Abstract
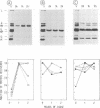
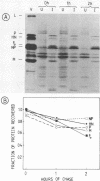
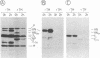
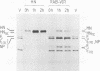
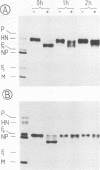
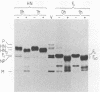
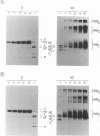
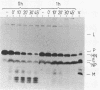
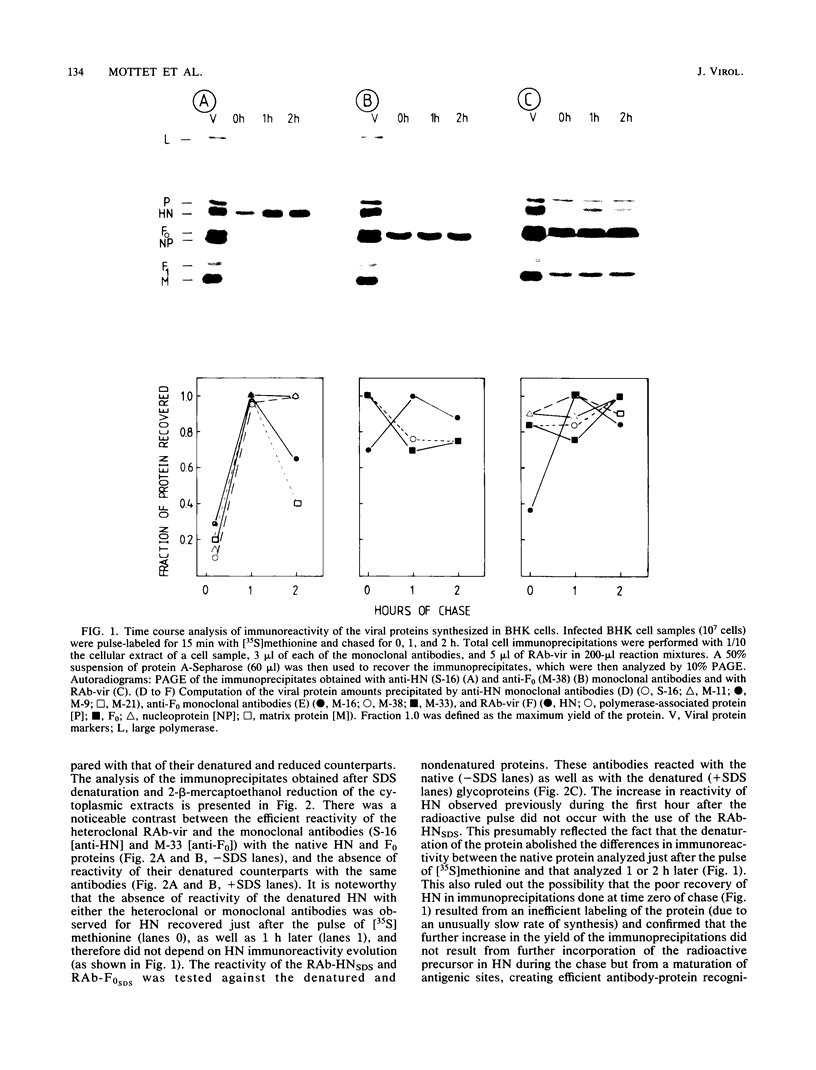
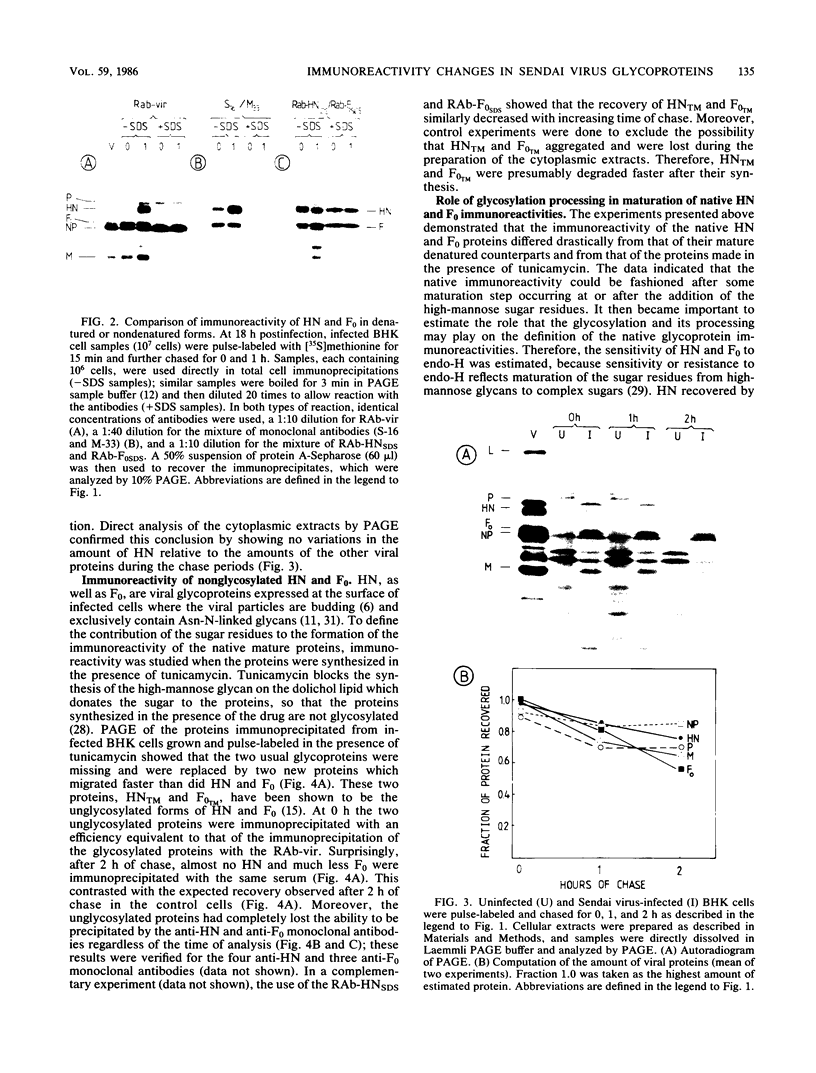
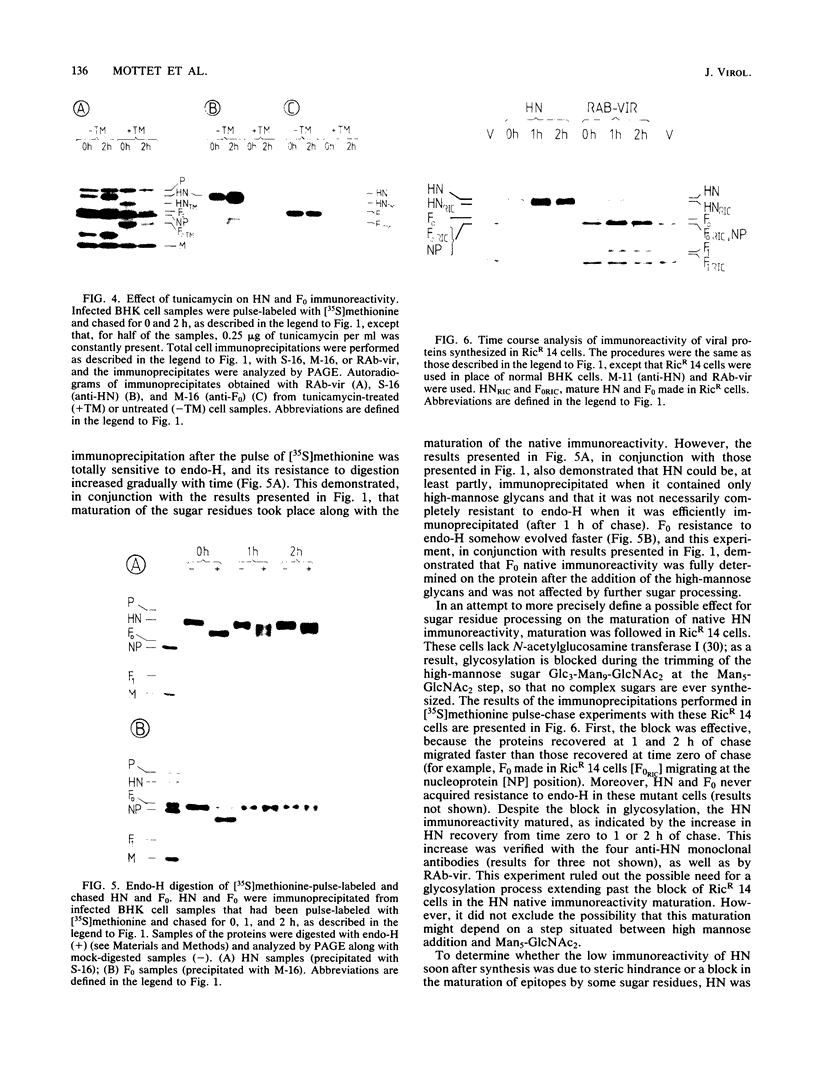
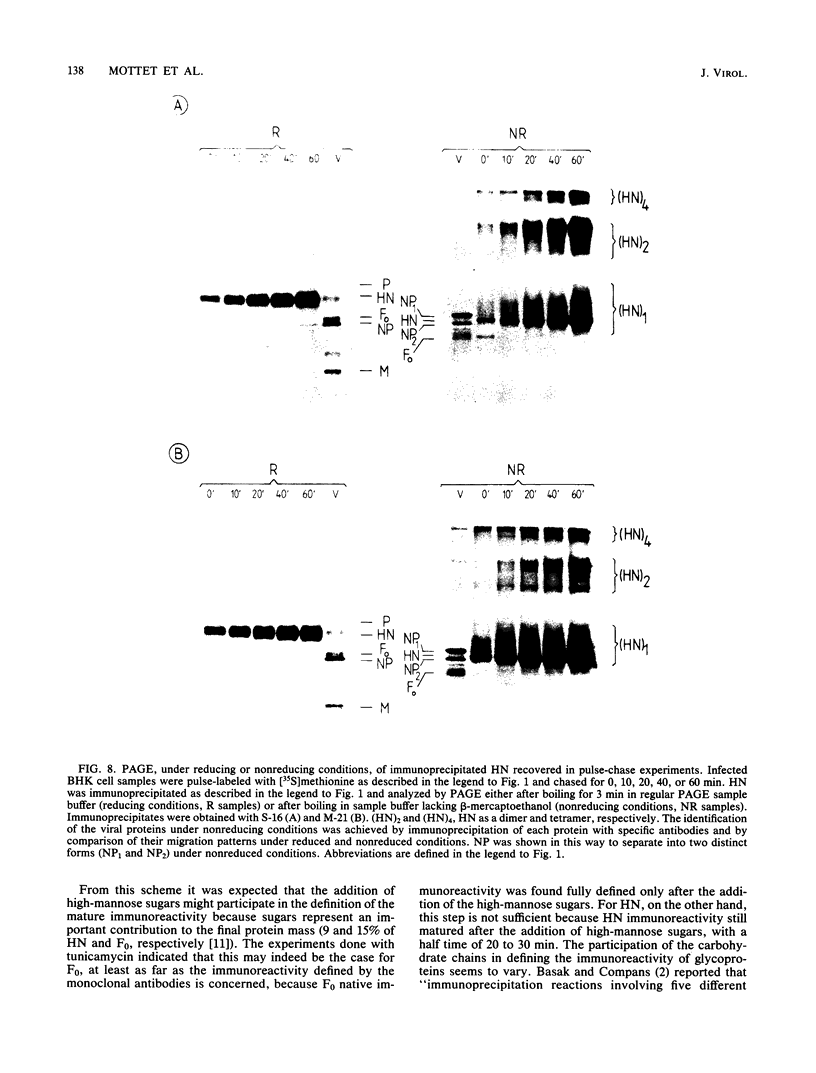
The immunoreactivity of the Sendai virus HN and F0 glycoproteins was shown to mature before reaching the final form exhibited by the native mature proteins. The maturation process differed for the two proteins. The native F0 immunoreactivity was shown to be defined cotranslationally, and the addition of high-mannose sugar residues may represent the final step in defining the maturation of immunoreactivity. On the other hand, native HN immunoreactivity was slowly fashioned during the hour after the completion of protein synthesis. Although addition of high-mannose sugar could constitute a necessary step in this slow maturation process, it was shown not to be sufficient. Processing of high-mannose sugars and HN self-association in homodimers and homotetramers were investigated as possible steps involved in the slow maturation of HN immunoreactivity. They were found not to play a significant role. On the other hand, conformational changes presumably took place during the maturation of HN immunoreactivity. Drastic immunoreactivity differences were also demonstrated between the native and denatured forms of the glycoproteins. Possible implications of these results in defining the pathways of glycoprotein synthesis are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander S., Elder J. H. Carbohydrate dramatically influences immune reactivity of antisera to viral glycoprotein antigens. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1328–1330. doi: 10.1126/science.6505693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basak S., Compans R. W. Studies on the role of glycosylation in the functions and antigenic properties of influenza virus glycoproteins. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):77–91. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90320-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blok J., Air G. M., Laver W. G., Ward C. W., Lilley G. G., Woods E. F., Roxburgh C. M., Inglis A. S. Studies on the size, chemical composition, and partial sequence of the neuraminidase (NA) from type A influenza viruses show that the N-terminal region of the NA is not processed and serves to anchor the NA in the viral membrane. Virology. 1982 May;119(1):109–121. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B. M., Giorgi C., Rose K., Kolakofsky D. Sequence determination of the Sendai virus fusion protein gene. J Gen Virol. 1985 Feb;66(Pt 2):317–331. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-2-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B., Giorgi C., Roux L., Raju R., Dowling P., Chollet A., Kolakofsky D. Sequence determination of the Sendai virus HN gene and its comparison to the influenza virus glycoproteins. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Alexander S. endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F: endoglycosidase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum that cleaves both high-mannose and complex glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4540–4544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A. The spontaneous insertion of proteins into and across membranes: the helical hairpin hypothesis. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M., Choppin P. W. Analysis of Sendai virus mRNAs with cDNA clones of viral genes and sequences of biologically important regions of the fusion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7732–7736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. C., Ivatt R. J. Synthesis and processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:555–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohama T., Shimizu K., Ishida N. Carbohydrate composition of the envelope glycoproteins of Sendai virus. Virology. 1978 Oct 15;90(2):226–234. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Protein-protein interactions within paramyxoviruses identified by native disulfide bonding or reversible chemical cross-linking. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):152–166. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.152-166.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G., Ward L. J. Intracellular processing of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein and the Newcastle disease virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein. Virus Res. 1984;1(3):225–239. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Homma M., Compans R. W. Effect of tunicamycin on the replication of Sendai virus. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):474–487. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. G., Barber C., Carey N. H., Hallewell R. A., Threlfall G., Emtage J. S. Complete nucleotide sequence of an influenza virus haemagglutinin gene from cloned DNA. Nature. 1979 Nov 29;282(5738):471–477. doi: 10.1038/282471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portner A. The HN glycoprotein of Sendai virus: analysis of site(s) involved in hemagglutinating and neuraminidase activities. Virology. 1981 Dec;115(2):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Gallione C. J. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus G and M proteins determined from cDNA clones containing the complete coding regions. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.519-528.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux L., Beffy P., Portner A. Restriction of cell surface expression of Sendai virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein correlates with its higher instability in persistently and standard plus defective interfering virus infected BHK-21 cells. Virology. 1984 Oct 15;138(1):118–128. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux L., Waldvogel F. A. Defective interfering particles of Sendai virus modulate HN expression at the surface of infected BHK cells. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90120-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux L., Waldvogel F. A. Instability of the viral M protein in BHK-21 cells persistently infected with Sendai virus. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):293–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90347-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini D. D., Kreibich G., Morimoto T., Adesnik M. Mechanisms for the incorporation of proteins in membranes and organelles. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):1–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuy W., Garten W., Linder D., Klenk H. D. The carboxyterminus of the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase of Newcastle disease virus is exposed at the surface of the viral envelope. Virus Res. 1984;1(5):415–426. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe J. C., Hightower L. E. Maturation of the envelope glycoproteins of Newcastle disease virus on cellular membranes. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):947–957. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.947-957.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Stevens D. J., Daniels R. S., Douglas A. R., Knossow M., Wilson I. A., Wiley D. C. A carbohydrate side chain on hemagglutinins of Hong Kong influenza viruses inhibits recognition by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1779–1783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Waterfield M. D. Studies on the primary structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):93–97. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara K. E., Tashiro M., Homma M. Intermolecular association of HANA glycoprotein of Sendai virus in relation to the expression of biological activities. Virology. 1982 Mar;117(2):444–455. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90483-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Maley F. Purification and properties of an endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Streptomyces griseus. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):811–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vischer P., Hughes R. C. Glycosyl transferases of baby-hamster-kidney (BHK) cells and ricin-resistant mutants. N-glycan biosynthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jul;117(2):275–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshima H., Nakanishi M., Okada Y., Kobata A. Carbohydrate structures of HVJ (Sendai virus) glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5355–5361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]