Abstract
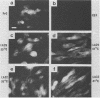
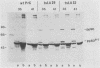
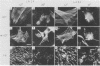
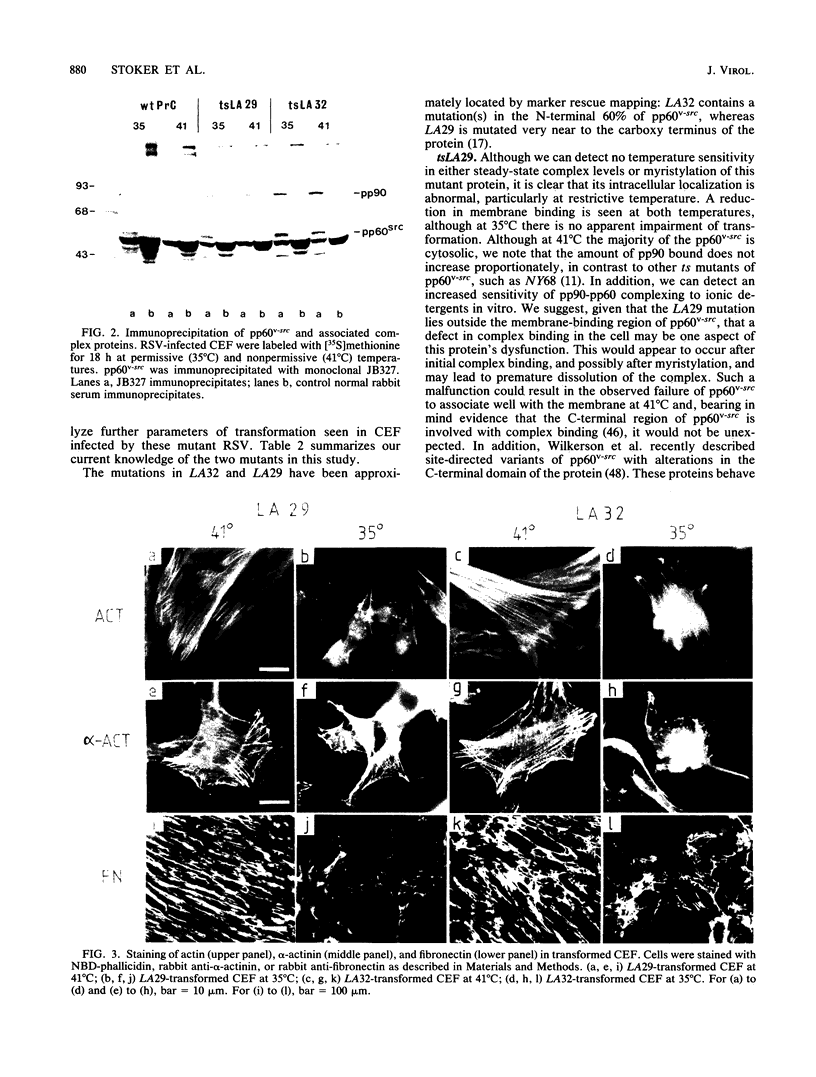
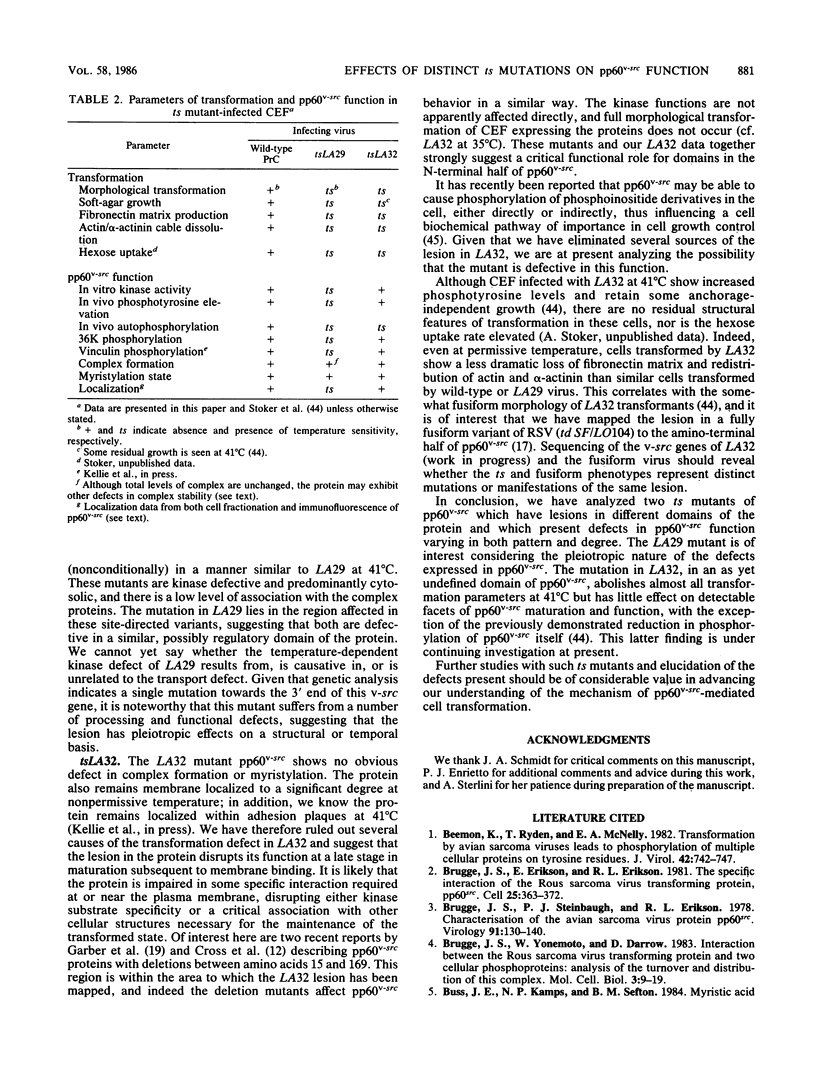
The transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus, pp60v-src, is known to be a tyrosine protein kinase, but the mechanism of cell transformation remains unclear. In further investigating pp60v-src structure and function, we have analyzed two temperature-sensitive (ts) Rous sarcoma virus src gene mutants, tsLA29 and tsLA32. The mutations in tsLA29 and tsLA32 map in the carboxy-terminal region and the amino-terminal half of pp60v-src, respectively, and encode mutant proteins with either temperature-labile (tsLA29) or -stable (tsLA32) kinase activities. Here we examined the intracellular processing and localization of these pp60v-src mutants and extended our characterization of transformation parameters expressed by cells infected by the Rous sarcoma virus variants. No obvious defects in functional integrity of the tsLA32 pp60v-src could yet be demonstrated, whereas the tsLA29 pp60v-src was perturbed not only in kinase activity, but also in aspects of protein processing and localization. Analysis of transformation parameters expressed by infected cells demonstrated the complete temperature lability of both mutants.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beemon K., Ryden T., McNelly E. A. Transformation by avian sarcoma viruses leads to phosphorylation of multiple cellular proteins on tyrosine residues. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):742–747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.742-747.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. The specific interaction of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, pp60src, with two cellular proteins. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):363–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Steinbaugh P. J., Erikson R. L. Characterization of the avian sarcoma virus protein p60src. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):130–140. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90361-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J., Yonemoto W., Darrow D. Interaction between the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein and two cellular phosphoproteins: analysis of the turnover and distribution of this complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;3(1):9–19. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L. Avian sarcoma virus-transforming protein, pp60src shows protein kinase activity specific for tyrosine. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):167–169. doi: 10.1038/285167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Changes in protein phosphorylation in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):165–178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Identification and characterization of cellular targets for tyrosine protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1108–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Reiss N. A., Schwartz R. J., Hunter T. Three glycolytic enzymes are phosphorylated at tyrosine in cells transformed by Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):218–223. doi: 10.1038/302218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Transit of pp60v-src to the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7117–7121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. N-terminal deletions in Rous sarcoma virus p60src: effects on tyrosine kinase and biological activities and on recombination in tissue culture with the cellular src gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2789–2795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David-Pfeuty T., Singer S. J. Altered distributions of the cytoskeletal proteins vinculin and alpha-actinin in cultured fibroblasts transformed by Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6687–6691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Identification of a cellular protein substrate phosphorylated by the avian sarcoma virus-transforming gene product. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. L., Collett M. S., Erikson E., Purchio A. F. Evidence that the avian sarcoma virus transforming gene product is a cyclic AMP-independent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6260–6264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fincham V. J., Chiswell D. J., Wyke J. A. Mapping of nonconditional and conditional mutants in the src gene of Prague strain Rous sarcoma virus. Virology. 1982 Jan 15;116(1):72–83. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90404-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis R. R., Schwarz R. T., Schmidt M. F. Phenotypes of Rous sarcoma virus-transformed fibroblasts: an argument for a multifunctional Src gene product. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1977;164(1-3):155–165. doi: 10.1007/BF02121311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Processing of p60v-src to its myristylated membrane-bound form. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2781–2788. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Krueger J. G., Hanafusa H., Goldberg A. R. Only membrane-associated RSV src proteins have amino-terminally bound lipid. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):161–163. doi: 10.1038/302161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Krueger J. G., Hanafusa H., Goldberg A. R. Temperature-sensitive membrane association of pp60src in tsNY68-infected cells correlates with increased tyrosine phosphorylation of membrane-associated proteins. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):73–86. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmer T. M., Erikson R. L. Development of anti-pp60src serum with antigen produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):462–465. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.462-465.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D., Radke K., Martin G. S. Tyrosine phosphorylation of a 50K cellular polypeptide associated with the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein pp60src. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):199–206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of NH2-terminal glycine of p60src prevents both myristoylation and morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4625–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellie S., Patel B., Pierce E. J., Critchley D. R. Capping of cholera toxin-ganglioside GM1 complexes on mouse lymphocytes is accompanied by co-capping of alpha-actinin. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):447–454. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Garber E. A., Goldberg A. R., Hanafusa H. Changes in amino-terminal sequences of pp60src lead to decreased membrane association and decreased in vivo tumorigenicity. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):889–896. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Garber E. A., Goldberg A. R. Subcellular localization of pp60src in RSV-transformed cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;107:51–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Structural and functional domains of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein (pp60src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Levintow L., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Evidence that the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus encodes a protein kinase associated with a phosphoprotein. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. The purified product of the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11973–11980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Lewis A. J., Brugge J. S. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the transforming proteins of avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.352-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maness P. F., Levy B. T. Highly purified pp60src induces the actin transformation in microinjected cells and phosphorylates selected cytoskeletal proteins in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;3(1):102–112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.1.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R., Nakamura K. D., Weber M. J. Identification of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins in untransformed and Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):653–665. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olden K., Yamada K. M. Mechanism of the decrease in the major cell surface protein of chick embryo fibroblasts after transformation. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):957–969. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann H., Levinson A. D., Levintow L., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Kawai S. Two cellular proteins that immunoprecipitate with the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):736–751. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchio A. F., Erikson E., Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a polypeptide encoded by the avian sarcoma virus src gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1567–1571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Gilmore T., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: a cellular substrate for transformation-specific protein phosphorylation contains phosphotyrosine. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):821–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Smith M. J., Srinivasan A. Nucleotide sequence of Abelson murine leukemia virus genome: structural similarity of its transforming gene product to other onc gene products with tyrosine-specific kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Ball E. H., Singer S. J. Vinculin: a cytoskeletal target of the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90512-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Beemon K., Eckhart W. Evidence that the phosphorylation of tyrosine is essential for cellular transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90327-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S., Cooper J. A., Scolnick E. M. The transforming proteins of Rous sarcoma virus, Harvey sarcoma virus and Abelson virus contain tightly bound lipid. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker A. W., Enrietto P. J., Wyke J. A. Functional domains of the pp60v-src protein as revealed by analysis of temperature-sensitive Rous sarcoma virus mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1508–1514. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Whitman M., Cantley L. C., Erikson R. L. Evidence that the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol and diacylglycerol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2117–2121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Bauer H., Birr C., Pipkorn R. Antibodies against synthetic peptides as a tool for functional analysis of the transforming protein pp60src. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):587–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90391-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tato F., Beamand J. A., Wyke J. A. A mutant of Rous sarcoma virus with a thermolabile defect in the virus envelope. Virology. 1978 Jul 1;88(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkerson V. W., Bryant D. L., Parsons J. T. Rous sarcoma virus variants that encode src proteins with an altered carboxy terminus are defective for cellular transformation. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):314–321. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.314-321.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyke J. A., Linial M. Temperature-sensitive avian sarcoma viruses: a physiological comparison of twenty mutants. Virology. 1973 May;53(1):152–161. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90474-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]