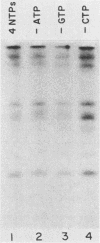
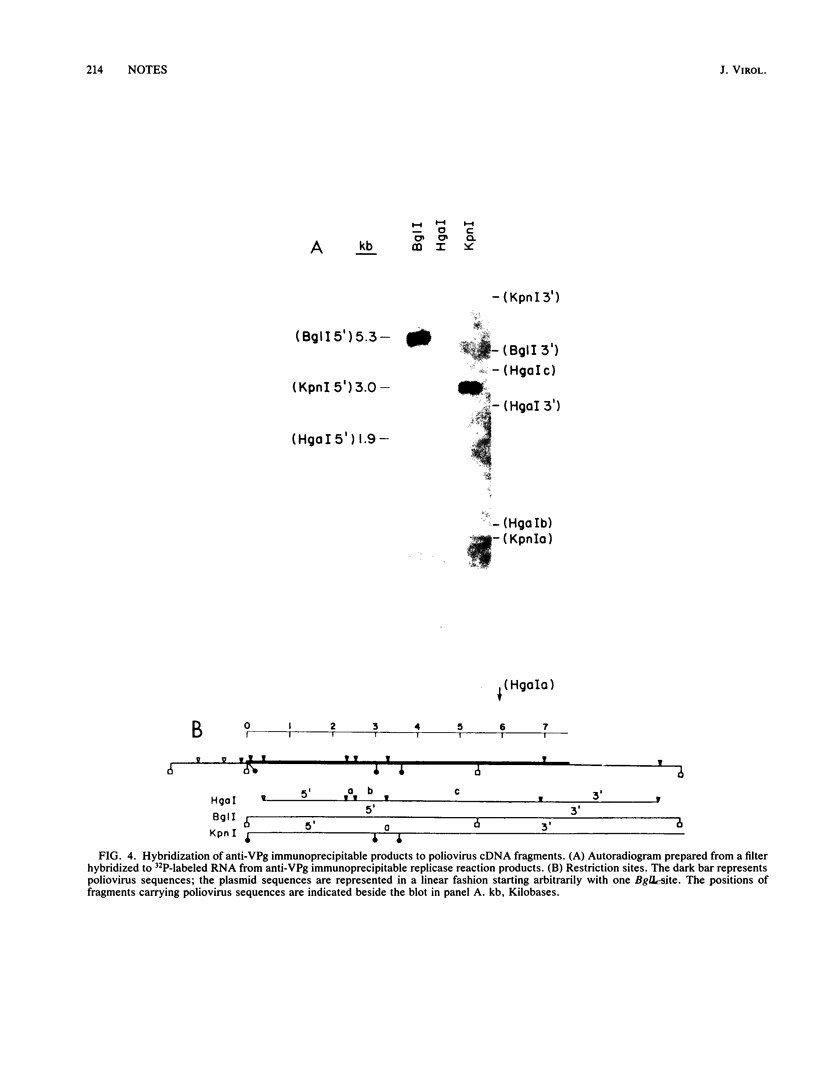
Abstract
Anti-VPg immunoprecipitable RNA labeled in vitro during a poliovirus RNA polymerase reaction was formed by the elongation of VPg-containing template fragments rather than by initiation with VPg. The reaction was dependent on a host factor (terminal uridylyl transferase). The incorporation of labeled UTP could be detected with only the host factor present.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews N. C., Levin D., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase stimulation by terminal uridylyl transferase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7628–7635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Anti-VPg antibody inhibition of the poliovirus replicase reaction and production of covalent complexes of VPg-related proteins and RNA. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):745–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. In vitro copying of viral positive strand RNA by poliovirus replicase. Characterization of the reaction and its products. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12359–12366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Purification and properties of a host cell protein required for poliovirus replication in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12351–12358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Zabel P., Baltimore D. Dependence of the activity of the poliovirus replicase on the host cell protein. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):423–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90516-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsch-Häsler K., Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Replication of picornaviruses. I. Evidence from in vitro RNA synthesis that poly(A) of the poliovirus genome is genetically coded. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1512–1517. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1512-1517.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Petterson R. F., Ambros V., Hewlett N. J., Baltimore D. Covalent linkage of a protein to a defined nucleotide sequence at the 5'-terminus of virion and replicative intermediate RNAs of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):961–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Van Dyke T. A. Isolation of a soluble and template-dependent poliovirus RNA polymerase that copies virion RNA in vitro. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):155–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.155-161.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. D., Navab M., Peterson C., Hocko J., Dasgupta A. Antibody to poliovirus genome-linked protein (VPg) precipitates in vitro synthesized RNA attached to VPg-precursor polypeptide(s). Virus Res. 1984;1(2):89–100. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Detjen B., Pozzatti R., Wimmer E. The location of the polio genome protein in viral RNAs and its implication for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):208–213. doi: 10.1038/268208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R. F., Ambros V., Baltimore D. Identification of a protein linked to nascent poliovirus RNA and to the polyuridylic acid of negative-strand RNA. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):357–365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.357-365.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Requirement of 3'-terminal poly(adenylic acid) for the infectivity of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2983–2987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegami T., Kuhn R. J., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Membrane-dependent uridylylation of the genome-linked protein VPg of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7447–7451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. A., Flanegan J. B. Identification of poliovirus polypeptide P63 as a soluble RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):732–740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.732-740.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. A., Rickles R. J., Flanegan J. B. Genome-length copies of poliovirion RNA are synthesized in vitro by the poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4610–4617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Polyadenylic acid at the 3'-terminus of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1877–1882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]