Figure 1.
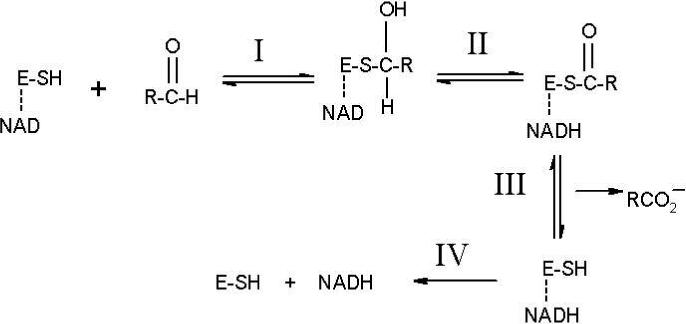
Traditional scheme for the catalytic cycle of ALDH. E-SH denotes the enzyme with Cys302 as the nucleophile and the line to NAD indicates that it is non-covalently bound prior to reacting the substrate. Reaction I: Nucleophilic activation and attack on the substrate by Cys302 to give a thiohemiacetal intermediate. Reaction II: Hydride transfer from the intermediate to NAD to form NADH and a thioester. Reaction III: Hydrolysis of the thioester with release of the carboxylic acid. Reaction IV: Release of NADH.
