Abstract
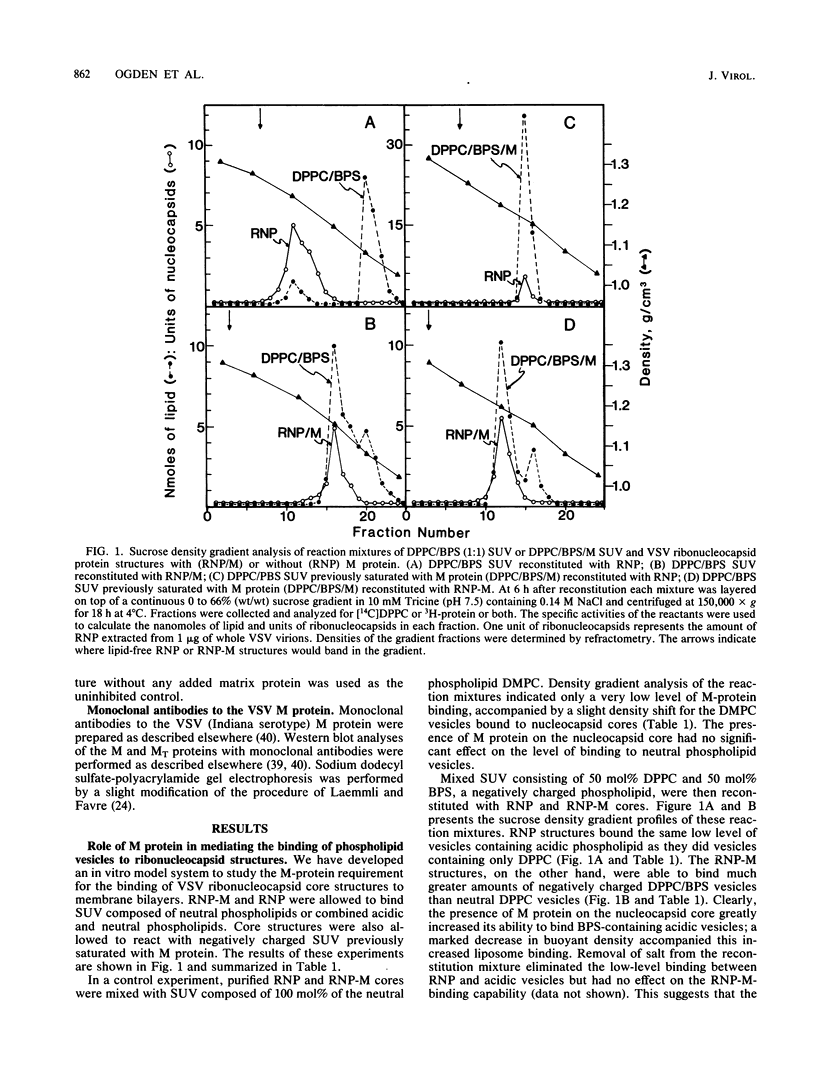
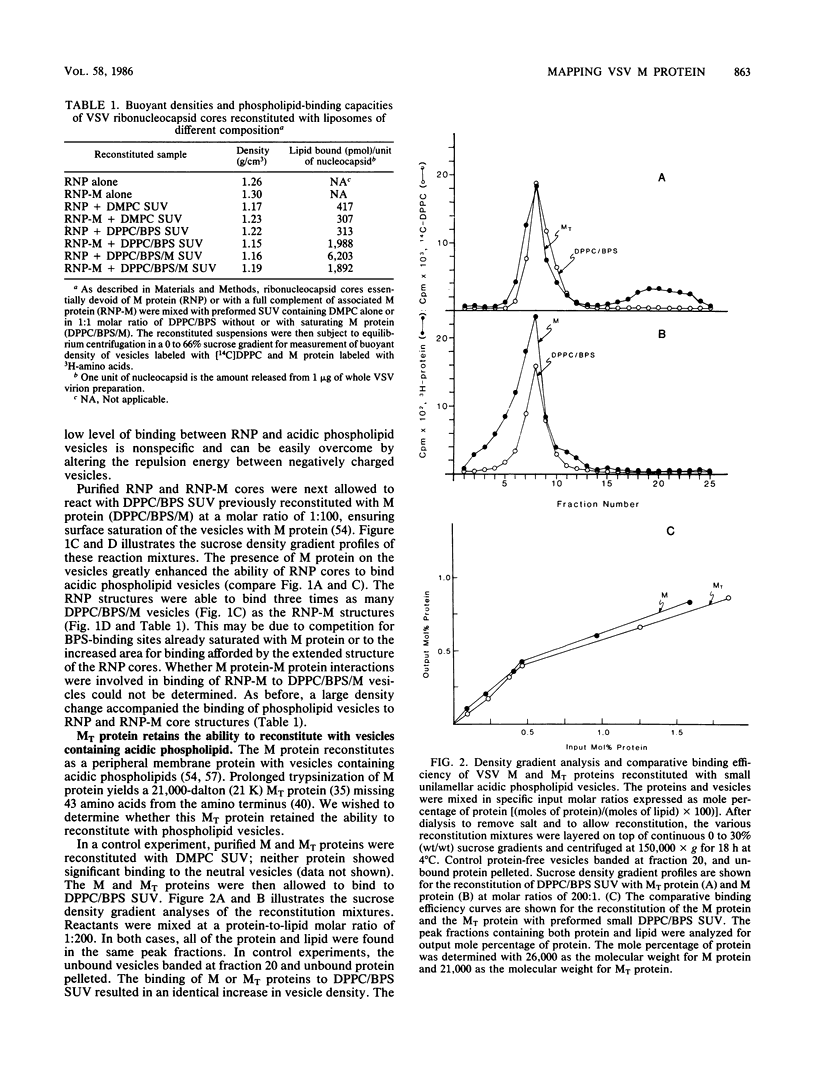
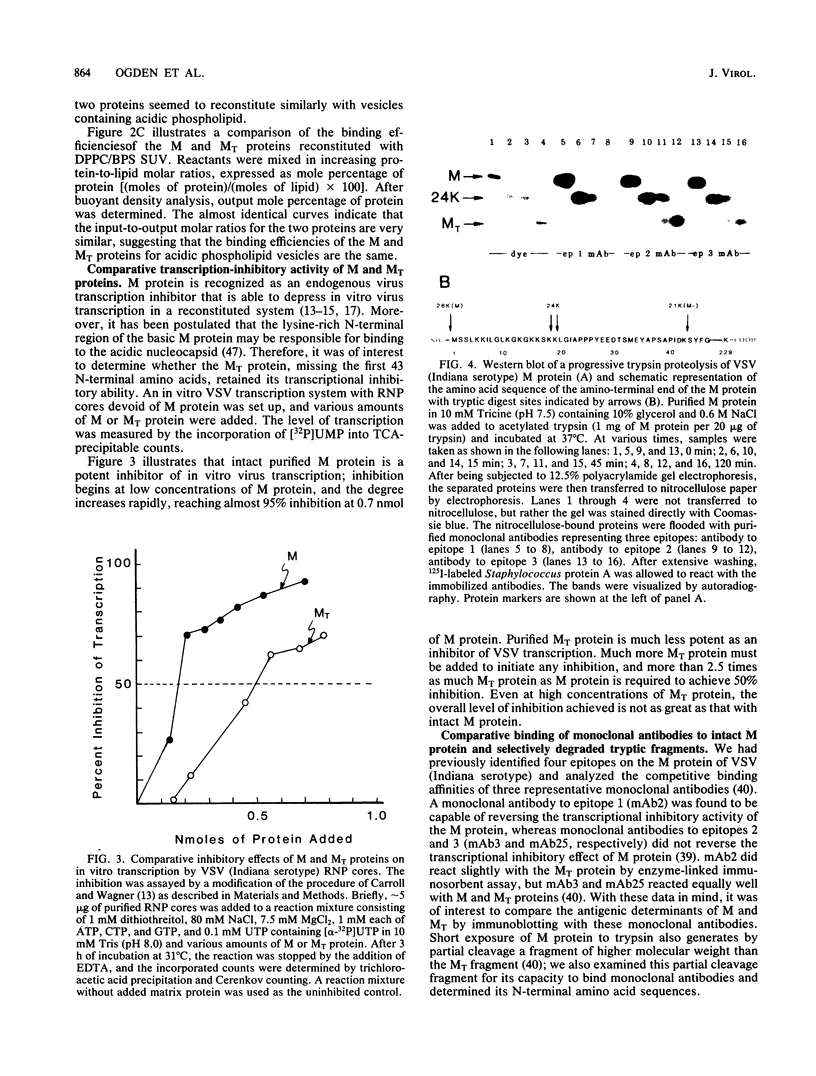
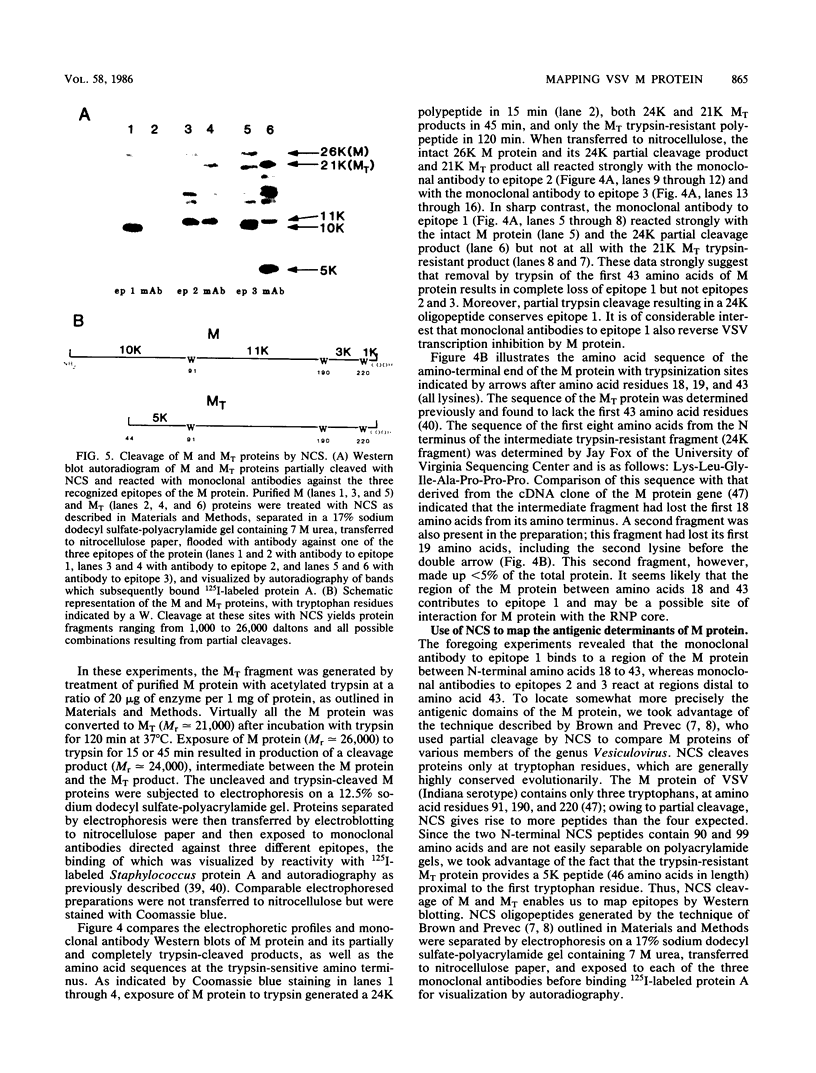
The matrix (M) protein of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) appears to function as a bridge between the ribonucleocapsid (RNP) core and the envelope in assembly of the virion. Two such properties would necessitate at least one site for interaction with the nucleocapsid and one with the envelope. In this study M protein was found to mediate the in vitro binding to RNP cores of phospholipid vesicles, representing membrane structures. The M protein could bind initially to either the vesicles or the RNP cores to promote RNP-vesicle association. A trypsin-resistant fragment (MT) of M protein, missing the initial 43 amino acids from its amino terminus, reconstituted with acidic phospholipid vesicles with the same binding efficiency as did whole M protein, suggesting that the carboxy-terminal 81% retained those regions of the M protein which interact with a lipid bilayer. The MT protein, however, was considerably less efficient than intact M protein as an inhibitor of in vitro virus transcription; almost 2.5-fold more MT protein than intact M protein was required for 50% inhibition of VSV transcription, indicating that a site for interaction with the RNP core may have been lost. A monoclonal antibody which is able to reverse the in vitro inhibition of transcription by M protein did not react by immunoblotting with MT protein. Partial tryptic digests of the M protein probed with this monoclonal antibody indicated that epitope 1 lies between amino acid residues 18 and 43. This region appears to be a site that promotes interaction of the M protein with the RNP core of VSV. Monoclonal antibodies to epitopes 2 and 3, which exhibit some overlap in binding to M protein but do not reverse transcription inhibition, were mapped by cleavage with N-chlorosuccinimide at regions in a carboxy direction from epitope 1.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson P. H. Gycoprotein and protein precursors to plasma membranes in vesicular stomatitis virus infected HeLa cells. J Supramol Struct. 1978;8(1):89–109. doi: 10.1002/jss.400080108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson P. H., Moyer S. A., Summers D. F. Assembly of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein and matrix protein into HeLa cell plasma membranes. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 15;102(3):613–631. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90338-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenholz Y., Gibbes D., Litman B. J., Goll J., Thompson T. E., Carlson R. D. A simple method for the preparation of homogeneous phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 14;16(12):2806–2810. doi: 10.1021/bi00631a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Repik P., Obijeski J. F., Moore N. F., Wagner R. R. Restitution of infectivity to spikeless vesicular stomatitis virus by solubilized viral components. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):75–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.75-84.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breindl M., Holland J. J. Studies on the in vitro transcription and translation of vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):106–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. T., Riedel B. Morphogenesis of vesicular stomatitis virus: electron microscope observations with freeze-fracture techniques. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):601–609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.601-609.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. G., Prevec L. Comparative analyses of vesiculovirus proteins utilizing partial cleavage fragments at tryptophan residues. Virology. 1979 May;95(1):244–248. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E., Prevec L. Linear mapping of tryptophan residues in Vesiculovirus M and N proteins by partial chemical cleavage. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):311–316. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.311-316.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burge B. W., Huang A. S. Conserved peptides in the proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90499-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capone J., Ghosh H. P. Association of the nucleocapsid protein N of vesicular stomatitis virus with phospholipid vesicles containing the matrix protein M. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;62(11):1174–1180. doi: 10.1139/o84-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capone J., Leblanc P., Gerber G. E., Ghosh H. P. Localization of membrane proteins by the use of a photoreactive fatty acid incorporated in vivo into vesicular stomatitis virus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1395–1398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll A. R., Wagner R. R. Reversal by certain polyanions of an endogenous inhibitor of the vesicular stomatitis virus-associated transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3361–3363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll A. R., Wagner R. R. Role of the membrane (M) protein in endogenous inhibition of in vitro transcription by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):134–142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.134-142.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton G. M., Little S. P., Hagen F. S., Huang A. S. The matrix (M) protein of vesicular stomatitis virus regulates transcription. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1455–1462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combard A., Printz Ane C. Inhibition of vesicular stomatitis virus transcriptase complex by the virion envelope M protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 14;88(1):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91704-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David A. E. Assembly of the vesicular stomatitis virus envelope: transfer of viral polypeptides from polysomes to cellular membranes. Virology. 1977 Jan;76(1):98–108. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90286-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De B. P., Thornton G. B., Luk D., Banerjee A. K. Purified matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus blocks viral transcription in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7137–7141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubovi E. J., Wagner R. R. Spatial relationships of the proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus: induction of reversible oligomers by cleavable protein cross-linkers and oxidation. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):500–509. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.500-509.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna Y., Lenard J. Sequence alterations in temperature-sensitive M-protein mutants (complementation group III) of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):655–659. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.655-659.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heggeness M. H., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Conformation of the helical nucleocapsids of paramyxoviruses and vesicular stomatitis virus: reversible coiling and uncoiling induced by changes in salt concentration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2631–2635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiuchi A., Roy P. Comparison of the primary sequence of spring viremia of carp virus M protein with that of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1984 Apr 15;134(1):238–243. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90290-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Baltimore D., Lodish H. F. Maturation of viral proteins in cells infected with temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1149-1158.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Baltimore D., Lodish H. F. Separate pathways of maturation of the major structural proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1128–1139. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1128-1139.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafay F. Envelope proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus: effect of temperature-sensitive mutations in complementation groups III and V. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1220–1228. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1220-1228.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Porter M. Heterogeneity of vesicular stomatitis virus particles: implications for virion assembly. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.52-58.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Weiss R. A. Selective isolation of mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus defective in production of the viral glycoprotein. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):177–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.177-189.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancarella D. A., Lenard J. Interactions of wild-type and mutant M protein of vesicular stomatitis virus with viral nucleocapsid and envelope in intact virions. Evidence from [125I]iodonaphthyl azide labeling and specific cross-linking. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6872–6877. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J. J., Compans R. W., Choppin P. W. Proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus and of phenotypically mixed vesicular stomatitis virus-simian virus 5 virions. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):722–729. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.722-729.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J. J. The effect of chemical and physical treatments on the lactoperoxidase-catalyzed iodination of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1977 Dec;83(2):482–485. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90200-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G., McQuain C. O. Assembly of viral membranes: nature of the association of vesicular stomatitis virus proteins to membranes. J Virol. 1978 Apr;26(1):115–125. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.1.115-125.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G. Site of synthesis of membrane and nonmembrane proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6955–6962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd J. A. Glycoprotein fragment associated with vesicular stomatitis virus after proteolytic digestion. Virology. 1974 Dec;62(2):573–577. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90419-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb W. W., Brown J. C. Role of the vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein in maintaining the viral nucleocapsid in the condensed form found in native virions. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):295–299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.295-299.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb W. W., Tobin G. J., McGowan J. J., Brown J. C. In vitro reassembly of vesicular stomatitis virus skeletons. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):1055–1062. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.1055-1062.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal R., Grinnell B. W., Snyder R. M., Wagner R. R. Regulation of viral transcription by the matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus probed by monoclonal antibodies and temperature-sensitive mutants. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):386–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.386-394.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal R., Grinnell B. W., Snyder R. M., Wiener J. R., Volk W. A., Wagner R. R. Monoclonal antibodies to the M protein of vesicular stomatitis virus (Indiana serotype) and to a cDNA M gene expression product. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):298–306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.298-306.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzer E. J., Moore N. F., Barenholz Y., Shaw J. M., Wagner R. R. Lipid organization of the membrane of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4544–4550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Vogt V. M. Identification of retrovirus matrix proteins by lipid-protein cross-linking. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 15;131(4):819–837. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrault J., Kingsbury D. T. Inhibitor of vesicular stomatitis virus transcriptase in purified virions. Nature. 1974 Mar 1;248(5443):45–47. doi: 10.1038/248045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Wagner R. R. Glycoprotein micelles isolated from vesicular stomatitis virus spontaneously partition into sonicated phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):543–547. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinney D. F., Emerson S. U. In vitro synthesis of triphosphate-initiated N-gene mRNA oligonucleotides is regulated by the matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):897–904. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.897-904.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidler J. A., Keller P. M., Elson E. L., Lenard J. A fluorescence photobleaching study of vesicular stomatitis virus infected BHK cells. Modulation of G protein mobility by M protein. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1345–1349. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Gallione C. J. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus G and M proteins determined from cDNA clones containing the complete coding regions. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.519-528.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloemer R. H., Wagner R. R. Association of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein with virion membrane: characterization of the lipophilic tail fragment. J Virol. 1975 Aug;16(2):237–240. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.2.237-240.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer T. J., Lodish H. F. Noninfectious vesicular stomatitis virus particles deficient in the viral nucleocapsid. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):443–447. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.443-447.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel W., Schreiber C., Scheefers H. Lipids with photosensitive groups as chemical probes for the structural analysis of biological membranes. On the localization of the G- and M-protein of vesicular stomatitis virus. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Aug;359(8):923–931. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1978.359.2.923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Heine J. W., Goldstein G., Schnaitman C. A. Use of antiviral-antiferritin hybrid antibody for localization of viral antigen in plasma membrane. J Virol. 1971 Feb;7(2):274–277. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.2.274-277.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A., Bennett P. L. Assembly of membrane glycoproteins studied by phenotypic mixing between mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus and retroviruses. Virology. 1980 Jan 30;100(2):252–274. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90518-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener J. R., Pal R., Barenholz Y., Wagner R. R. Effect of the vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein on the lateral organization of lipid bilayers containing phosphatidylglycerol: use of fluorescent phospholipid analogues. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 17;24(26):7651–7658. doi: 10.1021/bi00347a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener J. R., Pal R., Barenholz Y., Wagner R. R. Influence of the peripheral matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus on the membrane dynamics of mixed phospholipid vesicles: fluorescence studies. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2162–2170. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Lenard J. Interaction of wild-type and mutant M protein vesicular stomatitis virus with nucleocapsids in vitro. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1349–1354. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye Z., Pal R., Ogden J. R., Snyder R. M., Wagner R. R. Monoclonal antibodies to the matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus (New Jersey serotype) and their effects on viral transcription. Virology. 1985 Jun;143(2):657–662. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90408-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakowski J. J., Petri W. A., Jr, Wagner R. R. Role of matrix protein in assembling the membrane of vesicular stomatitis virus: reconstitution of matrix protein with negatively charged phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3902–3907. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakowski J. J., Wagner R. R. Localization of membrane-associated proteins in vesicular stomatitis virus by use of hydrophobic membrane probes and cross-linking reagents. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):93–102. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.93-102.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]