Abstract
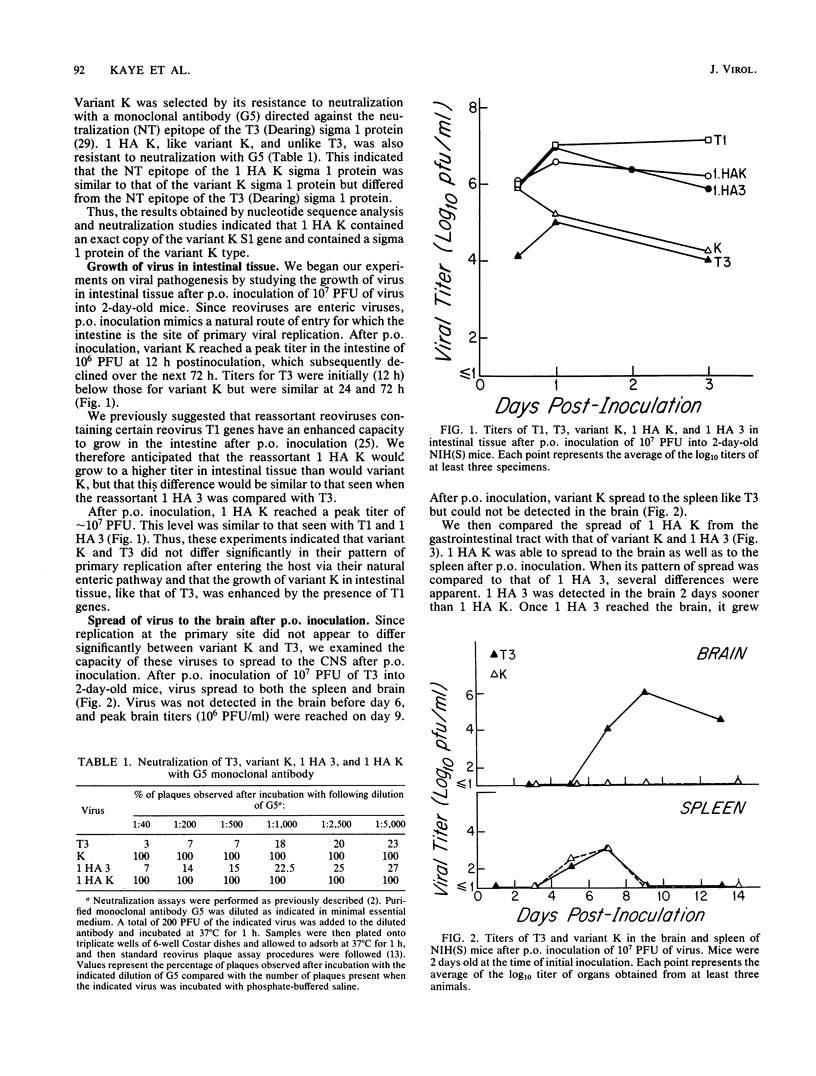
In this paper we provide a step by step comparison of the pathogenesis of murine infection caused by reovirus type 3 (Dearing) and an antigenic variant (K) selected by its resistance to neutralization with a monoclonal antibody (G5) directed against the T3 hemagglutinin. To show that specific changes in the biologic properties of variant K were due to mutation in the S1 double-stranded RNA segment (gene), which encodes the viral hemagglutinin, we generated a reassortant virus ("1 HA K") containing the variant K S1 gene and compared its properties to variant K and to a reassortant ("1 HA 3") containing the T3 (Dearing) S1 gene. These studies, in conjunction with our previous nucleotide sequence analysis of the S1 genes of variant K and T3 (Dearing) [R. Bassel-Duby, A. Jayasuriya, D. Chatterjee, N. Sonenberg, J. V. Maizel, Jr., and B. N. Fields, Nature (London) 315:421-423, 1985; R. Bassel-Duby, D. R. Spriggs, K. L. Tyler, and B. N. Fields, submitted for publication], indicate that a single amino acid change in the T3 hemagglutinin can alter viral growth and tropism within the central nervous system without affecting either its primary replication in the intestine or its pattern of spread to or within the central nervous system.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassel-Duby R., Jayasuriya A., Chatterjee D., Sonenberg N., Maizel J. V., Jr, Fields B. N. Sequence of reovirus haemagglutinin predicts a coiled-coil structure. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):421–423. doi: 10.1038/315421a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstin S. J., Spriggs D. R., Fields B. N. Evidence for functional domains on the reovirus type 3 hemagglutinin. Virology. 1982 Feb;117(1):146–155. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90514-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caton A. J., Brownlee G. G., Yewdell J. W., Gerhard W. The antigenic structure of the influenza virus A/PR/8/34 hemagglutinin (H1 subtype). Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):417–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulon P., Rollin P. E., Flamand A. Molecular basis of rabies virus virulence. II. Identification of a site on the CVS glycoprotein associated with virulence. J Gen Virol. 1983 Mar;64(Pt 3):693–696. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-3-693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulon P., Rollin P., Aubert M., Flamand A. Molecular basis of rabies virus virulence. I. Selection of avirulent mutants of the CVS strain with anti-G monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jul;61(Pt 50):97–100. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-61-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. K., Fields B. N. Use of an aberrant polypeptide as a marker in three-factor crosses: further evidence for independent reassortment as the mechanism of recombination between temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):345–362. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90341-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande K. L., Naeve C. W., Webster R. G. The neuraminidases of the virulent and avirulent A/Chicken/Pennsylvania/83 (H5N2) influenza A viruses: sequence and antigenic analyses. Virology. 1985 Nov;147(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90226-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzschold B., Wiktor T. J., Trojanowski J. Q., Macfarlan R. I., Wunner W. H., Torres-Anjel M. J., Koprowski H. Differences in cell-to-cell spread of pathogenic and apathogenic rabies virus in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):12–18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.12-18.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzschold B., Wunner W. H., Wiktor T. J., Lopes A. D., Lafon M., Smith C. L., Koprowski H. Characterization of an antigenic determinant of the glycoprotein that correlates with pathogenicity of rabies virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):70–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Dunn G., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Cann A. J., Stanway G., Almond J. W., Currey K., Maizel J. V., Jr Increased neurovirulence associated with a single nucleotide change in a noncoding region of the Sabin type 3 poliovaccine genome. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):548–550. doi: 10.1038/314548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Minor P. D., Schild G. S., Almond J. W. Critical role of an eight-amino acid sequence of VP1 in neutralization of poliovirus type 3. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):459–462. doi: 10.1038/304459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. N., Joklik W. K. Isolation and preliminary genetic and biochemical characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. Virology. 1969 Mar;37(3):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90217-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Scarano F., Janssen R. S., Najjar J. A., Pobjecky N., Nathanson N. An avirulent G1 glycoprotein variant of La Crosse bunyavirus with defective fusion function. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):757–763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.757-763.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J., Spindler K., Horodyski F., Grabau E., Nichol S., VandePol S. Rapid evolution of RNA genomes. Science. 1982 Mar 26;215(4540):1577–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.7041255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman R. S., Wolf J. L., Finberg R., Trier J. S., Fields B. N. The sigma 1 protein determines the extent of spread of reovirus from the gastrointestinal tract of mice. Virology. 1983 Jan 30;124(2):403–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90356-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knossow M., Daniels R. S., Douglas A. R., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Three-dimensional structure of an antigenic mutant of the influenza virus haemagglutinin. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):678–680. doi: 10.1038/311678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera P., Dolivo M., Coulon P., Flamand A. Pathways of the early propagation of virulent and avirulent rabies strains from the eye to the brain. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):158–162. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.158-162.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Air G. M., Webster R. G., Gerhard W., Ward C. W., Dopheide T. A. Antigenic drift in type A influenza virus: sequence differences in the hemagglutinin of Hong Kong (H3N2) variants selected with monoclonal hybridoma antibodies. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):226–237. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90540-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Air G. M., Webster R. G. Mechanism of antigenic drift in influenza virus. Amino acid sequence changes in an antigenically active region of Hong Kong (H3N2) influenza virus hemagglutinin. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 15;145(2):339–361. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90209-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löve A., Rydbeck R., Kristensson K., Orvell C., Norrby E. Hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein as a determinant of pathogenicity in mumps virus hamster encephalitis: analysis of mutants selected with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):67–74. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.67-74.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F., Cross R. K., Fields B. N. Genome RNAs and polypeptides of reovirus serotypes 1, 2, and 3. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):726–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.726-733.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F., Mustoe T. A., Sharpe A. H., Fields B. N. A genetic map of reovirus. II. Assignment of the double-stranded RNA-negative mutant groups C, D, and E to genome segments. Virology. 1978 Apr;85(2):531–534. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90459-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. H., Fields B. N. Molecular basis of reovirus virulence. Role of the M2 gene. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):853–868. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif I., Coulon P., Rollin P. E., Flamand A. Rabies virulence: effect on pathogenicity and sequence characterization of rabies virus mutations affecting antigenic site III of the glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):926–934. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.926-934.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Rueckert R. Evidence for at least two dominant neutralization antigens on human rhinovirus 14. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):137–143. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.137-143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs D. R., Bronson R. T., Fields B. N. Hemagglutinin variants of reovirus type 3 have altered central nervous system tropism. Science. 1983 Apr 29;220(4596):505–507. doi: 10.1126/science.6301010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs D. R., Fields B. N. Attenuated reovirus type 3 strains generated by selection of haemagglutinin antigenic variants. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):68–70. doi: 10.1038/297068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G., Hughes P. J., Mountford R. C., Reeve P., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Almond J. W. Comparison of the complete nucleotide sequences of the genomes of the neurovirulent poliovirus P3/Leon/37 and its attenuated Sabin vaccine derivative P3/Leon 12a1b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1539–1543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler K. L., Bronson R. T., Byers K. B., Fields B. Molecular basis of viral neurotropism: experimental reovirus infection. Neurology. 1985 Jan;35(1):88–92. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.1.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Laver W. G., Air G. M., Schild G. C. Molecular mechanisms of variation in influenza viruses. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):115–121. doi: 10.1038/296115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Powers M. L., Fields B. N. Absolute linkage of virulence and central nervous system cell tropism of reoviruses to viral hemagglutinin. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):609–616. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor T. J., Koprowski H. Antigenic variants of rabies virus. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):99–112. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J. Structural identification of the antibody-binding sites of Hong Kong influenza haemagglutinin and their involvement in antigenic variation. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):373–378. doi: 10.1038/289373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


