Abstract
The nucleotide sequences encoding the matrix (M) proteins of measles virus (MV) and canine distemper virus (CDV) were determined from cDNA clones containing these genes in their entirety. In both cases, single open reading frames specifying basic proteins of 335 amino acid residues were predicted from the nucleotide sequences. Both viral messages were composed of approximately 1,450 nucleotides and contained 400 nucleotides of presumptive noncoding sequences at their respective 3' ends. MV and CDV M-protein-coding regions were 67% homologous at the nucleotide level and 76% homologous at the amino acid level. Only chance homology was observed in the 400-nucleotide trailer sequences. Comparisons of the M protein sequences of MV and CDV with the sequence reported for Sendai virus (B. M. Blumberg, K. Rose, M. G. Simona, L. Roux, C. Giorgi, and D. Kolakofsky, J. Virol. 52:656-663; Y. Hidaka, T. Kanda, K. Iwasaki, A. Nomoto, T. Shioda, and H. Shibuta, Nucleic Acids Res. 12:7965-7973) indicated the greatest homology among these M proteins in the carboxyterminal third of the molecule. Secondary-structure analyses of this shared region indicated a structurally conserved, hydrophobic sequence which possibly interacted with the lipid bilayer.
Full text
PDF







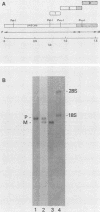
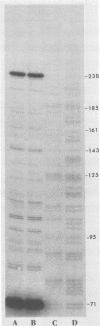
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellini W. J., Englund G., Richardson C. D., Rozenblatt S. Positive identification of a measles virus cDNA clone encoding a region of the phosphoprotein. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):939–942. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.939-942.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellini W. J., Englund G., Rozenblatt S., Arnheiter H., Richardson C. D. Measles virus P gene codes for two proteins. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):908–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.908-919.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B. M., Rose K., Simona M. G., Roux L., Giorgi C., Kolakofsky D. Analysis of the Sendai virus M gene and protein. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):656–663. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.656-663.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bächi T. Intramembrane structural differentiation in Sendai virus maturation. Virology. 1980 Oct 15;106(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büechi M., Bächi T. Microscopy of internal structures of Sendai virus associated with the cytoplasmic surface of host membranes. Virology. 1982 Jul 30;120(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Conformational parameters for amino acids in helical, beta-sheet, and random coil regions calculated from proteins. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):211–222. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Krauter K., Walling L., Weinberger C., Ray M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in the production of liver-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuffre R. M., Tovell D. R., Kay C. M., Tyrrell D. L. Evidence for an interaction between the membrane protein of a paramyxovirus and actin. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):963–968. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.963-968.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriades A. The membrane protein of influenza virus: extraction from virus and infected cell with acidic chloroform-methanol. Virology. 1973 Aug;54(2):369–383. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90150-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. W., Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. The polypeptides of canine distemper virus: synthesis in infected cells and relatedness to the polypeptides of other morbilliviruses. Virology. 1980 Jan 30;100(2):433–449. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90534-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heggeness M. H., Smith P. R., Choppin P. W. In vitro assembly of the nonglycosylated membrane protein (M) of Sendai virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6232–6236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka Y., Kanda T., Iwasaki K., Nomoto A., Shioda T., Shibuta H. Nucleotide sequence of a Sendai virus genome region covering the entire M gene and the 3' proximal 1013 nucleotides of the F gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):7965–7973. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.7965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Protein-protein interactions within paramyxoviruses identified by native disulfide bonding or reversible chemical cross-linking. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):152–166. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.152-166.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto T. Assembly of paramyxoviruses. Microbiol Immunol. 1982;26(4):285–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1982.tb00180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J. J., Compans R. W., Lackland H., Choppin P. W. Isolation and characterization of the nonglycosylated membrane protein and a nucleocapsid complex from the paramyxovirus SV5. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):365–374. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90438-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orvell C., Norrby E. Immunological relationships between homologous structural polypeptides of measles and canine distemper virus. J Gen Virol. 1980 Oct;50(2):231–245. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-2-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeples M. E., Bratt M. A. Mutation in the matrix protein of Newcastle disease virus can result in decreased fusion glycoprotein incorporation into particles and decreased infectivity. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):81–90. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.81-90.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. D., Berkovich A., Rozenblatt S., Bellini W. J. Use of antibodies directed against synthetic peptides for identifying cDNA clones, establishing reading frames, and deducing the gene order of measles virus. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):186–193. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.186-193.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux L., Beffy P., Portner A. Restriction of cell surface expression of Sendai virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein correlates with its higher instability in persistently and standard plus defective interfering virus infected BHK-21 cells. Virology. 1984 Oct 15;138(1):118–128. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenblatt S., Eizenberg O., Ben-Levy R., Lavie V., Bellini W. J. Sequence homology within the morbilliviruses. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):684–690. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.684-690.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenblatt S., Eizenberg O., Englund G., Bellini W. J. Cloning and characterization of DNA complementary to the canine distemper virus mRNA encoding matrix, phosphoprotein, and nucleocapsid protein. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):691–694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.691-694.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenblatt S., Gesang C., Lavie V., Neumann F. S. Cloning and characterization of DNA complementary to the measles virus mRNA encoding hemagglutinin and matrix protein. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):790–797. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.790-797.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satake M., Venkatesan S. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding respiratory syncytial virus matrix protein. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):92–99. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.92-99.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K., Isida N. The smallest protein of Sendi virus: its candidate function of binding nucleocaspsid to envelope. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):427–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell D. L., Ehrnst A. Transmembrane communication in cells chronically infected with measles virus. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):396–402. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Nagai Y'Yoshii S., Maeno K., Matsumoto T. Membrane (M) protein of HVJ (Sendai virus): its role in virus assembly. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):143–161. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]