Abstract
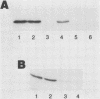
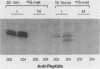
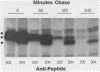
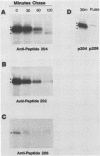
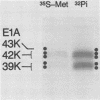
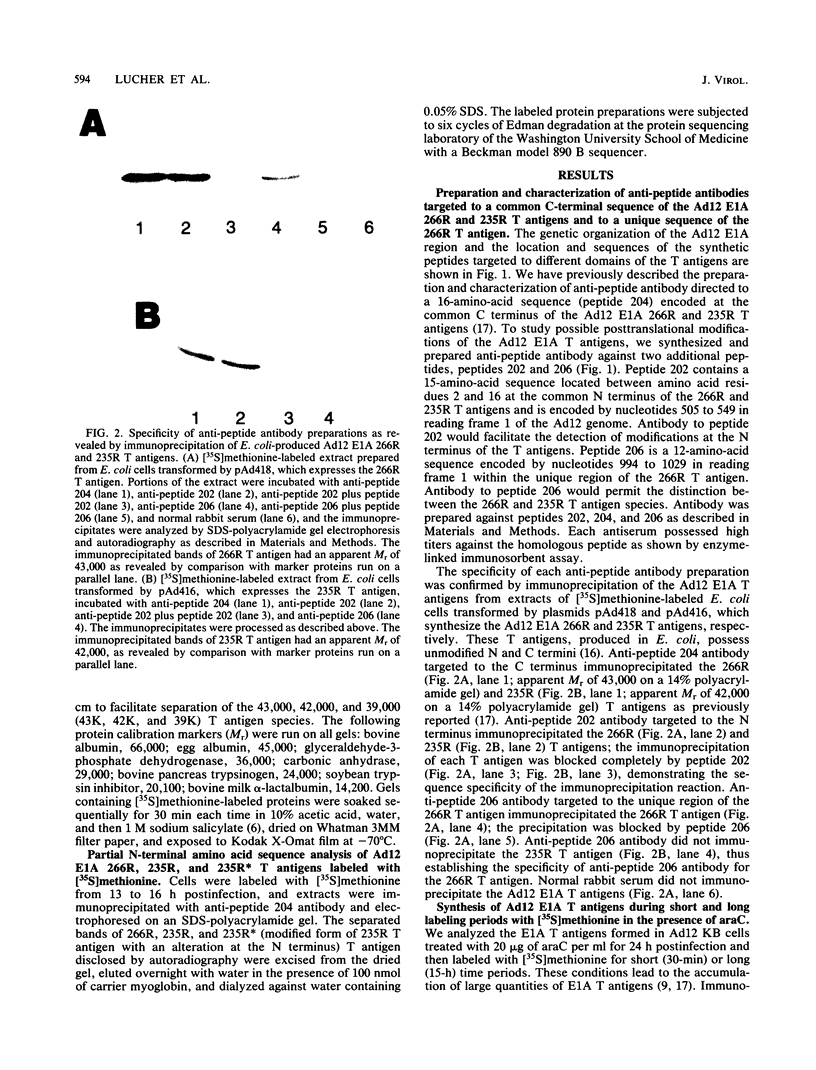
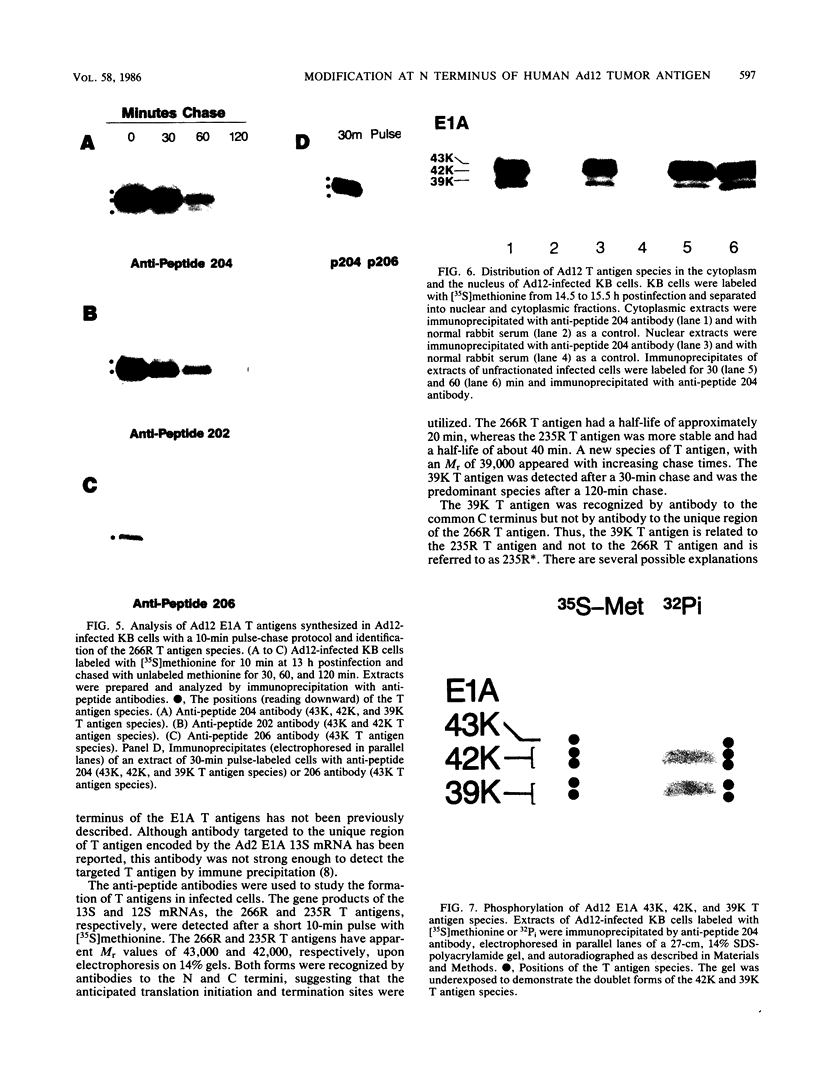
The adenovirus E1A transforming region, which encodes immortalization, partial cell transformation, and gene activation functions, expresses two early mRNAs, 13S and 12S. Multiple-T antigen species with different electrophoretic mobilities are formed from each mRNA, presumably by unknown posttranslational modifications. The adenovirus type 12 (Ad12) 13S and 12S mRNAs encode E1A T antigens of 266 and 235 amino acid residues (266R and 235R), respectively. To study possible posttranslational processing at the N and C termini and to distinguish between the Ad12 266R and 235R T antigens, we prepared antibodies targeted to synthetic peptides encoded at the common C (peptide 204) and N (peptide 202) termini of the 266R and 235R T antigens and at the unique internal domain of the 266R T antigen (peptide 206). The specificity of each anti-peptide antibody was confirmed by immunoprecipitation of the 266R and 235R T antigens produced in Escherichia coli. Immunoprecipitation analysis of the E1A T antigens synthesized in Ad12-infected KB cells revealed the following. Antibody to the common C terminus recognized three T antigens with apparent Mrs of 43,000, 42,000, and 39,000 (43K, 42K, and 39K). All three forms were phosphorylated and were present in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The 43K and 42K T antigens were rapidly synthesized during a 10-min pulse with [35S]methionine in Ad12-infected cells. The 43K T antigen had a half-life of 20 min, the 42K T antigen had a longer half-life of about 40 min, and the 39K T antigen became the predominant E1A T antigen. Antibodies to the unique region immunoprecipitated the 43K T antigen but not the 42K and 39K T antigens. Antibody to the N terminus immunoprecipitated the 43K and 42K T antigens but not the 39K T antigen, suggesting that the 39K T antigen possessed a modified N terminus. Partial N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis showed that the 43K and 42K T antigens contain methionine at residues 1 and 5, as predicted from the DNA sequence, whereas no methionine was released from the 39K T antigen during the first six cycles of Edman degradation. We propose that the short-lived 43K T antigen is the primary product of the 13S mRNA, the 266R T antigen; the somewhat more stable 42K T antigen is the primary product of the 12S mRNA, the 235R T antigen.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernards R., Schrier P. I., Houweling A., Bos J. L., van der Eb A. J., Zijlstra M., Melief C. J. Tumorigenicity of cells transformed by adenovirus type 12 by evasion of T-cell immunity. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):776–779. doi: 10.1038/305776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L., Jochemsen A. G., Bernards R., Schrier P. I., van Ormondt H., van der Eb A. J. Deletion mutants of region E1a of AD12 E1 plasmids: effect on oncogenic transformation. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackmann K. H., Green M., Wold W. S., Cartas M., Matsuo T., Hashimoto S. Identification and peptide mapping of human adenovirus type 2-induced early polypeptides isolated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and immunoprecipitation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6772–6779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlock L. R., Jones N. C. Transformation-defective mutant of adenovirus type 5 containing a single altered E1a mRNA species. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):657–664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.657-664.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downey J. F., Evelegh C. M., Branton P. E., Bayley S. T. Peptide maps and N-terminal sequences of polypeptides from early region 1A of human adenovirus 5. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):30–37. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.30-37.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R. Localization of the adenovirus E1Aa protein, a positive-acting transcriptional factor, in infected cells infected cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):829–838. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. B., Tsukamoto A., Montell C., Berk A. J. Enhanced expression of adenovirus transforming proteins. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):276–285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.276-285.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Harrison T., Williams J. Defective transforming capacity of adenovirus type 5 host-range mutants. Virology. 1978 May 1;86(1):10–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Brackmann K. H., Lucher L. A., Symington J. S., Kramer T. A. Human adenovirus 2 E1B-19K and E1B-53K tumor antigens: antipeptide antibodies targeted to the NH2 and COOH termini. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):604–615. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.604-615.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Wold W. S., Brackmann K. H., Cartas M. A. Identification of families of overlapping polypeptides coded by early "transforming" gene region 1 of human adenovirus type 2. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):275–286. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90339-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert D. N., Spector D. J., Raskas H. J. In vitro translation products specified by the transforming region of adenovirus type 2. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):621–629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.621-629.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz D. R., Chinnadurai G. Evidence that a second tumor antigen coded by adenovirus early gene region E1a is required for efficient cell transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):163–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelman D., Lucher L. A., Brackmann K. H., Symington J. S., Ptashne M., Green M. Synthesis in Escherichia coli of human adenovirus type 12 transforming proteins encoded by early region 1A 13S mRNA and 12S mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6300–6304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucher L. A., Kimelman D., Symington J. S., Brackmann K. H., Cartas M. A., Thornton H., Green M. Identification of adenovirus 12-encoded E1A tumor antigens synthesized in infected and transformed mammalian cells and in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):136–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.136-144.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucher L. A., Loewenstein P. M., Green M. Phosphorylation in vitro of Escherichia coli-produced 235R and 266R tumor antigens encoded by human adenovirus type 12 early transformation region 1A. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):183–193. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.183-193.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Courtois G., Eng C., Berk A. Complete transformation by adenovirus 2 requires both E1A proteins. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):951–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perricaudet M., le Moullec J. M., Tiollais P., Pettersson U. Structure of two adenovirus type 12 transforming polypeptides and their evolutionary implications. Nature. 1980 Nov 13;288(5787):174–176. doi: 10.1038/288174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Jones R. L., Cepko C. L., Sharp P. A., Roberts B. E. Expression of early adenovirus genes requires a viral encoded acidic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6121–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier P. I., Bernards R., Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Expression of class I major histocompatibility antigens switched off by highly oncogenic adenovirus 12 in transformed rat cells. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):771–775. doi: 10.1038/305771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugisaki H., Sugimoto K., Takanami M., Shiroki K., Saito I., Shimojo H., Sawada Y., Uemizu Y., Uesugi S., Fujinaga K. Structure and gene organization in the transformed Hind III-G fragment of Ad12. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):777–786. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90324-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee S. P., Rowe D. T., Tremblay M. L., McDermott M., Branton P. E. Identification of human adenovirus early region 1 products by using antisera against synthetic peptides corresponding to the predicted carboxy termini. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):1003–1013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.1003-1013.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]