Abstract
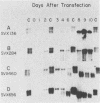
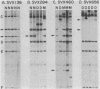
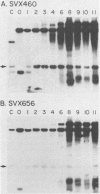
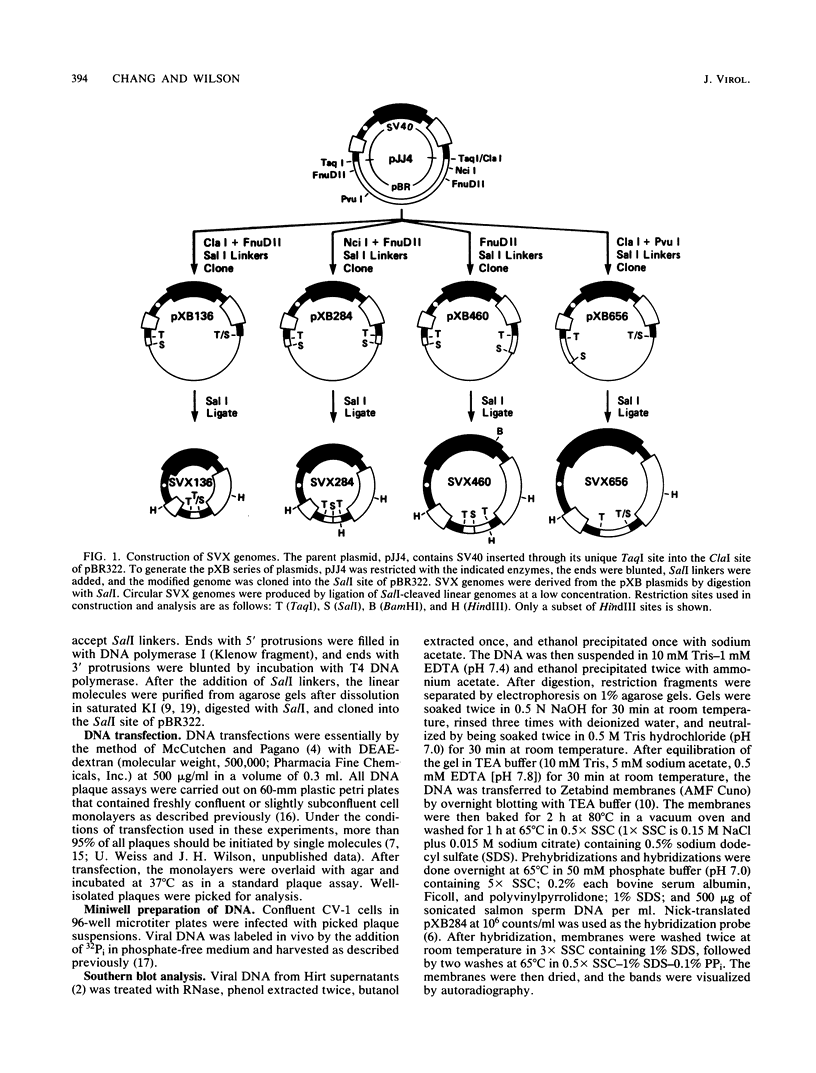
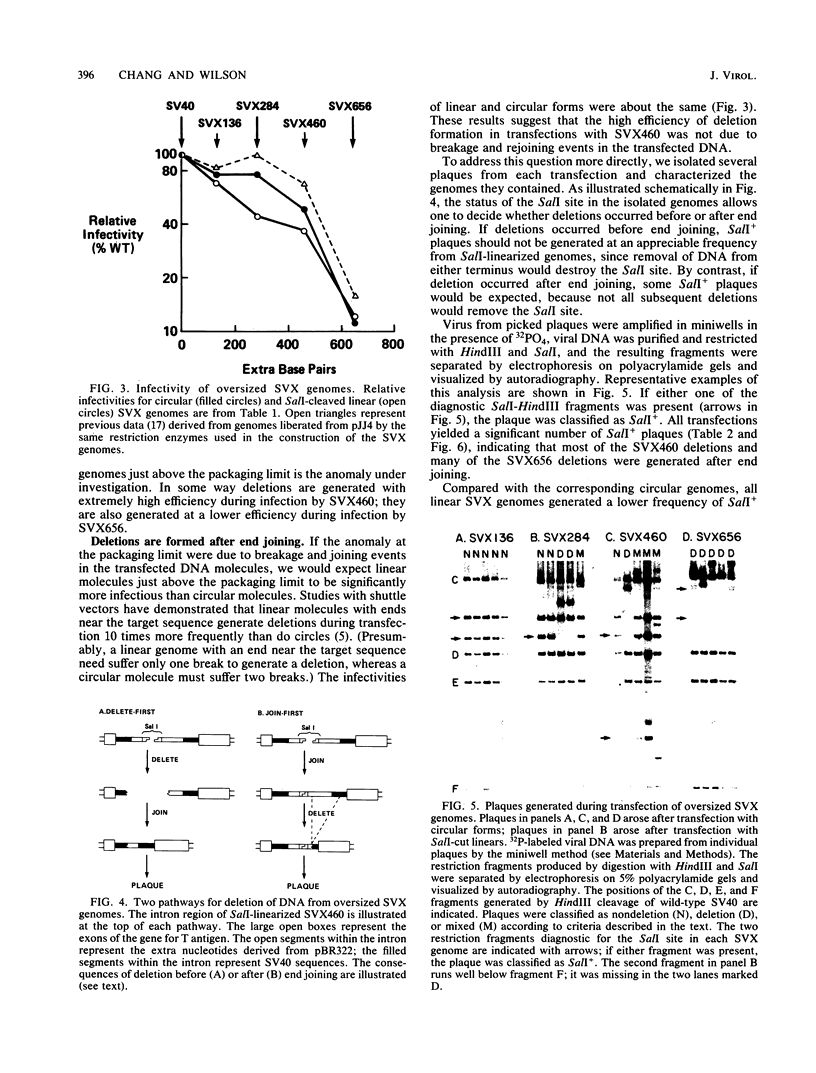
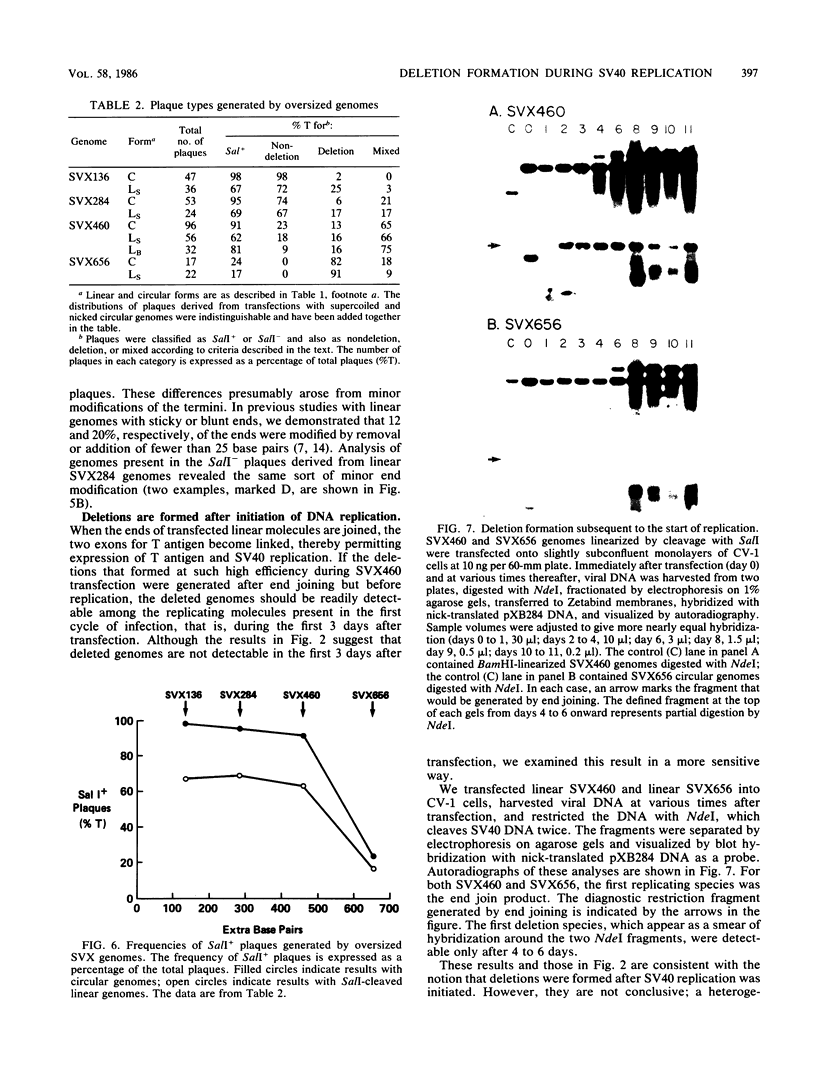
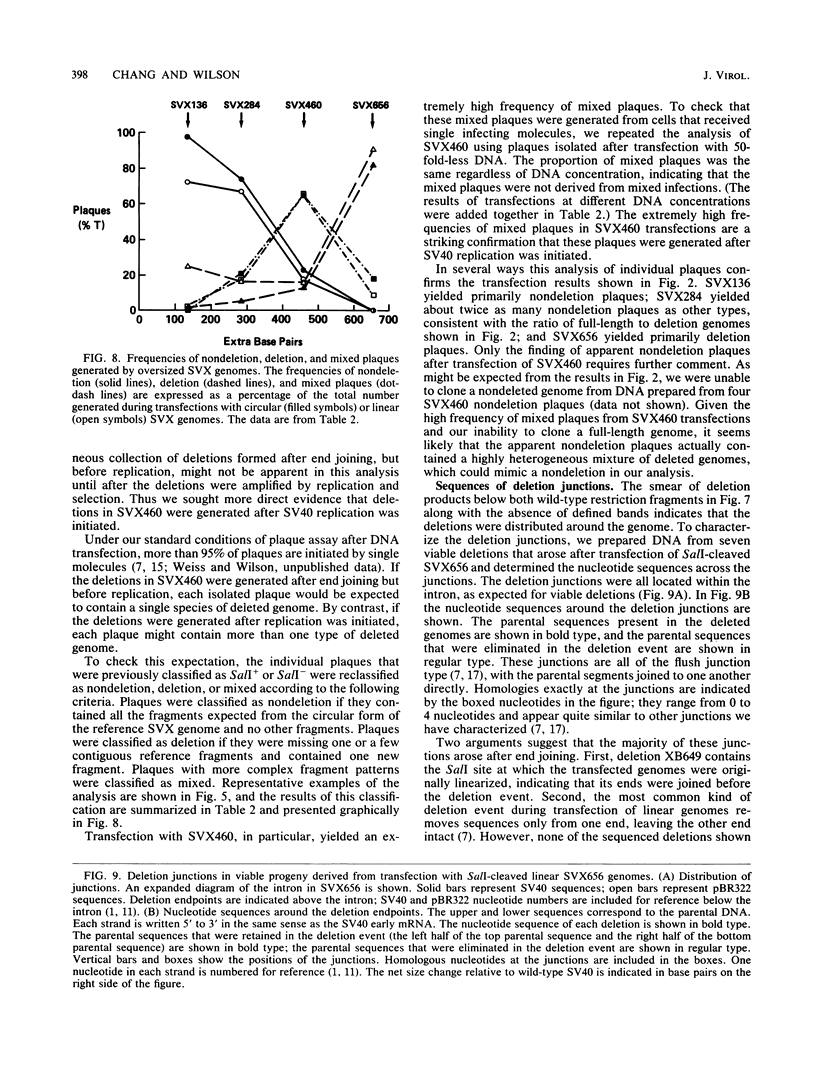
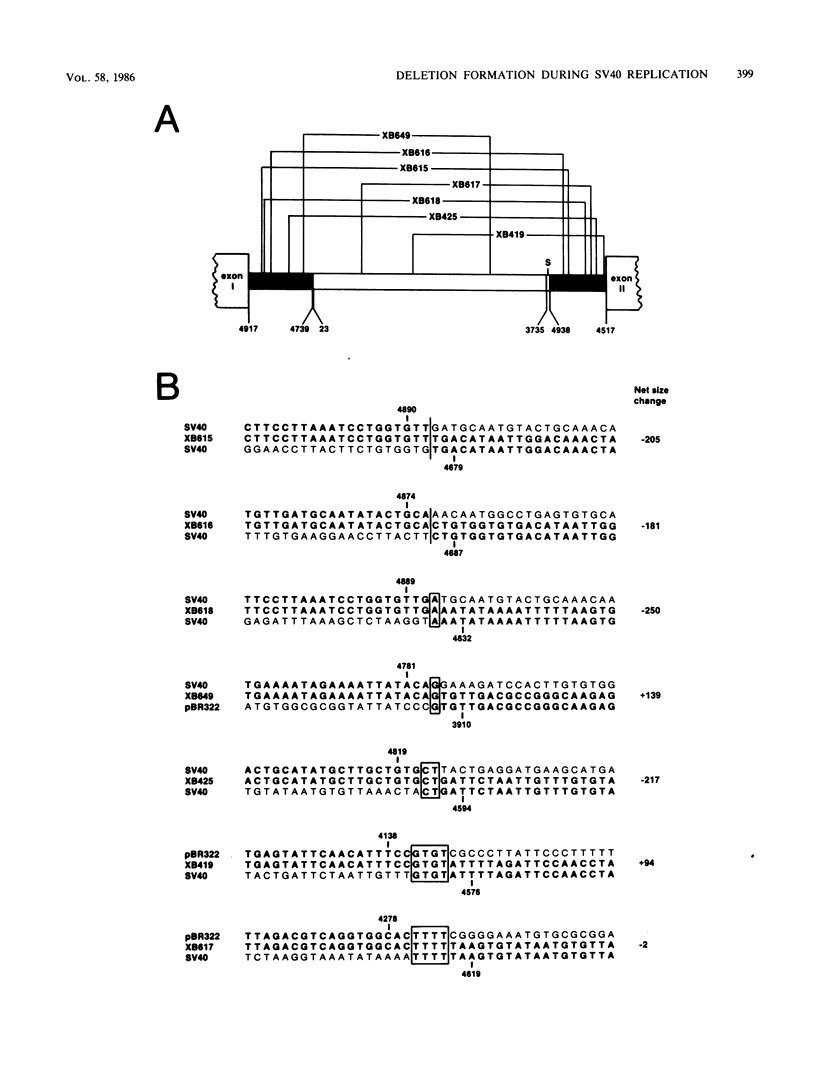
Transfected DNA is frequently broken and rejoined in mammalian cells by recombination processes that depend on minimal nucleotide sequence homology. Although measurements of breakage and joining account reasonably well for the frequent formation of deletions during transfection, they are inadequate to explain the high frequency of deletion formation by simian virus 40 (SV40) genomes that are slightly larger than the packaging limit of the capsid. To investigate this anomaly, we constructed and transfected into CV-1 cells a series of modified SV40 genomes containing 136, 284, 460, and 656 extra base pairs in the intron of the gene encoding T antigen. These experiments indicate that the effective packaging limit of an SV40 capsid lies between 284 and 460 extra base pairs. Further analysis of these transfections suggests that molecules just above the effective packaging limit may be encapsidated and transmitted between cells at low efficiency, thereby allowing multiple rounds of replication and multiple opportunities to generate and package genomes that contain deletions. The junctional sequences in several such deletions were determined; they were similar to the junctions in deletions that were formed before replication began, suggesting that the enzymatic machinery responsible for both types of deletion may be similar.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebkowski J. S., DuBridge R. B., Antell E. A., Greisen K. S., Calos M. P. Transfected DNA is mutated in monkey, mouse, and human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1951–1960. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razzaque A., Mizusawa H., Seidman M. M. Rearrangement and mutagenesis of a shuttle vector plasmid after passage in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3010–3014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Porter T. N., Wilson J. H. Mechanisms of nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2599–2607. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Sugden B., Sambrook J. Detection of two restriction endonuclease activities in Haemophilus parainfluenzae using analytical agarose--ethidium bromide electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3055–3063. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai H. T., Smith C. A., Sharp P. A., Vinograd J. Sequence heterogeneity in closed simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):317–325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.317-325.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Gudewicz T., Porter T., White A., Wilson J. H. How damaged is the biologically active subpopulation of transfected DNA? Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):387–398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Vernaleone F., Wilson J. H. Topological requirements for homologous recombination among DNA molecules transfected into mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2080–2089. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H., Berget P. B., Pipas J. M. Somatic cells efficiently join unrelated DNA segments end-to-end. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1258–1269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H., DePamphilis M., Berg P. Simian virus 40-permissive cell interactions: selection and characterization of spontaneously arising monkey cells that are resistant to simian virus 40 infection. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):391–399. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.391-399.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H. Interference in SV40 DNA infections: a possible basis for cellular competence. Virology. 1978 Dec;91(2):380–388. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]