Abstract
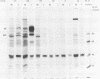
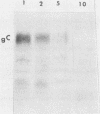
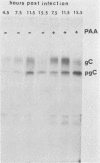
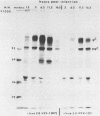
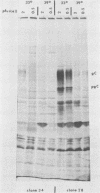
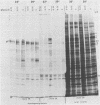
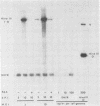
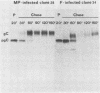
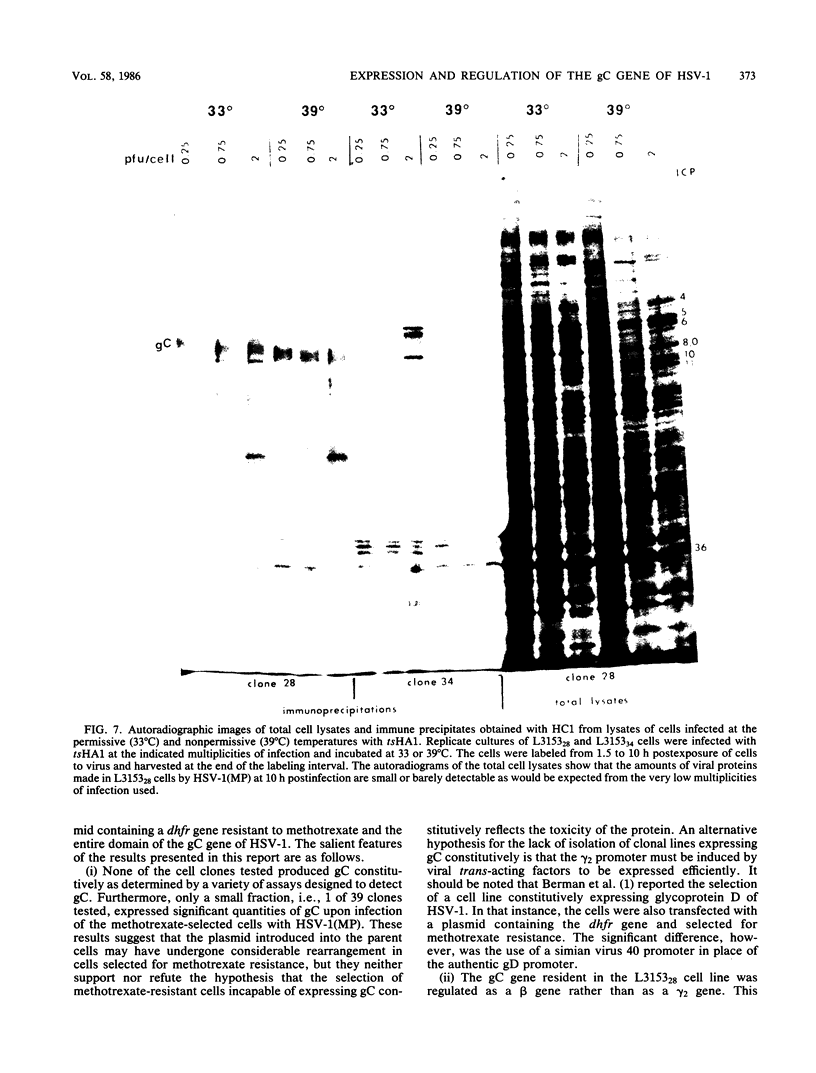
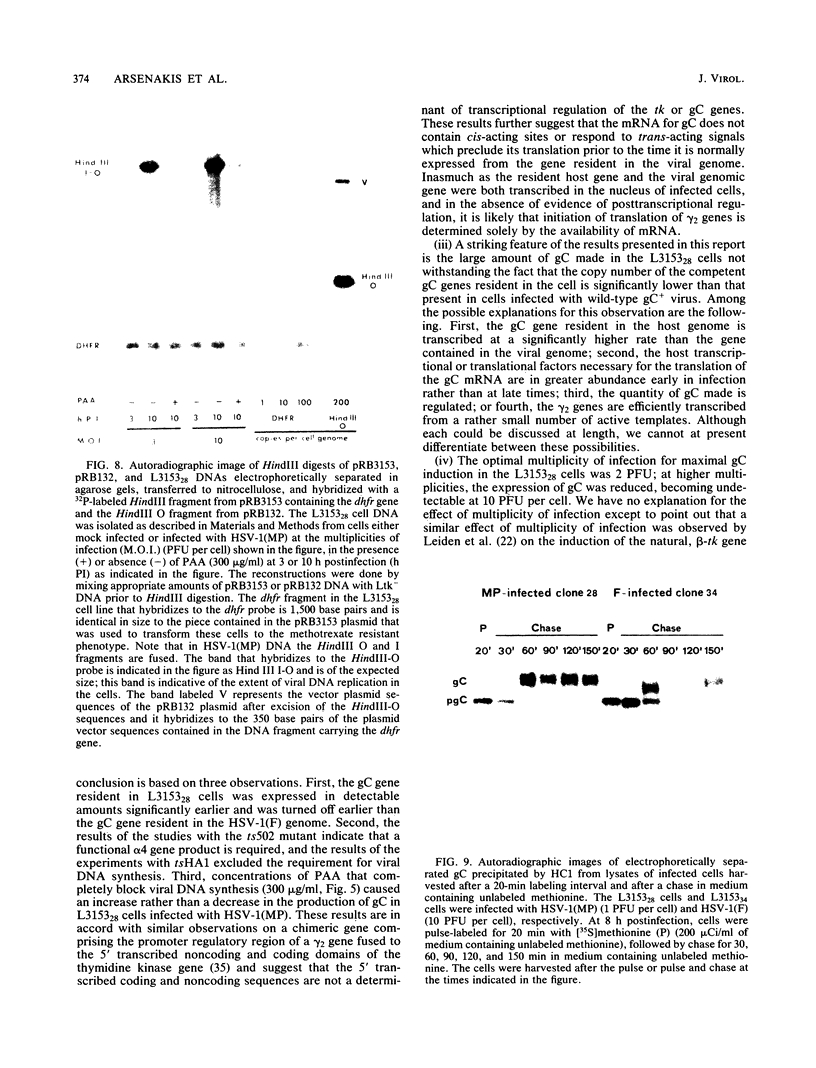
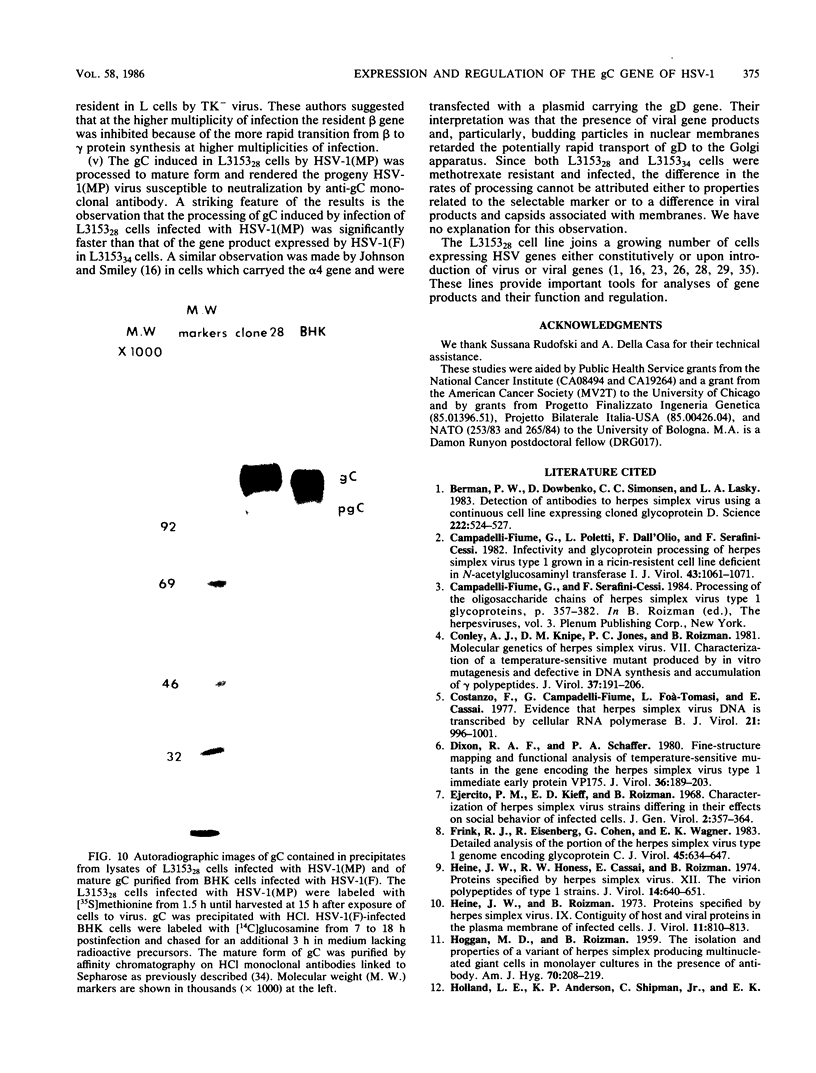
Ltk- cells were transfected with a plasmid containing the entire domain of glycoprotein C (gC), a true gamma or gamma 2 gene of herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) and the methotrexate-resistant mouse dihydrofolate reductase mutant gene. The resulting methotrexate-resistant cell line was cloned; of the 39 clonal lines tested only 1, L3153(28), expressed gC after infection with HSV-1(MP), a gC- mutant, and none expressed gC constitutively. The induction of gC was optimal at multiplicities ranging between 0.5 and 2 PFU per cell, and the quantities produced were equivalent to or higher than those made by methotrexate-resistant gC- L cells infected with wild-type (gC+) virus. The gC gene resident in the L3153(28) cells was regulated as a beta gene inasmuch as the amounts of gC made in infected L3153(28) cells exposed to concentrations of phosphonoacetate that inhibited viral DNA synthesis were higher than those made in the absence of the drug, gC was induced at both permissive and nonpermissive temperatures by the DNA- mutant tsHA1 carrying a lesion in the gene specifying the major DNA-binding protein and which does not express gamma 2 genes at the nonpermissive temperature, and gC was induced only at the permissive temperature in cells infected with ts502 containing a mutation in the alpha 4 gene. The gC induced in L3153(28) cells was made earlier and processed faster to the mature form than that induced in a gC- clone of methotrexate-resistant cells infected with wild-type virus. Unlike virus stocks made in gC- cells, HSV-1(MP) made in L3153(28) cells was susceptible to neutralization by anti-gC monoclonal antibody.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman P. W., Dowbenko D., Lasky L. A., Simonsen C. C. Detection of antibodies to herpes simplex virus with a continuous cell line expressing cloned glycoprotein D. Science. 1983 Nov 4;222(4623):524–527. doi: 10.1126/science.6312563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campadelli-Fiume G., Poletti L., Dall'Olio F., Serafini-Cessi F. Infectivity and glycoprotein processing of herpes simplex virus type 1 grown in a ricin-resistant cell line deficient in N-acetylglucosaminyl transferase I. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1061–1071. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1061-1071.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley A. J., Knipe D. M., Jones P. C., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VII. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant produced by in vitro mutagenesis and defective in DNA synthesis and accumulation of gamma polypeptides. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):191–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.191-206.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo F., Campadelli-Fiume G., Foa-Tomasi L., Cassai E. Evidence that herpes simplex virus DNA is transcribed by cellular RNA polymerase B. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):996–1001. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.996-1001.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Schaffer P. A. Fine-structure mapping and functional analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early protein VP175. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):189–203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.189-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Eisenberg R., Cohen G., Wagner E. K. Detailed analysis of the portion of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome encoding glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):634–647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.634-647.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOGGAN M. D., ROIZMAN B. The isolation and properties of a variant of Herpes simplex producing multinucleated giant cells in monolayer cultures in the presence of antibody. Am J Hyg. 1959 Sep;70:208–219. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. IX. Contiguity of host and viral proteins in the plasma membrane of infected cells. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):810–813. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.810-813.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland L. E., Anderson K. P., Shipman C., Jr, Wagner E. K. Viral DNA synthesis is required for the efficient expression of specific herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA species. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):10–24. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90479-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland T. C., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Holland L. E., Marlin S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Physical mapping of the mutation in an antigenic variant of herpes simplex virus type 1 by use of an immunoreactive plaque assay. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):649–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.649-652.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Smiley J. R. Intracellular transport of herpes simplex virus gD occurs more rapidly in uninfected cells than in infected cells. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):682–689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.682-689.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. VIII. The transcription program consists of three phases during which both extent of transcription and accumulation of RNA in the cytoplasm are regulated. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):299–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.299-314.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R., PIEKARSKI L. J., HSU T. C. DELETION OF THYMIDINE KINASE ACTIVITY FROM L CELLS RESISTANT TO BROMODEOXYURIDINE. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Aug;31:297–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. 3. Viruses differing in their effects on the social behavior of infected cells specify different membrane glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):865–871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Ruyechan W. T., Roizman B., Halliburton I. W. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus: demonstration of regions of obligatory and nonobligatory identity within diploid regions of the genome by sequence replacement and insertion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3896–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kousoulas K. G., Pellett P. E., Pereira L., Roizman B. Mutations affecting conformation or sequence of neutralizing epitopes identified by reactivity of viable plaques segregate from syn and ts domains of HSV-1(F) gB gene. Virology. 1984 Jun;135(2):379–394. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiden J. M., Buttyan R., Spear P. G. Herpes simplex virus gene expression in transformed cells. I. Regulation of the viral thymidine kinase gene in transformed L cells by products of superinfecting virus. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):413–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.413-424.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Differentiation between alpha promoter and regulator regions of herpes simplex virus 1: the functional domains and sequence of a movable alpha regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Pereira L., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA. X. Mapping of viral genes by analysis of polypeptides and functions specified by HSV-1 X HSV-2 recombinants. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):389–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.389-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Klassen T., Baringer J. R. Type-common and type-specific monoclonal antibody to herpes simplex virus type 1. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):724–732. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.724-732.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson R. H., Bacchetti S., Smiley J. R. Cells that constitutively express the herpes simplex virus immediate-early protein ICP4 allow efficient activation of viral delayed-early genes in trans. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):414–421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.414-421.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Conley A. J., Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Cloning of reiterated and nonreiterated herpes simplex virus 1 sequences as BamHI fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4201–4205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Norrild B., Simpson T., Roizman B. Chicken ovalbumin gene fused to a herpes simplex virus alpha promoter and linked to a thymidine kinase gene is regulated like a viral gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;2(3):233–240. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.3.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruyechan W. T., Morse L. S., Knipe D. M., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. II. Mapping of the major viral glycoproteins and of the genetic loci specifying the social behavior of infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):677–697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.677-697.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Cessi F., Dall'Olio F., Pereira L., Campadelli-Fiume G. Processing of N-linked oligosaccharides from precursor- to mature-form herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein gC. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):838–844. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.838-844.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Cessi F., Dall'Olio F., Scannavini M., Campadelli-Fiume G. Processing of herpes simplex virus-1 glycans in cells defective in glycosyl transferases of the Golgi system: relationship to cell fusion and virion egress. Virology. 1983 Nov;131(1):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90533-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Cessi F., Dall'Olio F., Scannavini M., Costanzo F., Campadelli-Fiume G. N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activity involved in O-glycosylation of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):325–329. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.325-329.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Roizman B. gamma 2-Thymidine kinase chimeras are identically transcribed but regulated a gamma 2 genes in herpes simplex virus genomes and as beta genes in cell genomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):518–528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Isolation and expression of an altered mouse dihydrofolate reductase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2495–2499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. I. Identification of four glycoprotein precursors and their products in type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):991–1008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.991-1008.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. V. Purification and structural proteins of the herpesvirion. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):143–159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.143-159.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Silverstein S., Lee L. S., Pellicer A., Cheng Y. c., Axel R. Transfer of purified herpes virus thymidine kinase gene to cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]