transfusion from a previously infected chimpanzee. All five animals that received more than one 50% tissue culture infective dose were persistently infected with LAV or chimpanzee-passaged LAV for up to 18 months. During this time they developed no illnesses, but they exhibited various degrees of inguinal and axillary lymphadenopathy and significant reductions in rates of weight gain. Detailed blood chemistry and hematologic evaluations revealed no consistent abnormalities, with the exception of immunoglobulin G (IgG) hypergammaglobulinemia, which became apparent in one animal 6 months postinfection and continued at more than 1 year postinfection. Transient depressions followed by increases in the numbers of T4 cells to levels greater than normal were observed in all animals after virus inoculation. However, the number of LAV-infected peripheral blood cells decreased with time after infection. Results of enzyme immunoassays showed that all infected animals seroconverted to IgG anti-LAV within 1 month postinfection and that antibody titers remained high throughout the period of observation. In contrast, only three of the five LAV-infected chimpanzees had detectable IgM antibody responses, and these preceded IgG-specific serum antibodies by 1 to 2 weeks. Virus morphologically and serologically identical to LAV was isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of all infected animals at all times tested and from bone marrow cells taken from one animal 8 months after infection. One chimpanzee that was exposed to LAV only by sharing a cage with an infected chimpanzee developed lymphadenopathy and an IgM response to LAV, both of which were transient; however, no persistent IgG antibody response to LAV developed, and no virus was recovered from peripheral blood cells during a year of follow-up. Thus, LAV readily infected chimpanzees following intravenous inoculation and persisted for extended periods despite the presence of high titers of antiviral antibodies. However, the virus was not easily transmitted from infected to uninfected chimpanzees during daily cage contact.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alter H. J., Eichberg J. W., Masur H., Saxinger W. C., Gallo R., Macher A. M., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S. Transmission of HTLV-III infection from human plasma to chimpanzees: an animal model for AIDS. Science. 1984 Nov 2;226(4674):549–552. doi: 10.1126/science.6093251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner W. A., Biggar R. J., Weiss S. H., Melbye M., Goedert J. J. Epidemiology of human T-lymphotropic virus type III and the risk of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Nov;103(5):665–670. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-5-665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger H., Weiser B., Robinson W. S., Lifson J., Engleman E., Rouzioux C., Brun-Vézinet F., Barré-Sinoussi F., Montagnier L., Chermann J. C. Transient antibody to lymphadenopathy-associated virus/human T-lymphotropic virus type III and T-lymphocyte abnormalities in the wife of a man who developed the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Oct;103(4):545–547. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-4-545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carne C. A., Weller I. V., Sutherland S., Cheingsong-Popov R., Ferns R. B., Williams P., Mindel A., Tedder R., Adler M. W. Rising prevalence of human T-lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III) infection in homosexual men in London. Lancet. 1985 Jun 1;1(8440):1261–1262. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92324-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavel F., Klatzmann D., Montagnier L. Deficient LAV1 neutralising capacity of sera from patients with AIDS or related syndromes. Lancet. 1985 Apr 13;1(8433):879–880. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92243-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey J. L., Prince H., Weaver M., Groopman J., Visscher B., Schwartz K., Detels R. Quantitative changes in T helper or T suppressor/cytotoxic lymphocyte subsets that distinguish acquired immune deficiency syndrome from other immune subset disorders. Am J Med. 1984 Jan;76(1):95–100. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90756-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feorino P. M., Jaffe H. W., Palmer E., Peterman T. A., Francis D. P., Kalyanaraman V. S., Weinstein R. A., Stoneburner R. L., Alexander W. J., Raevsky C. Transfusion-associated acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Evidence for persistent infection in blood donors. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 16;312(20):1293–1296. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505163122005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feorino P. M., Kalyanaraman V. S., Haverkos H. W., Cabradilla C. D., Warfield D. T., Jaffe H. W., Harrison A. K., Gottlieb M. S., Goldfinger D., Chermann J. C. Lymphadenopathy associated virus infection of a blood donor--recipient pair with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Science. 1984 Jul 6;225(4657):69–72. doi: 10.1126/science.6328663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis D. P., Feorino P. M., Broderson J. R., McClure H. M., Getchell J. P., McGrath C. R., Swenson B., McDougal J. S., Palmer E. L., Harrison A. K. Infection of chimpanzees with lymphadenopathy-associated virus. Lancet. 1984 Dec 1;2(8414):1276–1277. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92824-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis D. P., Jaffe H. W., Fultz P. N., Getchell J. P., McDougal J. S., Feorino P. M. The natural history of infection with the lymphadenopathy-associated virus/human T-lymphotropic virus type III. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Nov;103(5):719–722. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-5-719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek D. C., Amyx H. L., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Asher D. M., Rodgers-Johnson P., Epstein L. G., Sarin P. S., Gallo R. C., Maluish A., Arthur L. O. Infection of chimpanzees by human T-lymphotropic retroviruses in brain and other tissues from AIDS patients. Lancet. 1985 Jan 5;1(8419):55–56. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Shearer G. M., Kaplan M., Haynes B. F., Palker T. J., Redfield R., Oleske J., Safai B. Frequent detection and isolation of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.6200936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert J. J., Sarngadharan M. G., Biggar R. J., Weiss S. H., Winn D. M., Grossman R. J., Greene M. H., Bodner A. J., Mann D. L., Strong D. M. Determinants of retrovirus (HTLV-III) antibody and immunodeficiency conditions in homosexual men. Lancet. 1984 Sep 29;2(8405):711–716. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92624-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groopman J. E., Salahuddin S. Z., Sarngadharan M. G., Markham P. D., Gonda M., Sliski A., Gallo R. C. HTLV-III in saliva of people with AIDS-related complex and healthy homosexual men at risk for AIDS. Science. 1984 Oct 26;226(4673):447–449. doi: 10.1126/science.6093247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gürtler L. G., Wernicke D., Eberle J., Zoulek G., Deinhardt F., Schramm W. Increase in prevalence of anti-HTLV-III in haemophiliacs. Lancet. 1984 Dec 1;2(8414):1275–1276. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92823-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Rota T. R., Hirsch M. S. Antibody to lymphadenopathy-associated virus in AIDS. N Engl J Med. 1985 Mar 7;312(10):649–650. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198503073121015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover E. A., Rojko J. L., Wilson P. L., Olsen R. G. Determinants of susceptibility and resistance to feline leukemia virus infection. I. Role of macrophages. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Oct;67(4):889–898. doi: 10.1093/jnci/67.4.889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe H. W., Darrow W. W., Echenberg D. F., O'Malley P. M., Getchell J. P., Kalyanaraman V. S., Byers R. H., Drennan D. P., Braff E. H., Curran J. W. The acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in a cohort of homosexual men. A six-year follow-up study. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Aug;103(2):210–214. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-2-210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Barré-Sinoussi F., Nugeyre M. T., Danquet C., Vilmer E., Griscelli C., Brun-Veziret F., Rouzioux C., Gluckman J. C., Chermann J. C. Selective tropism of lymphadenopathy associated virus (LAV) for helper-inducer T lymphocytes. Science. 1984 Jul 6;225(4657):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.6328660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiss J. K., Kitchen L. W., Prince H. E., Kasper C. K., Essex M. Antibody to human T-lymphotropic virus type III in wives of hemophiliacs. Evidence for heterosexual transmission. Ann Intern Med. 1985 May;102(5):623–626. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-102-5-623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Hoffman A. D., Kramer S. M., Landis J. A., Shimabukuro J. M., Oshiro L. S. Isolation of lymphocytopathic retroviruses from San Francisco patients with AIDS. Science. 1984 Aug 24;225(4664):840–842. doi: 10.1126/science.6206563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Kaminsky L. S., Morrow W. J., Steimer K., Luciw P., Dina D., Hoxie J., Oshiro L. Infection by the retrovirus associated with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Clinical, biological, and molecular features. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Nov;103(5):694–699. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-5-694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Shimabukuro J., Hollander H., Mills J., Kaminsky L. Isolation of AIDS-associated retroviruses from cerebrospinal fluid and brain of patients with neurological symptoms. Lancet. 1985 Sep 14;2(8455):586–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney M. J., Cox F., Wray B. B., Guill M. F., Hagler J., Williams D. AIDS in a child 5 1/2 years after a transfusion. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 9;312(19):1256–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Cort S. P., Kennedy M. S., Cabridilla C. D., Feorino P. M., Francis D. P., Hicks D., Kalyanaraman V. S., Martin L. S. Immunoassay for the detection and quantitation of infectious human retrovirus, lymphadenopathy-associated virus (LAV). J Immunol Methods. 1985 Jan 21;76(1):171–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90489-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montagnier L. Lymphadenopathy-associated virus: from molecular biology to pathogenicity. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Nov;103(5):689–693. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-5-689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Wolinsky J. S., Clements J. E., Strandberg J. D., Griffin D. E., Cork L. C. Slow virus replication: the role of macrophages in the persistence and expression of visna viruses of sheep and goats. J Gen Virol. 1982 Apr;59(Pt 2):345–356. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-2-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson J. K., McDougal J. S., Spira T. J., Cross G. D., Jones B. M., Reinherz E. L. Immunoregulatory subsets of the T helper and T suppressor cell populations in homosexual men with chronic unexplained lymphadenopathy. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jan;73(1):191–201. doi: 10.1172/JCI111190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterman T. A., Jaffe H. W., Feorino P. M., Getchell J. P., Warfield D. T., Haverkos H. W., Stoneburner R. L., Curran J. W. Transfusion-associated acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in the United States. JAMA. 1985 Nov 22;254(20):2913–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piot P., Quinn T. C., Taelman H., Feinsod F. M., Minlangu K. B., Wobin O., Mbendi N., Mazebo P., Ndangi K., Stevens W. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in a heterosexual population in Zaire. Lancet. 1984 Jul 14;2(8394):65–69. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90241-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfield R. R., Markham P. D., Salahuddin S. Z., Sarngadharan M. G., Bodner A. J., Folks T. M., Ballou W. R., Wright D. C., Gallo R. C. Frequent transmission of HTLV-III among spouses of patients with AIDS-related complex and AIDS. JAMA. 1985 Mar 15;253(11):1571–1573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert-Guroff M., Brown M., Gallo R. C. HTLV-III-neutralizing antibodies in patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. Nature. 1985 Jul 4;316(6023):72–74. doi: 10.1038/316072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojko J. L., Hoover E. A., Mathes L. E., Olsen R. G., Schaller J. P. Pathogenesis of experimental feline leukemia virus infection. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Sep;63(3):759–768. doi: 10.1093/jnci/63.3.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin S. Z., Markham P. D., Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Orndorff S., Fladagar A., Patel A., Gold J., Gallo R. C. Isolation of infectious human T-cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III) from patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) or AIDS-related complex (ARC) and from healthy carriers: a study of risk groups and tissue sources. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5530–5534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. M., Harper M. E., Hahn B. H., Epstein L. G., Gajdusek D. C., Price R. W., Navia B. A., Petito C. K., O'Hara C. J., Groopman J. E. HTLV-III infection in brains of children and adults with AIDS encephalopathy. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.2981429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider W. D., Simpson D. M., Nielsen S., Gold J. W., Metroka C. E., Posner J. B. Neurological complications of acquired immune deficiency syndrome: analysis of 50 patients. Ann Neurol. 1983 Oct;14(4):403–418. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A., Clapham P. R., Cheingsong-Popov R., Dalgleish A. G., Carne C. A., Weller I. V., Tedder R. S. Neutralization of human T-lymphotropic virus type III by sera of AIDS and AIDS-risk patients. Nature. 1985 Jul 4;316(6023):69–72. doi: 10.1038/316069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



