Abstract
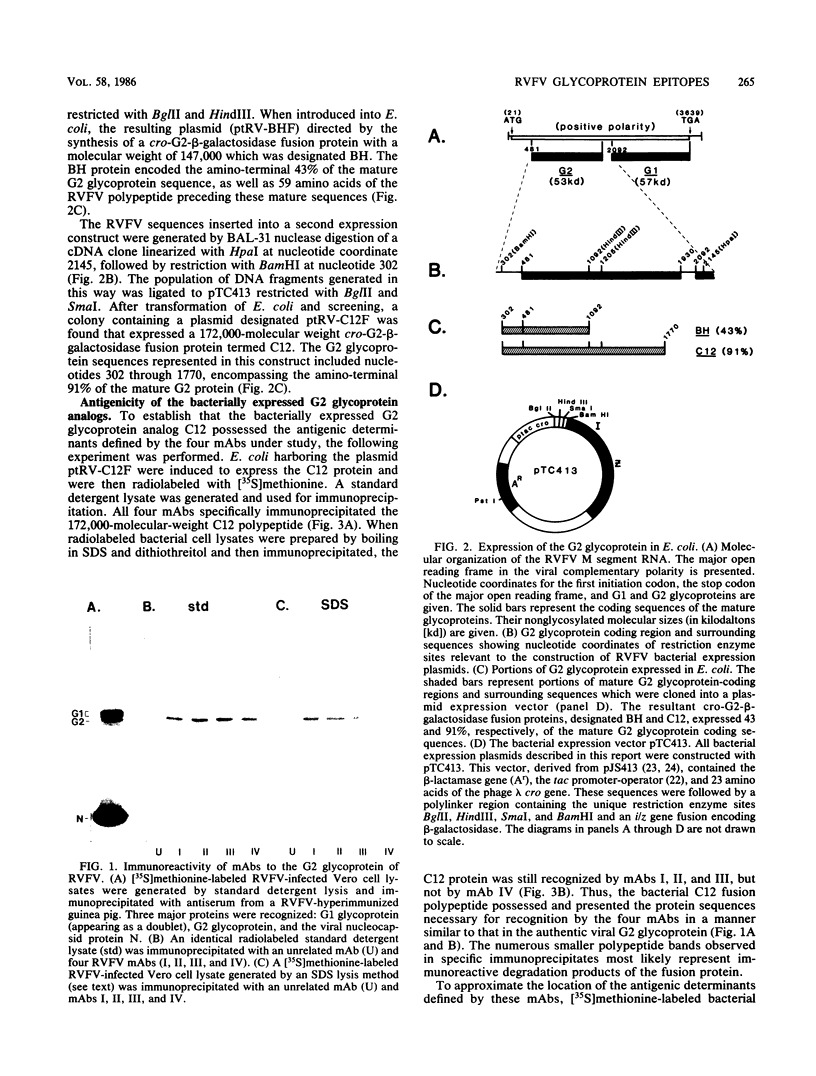
Four distinct antigenic determinants along the G2 glycoprotein encoded by the M segment RNA of the Phlebovirus Rift Valley fever virus were localized. These epitopes were defined by four monoclonal antibodies, three of which were capable of neutralizing virus infectivity; one was nonneutralizing. Immunoprecipitation by these monoclonal antibodies of either denatured or native antigen characterized the epitopes as having linear or higher order structure. Molecular cloning of G2 glycoprotein-coding sequences into a bacterial expression plasmid utilizing a beta-galactosidase fusion protein system was employed for epitope localization. A nuclease BAL 31 plasmid expression library, in which processive regions of the 3' end of the G2 glycoprotein coding sequences were deleted, allowed for approximation of the carboxy-terminal limit of the antigenic determinants. Further subcloning of limited G2 polypeptide sequences into the bacterial expression vector permitted more refined localization of the epitopes. The characteristics of the immunoreactivity of these small peptide regions (between 11 and 34 amino acids) produced in bacteria as G2-beta-galactosidase fusion proteins were similar to those of the authentic Rift Valley fever virus G2 glycoprotein. These defined antigenic determinants and their importance in virus infectivity are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop D. H., Calisher C. H., Casals J., Chumakov M. P., Gaidamovich S. Y., Hannoun C., Lvov D. K., Marshall I. D., Oker-Blom N., Pettersson R. F. Bunyaviridae. Intervirology. 1980;14(3-4):125–143. doi: 10.1159/000149174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a transformation-specific antigen induced by an avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):346–348. doi: 10.1038/269346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Purchio A. F., Keegan K., Frazier S., Hays W., Anderson D. K., Parker M. D., Schmaljohn C., Schmidt J., Dalrymple J. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of the M RNA segment of Rift Valley fever virus. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):228–245. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90320-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentsch J. R., Rozhon E. J., Klimas R. A., El Said L. H., Shope R. E., Bishop D. H. Evidence from recombinant bunyavirus studies that the M RNA gene products elicit neutralizing antibodies. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):190–204. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90080-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grady L. J., Sanders M. L., Campbell W. P. Evidence for three separate antigenic sites on the G1 protein of La Crosse Virus. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90490-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogstraal H., Meegan J. M., Khalil G. M., Adham F. K. The Rift Valley fever epizootic in Egypt 1977-78. 2. Ecological and entomological studies. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(6):624–629. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara T., Akashi H., Bishop D. H. Novel coding strategy (ambisense genomic RNA) revealed by sequence analyses of Punta Toro Phlebovirus S RNA. Virology. 1984 Jul 30;136(2):293–306. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara T., Smith J., Dalrymple J. M., Bishop D. H. Complete sequences of the glycoproteins and M RNA of Punta Toro phlebovirus compared to those of Rift Valley fever virus. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):246–259. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90321-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughlin L. W., Meegan J. M., Strausbaugh L. J., Morens D. M., Watten R. H. Epidemic Rift Valley fever in Egypt: observations of the spectrum of human illness. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(6):630–633. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meegan J. M., Hoogstraal H., Moussa M. I. An epizootic of Rift Valley fever in Egypt in 1977. Vet Rec. 1979 Aug 11;105(6):124–125. doi: 10.1136/vr.105.6.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meegan J. M. The Rift Valley fever epizootic in Egypt 1977-78. 1. Description of the epizzotic and virological studies. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(6):618–623. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice R. M., Erlick B. J., Rosato R. R., Eddy G. A., Mohanty S. B. Biochemical characterization of Rift Valley fever virus. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):256–260. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. R., Bennett G. N. Construction and analysis of in vivo activity of E. coli promoter hybrids and promoter mutants that alter the -35 to -10 spacing. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(2):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Weis J. H., Salstrom J. S., Enquist L. W. Bacterial synthesis of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 glycoprotein D antigens. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Jul;83(1 Suppl):102s–111s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12281828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J. H., Enquist L. W., Salstrom J. S., Watson R. J. An immunologically active chimaeric protein containing herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):72–74. doi: 10.1038/302072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]