Abstract
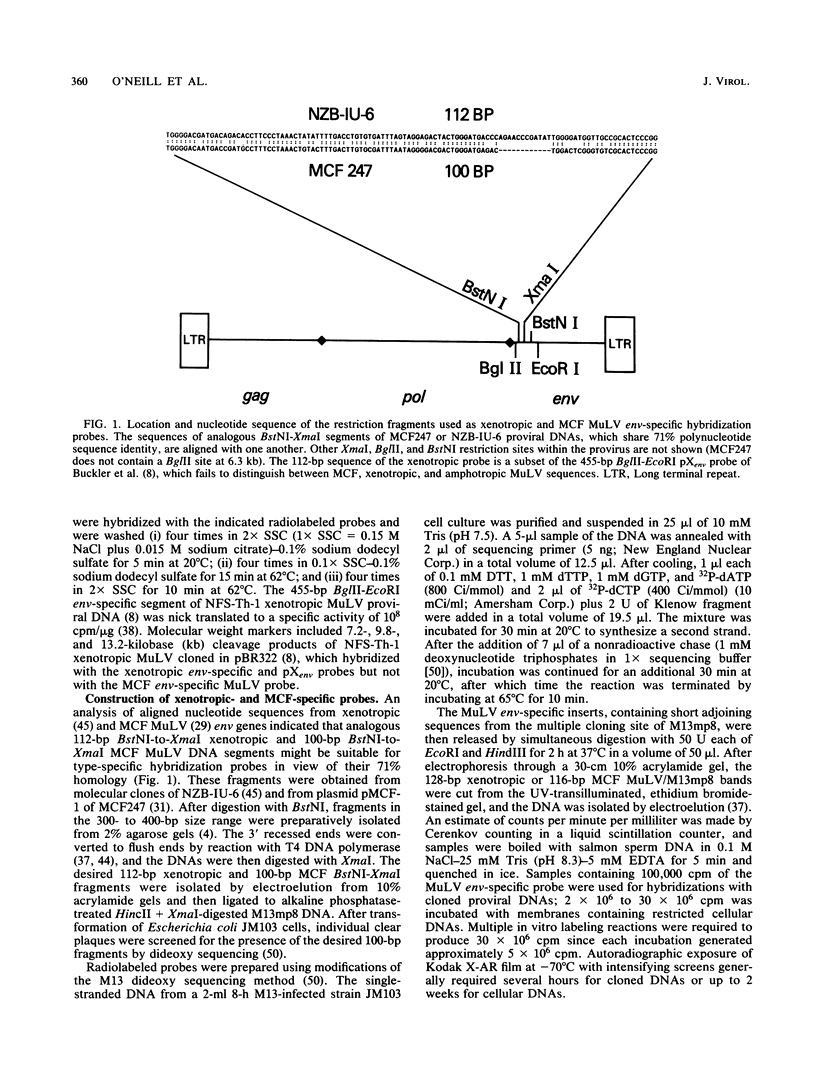
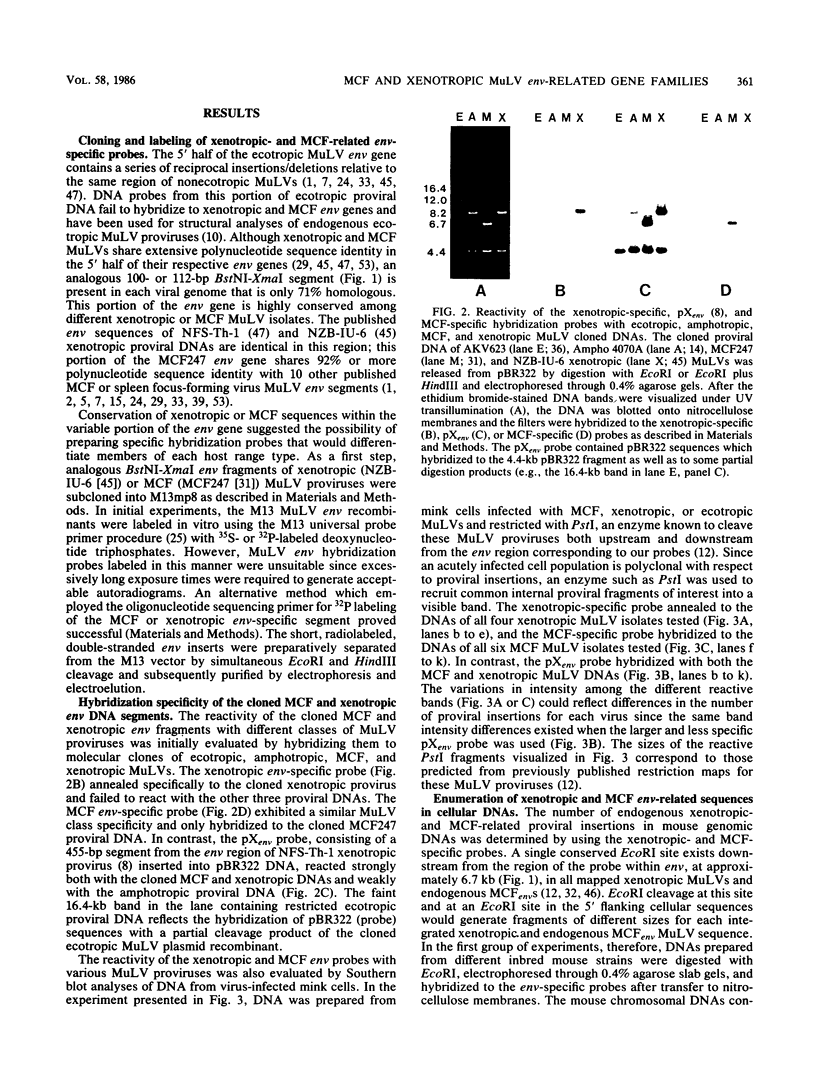
We have derived hybridization probes from analogous 100-base-pair segments located within the N-terminal region of gp70 coding sequences which differentiate xenotropic from mink cell focus-forming (MCF)-related murine leukemia virus (MuLV) DNAs. The MCF probe annealed to the integrated proviruses of all six MCF MuLV isolates tested; the xenotropic probe hybridized to the DNAs of all four xenotropic proviral isolates examined. No cross-hybridization was observed, and neither probe reacted with the env segments of amphotropic or ecotropic MuLV DNAs. Southern blot analysis of HindIII- or EcoRI-digested genomic DNAs from a variety of inbred laboratory mice demonstrated the presence of more MCF- than xenotropic MuLV-related segments in every strain tested.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi A., Sakai K., Kitamura N., Nakanishi S., Niwa O., Matsuyama M., Ishimoto A. Characterization of the env gene and long terminal repeat of molecularly cloned Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus DNA. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):813–821. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.813-821.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amanuma H., Katori A., Obata M., Sagata N., Ikawa Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of the gene for the specific glycoprotein (gp55) of Friend spleen focus-forming virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3913–3917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassin R. H., Ruscetti S., Ali I., Haapala D. K., Rein A. Normal DBA/2 mouse cells synthesize a glycoprotein which interferes with MCF virus infection. Virology. 1982 Nov;123(1):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bestwick R. K., Boswell B. A., Kabat D. Molecular cloning of biologically active Rauscher spleen focus-forming virus and the sequences of its env gene and long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):695–705. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.695-705.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt C., Mileham K., Haas M., Nesbitt M. N., Harper M. E., Simon M. I. Chromosomal mapping of the mink cell focus-inducing and xenotropic env gene family in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6298–6302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosselman R. A., van Straaten F., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M., Vogt M. Analysis of the env gene of a molecularly cloned and biologically active Moloney mink cell focus-forming proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):19–31. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.19-31.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler C. E., Hoggan M. D., Chan H. W., Sears J. F., Khan A. S., Moore J. L., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Martin M. A. Cloning and characterization of an envelope-specific probe from xenotropic murine leukemia proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):228–236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.228-236.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan R., Lieber M. M., Todaro G. J. Nucleic acid homology of murine xenotropic type C viruses. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1378–1384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1378-1384.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan H. W., Bryan T., Moore J. L., Staal S. P., Rowe W. P., Martin M. A. Identification of ecotropic proviral sequences in inbred mouse strains with a cloned subgenomic DNA fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5779–5783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Cloyd M. W., Linemeyer D. L., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Cellular origin and role of mink cell focus-forming viruses in murine thymic lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):25–31. doi: 10.1038/295025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Gupta S., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Origin of mink cytopathic focus-forming (MCF) viruses:comparison with ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia virus genomes. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Teich N. M., Levine A. S., Rowe W. P. Qualitative and quantitative studies of AKR-type murine leukemia virus sequences in mouse DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):1085–1101. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Oliff A. I., Linemeyer D. L., Lander M. R., Lowy D. R. Genomes of murine leukemia viruses isolated from wild mice. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):777–791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.777-791.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. P., Mak T. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of an infectious clone of Friend spleen focus-forming provirus: gp55 is an envelope fusion glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5037–5041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Cell-surface antigens associated with recombinant mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):702–712. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Lymphomagenicity of recombinant mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):542–552. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Isolation of a recombinant murine leukemia virus utilizing a new primer tRNA. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):37–45. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.37-45.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Gautsch J. W., Jensen F. C., Lerner R. A., Chused T. M., Morse H. C., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Differential expression of two distinct xenotropic viruses in NZB mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Mar;15(3):493–501. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Cloyd M. W. Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses specifically recombine with different endogenous retroviral sequences to generate mink cell focus-forming viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):459–463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Yetter R. A., Morse H. C., 3rd A mouse gene on chromosome 5 that restricts infectivity of mink cell focus-forming recombinant murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):16–24. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoggan M. D., Buckler C. E., Sears J. F., Rowe W. P., Martin M. A. Organization and stability of endogenous xenotropic murine leukemia virus proviral DNA in mouse genomes. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):473–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.473-477.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland C. A., Wozney J., Hopkins N. Nucleotide sequence of the gp70 gene of murine retrovirus MCF 247. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):413–420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.413-420.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N., Messing J. The making of strand-specific M13 probes. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Laigret F., Martin M. A., Repaske R. Characterization of a molecularly cloned retroviral sequence associated with Fv-4 resistance. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):768–777. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.768-777.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimoto A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Detection and quantitation of phenotypically mixed viruses: mixing of ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1977 Sep;81(2):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel M. A., Vanderryn D. F., Meltzer M. L., Martin M. A. Characterization of polyoma viral DNA sequences in polyoma-induced hamster tumor cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3798–3805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. S., Martin M. A. Endogenous murine leukemia proviral long terminal repeats contain a unique 190-base-pair insert. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2699–2703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis establishes the role of endogenous murine leukemia virus DNA segments in formation of recombinant mink cell focus-forming murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):864–871. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.864-871.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. S., Repaske R., Garon C. F., Chan H. W., Rowe W. P., Martin M. A. Characterization of proviruses cloned from mink cell focus-forming virus-infected cellular DNA. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):435–448. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.435-448.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. S., Rowe W. P., Martin M. A. Cloning of endogenous murine leukemia virus-related sequences from chromosomal DNA of BALB/c and AKR/J mice: identification of an env progenitor of AKR-247 mink cell focus-forming proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):625–636. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.625-636.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Zimmermann W., Oliff A., Friedrich R. Molecular analysis of the envelope gene and long terminal repeat of Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus: implications for the functions of these sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):828–840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.828-840.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., Rowe W. P. Genetic mapping of xenotropic murine leukemia virus-inducing loci in five mouse strains. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):219–228. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A. Xenotropic type C viruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;79:111–213. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66853-1_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Rands E., Chattopadhyay S. K., Garon C. F., Hager G. L. Molecular cloning of infectious integrated murine leukemia virus DNA from infected mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):614–618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark G. E., Rapp U. R. Envelope gene sequence of two in vitro-generated mink cell focus-forming murine leukemia viruses which contain the entire gp70 sequence of the endogenous nonecotropic parent. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):530–539. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.530-539.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meruelo D., Rossomando A., Offer M., Buxbaum J., Pellicer A. Association of endogenous viral loci with genes encoding murine histocompatibility and lymphocyte differentiation antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5032–5036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse H. C., 3rd, Kozak C. A., Yetter R. A., Hartley J. W. Unique features of retrovirus expression in F/St mice. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.1-7.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikbakht K. N., Ou C. Y., Boone L. R., Glover P. L., Yang W. K. Nucleotide sequence analysis of endogenous murine leukemia virus-related proviral clones reveals primer-binding sites for glutamine tRNA. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):889–893. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.889-893.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H., Kutter E., Nakanishi M. A restriction map of the bacteriophage T4 genome. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(2):421–435. doi: 10.1007/BF00425473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill R. R., Buckler C. E., Theodore T. S., Martin M. A., Repaske R. Envelope and long terminal repeat sequences of a cloned infectious NZB xenotropic murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):100–106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.100-106.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repaske R., O'Neill R. R., Khan A. S., Martin M. A. Nucleotide sequence of the env-specific segment of NFS-Th-1 xenotropic murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.204-211.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P. Leukemia virus genomes in the chromosomal DNA of the mouse. Harvey Lect. 1978;71:173–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti S., Davis L., Feild J., Oliff A. Friend murine leukemia virus-induced leukemia is associated with the formation of mink cell focus-inducing viruses and is blocked in mice expressing endogenous mink cell focus-inducing xenotropic viral envelope genes. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):907–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varnier O. E., Hoffman A. D., Nexø B. A., Levy J. A. Murine xenotropic type C viruses. V. Biologic and structural differences among three cloned retroviruses isolated from kidney cells from one NZB mouse. Virology. 1984 Jan 15;132(1):79–94. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff L., Scolnick E., Ruscetti S. Envelope gene of the Friend spleen focus-forming virus: deletion and insertions in 3' gp70/p15E-encoding region have resulted in unique features in the primary structure of its protein product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4718–4722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]