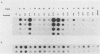Abstract
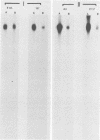
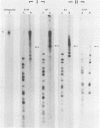
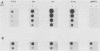
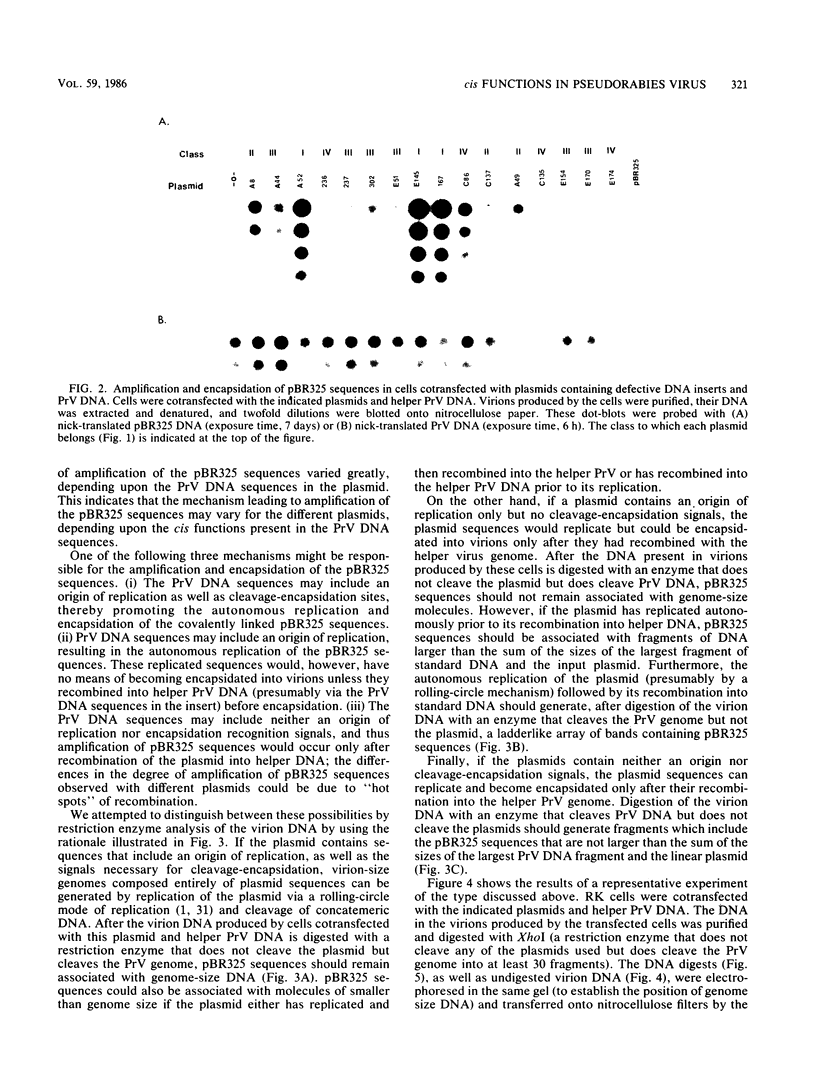
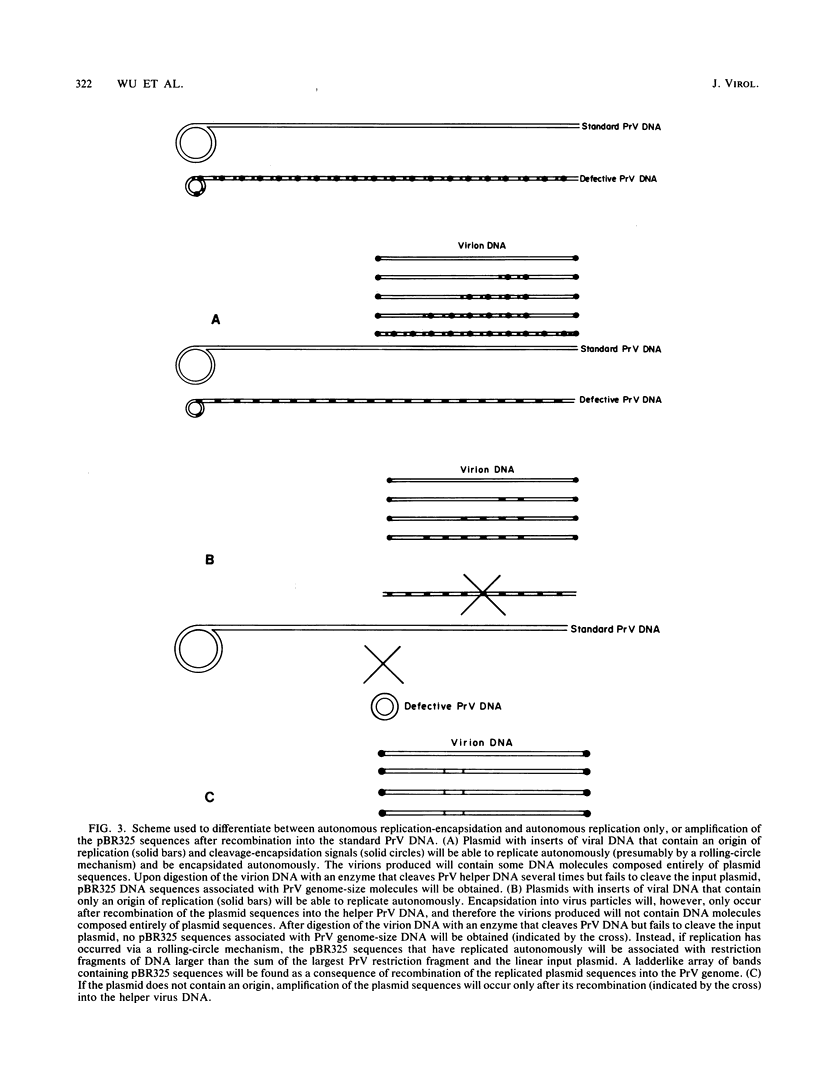
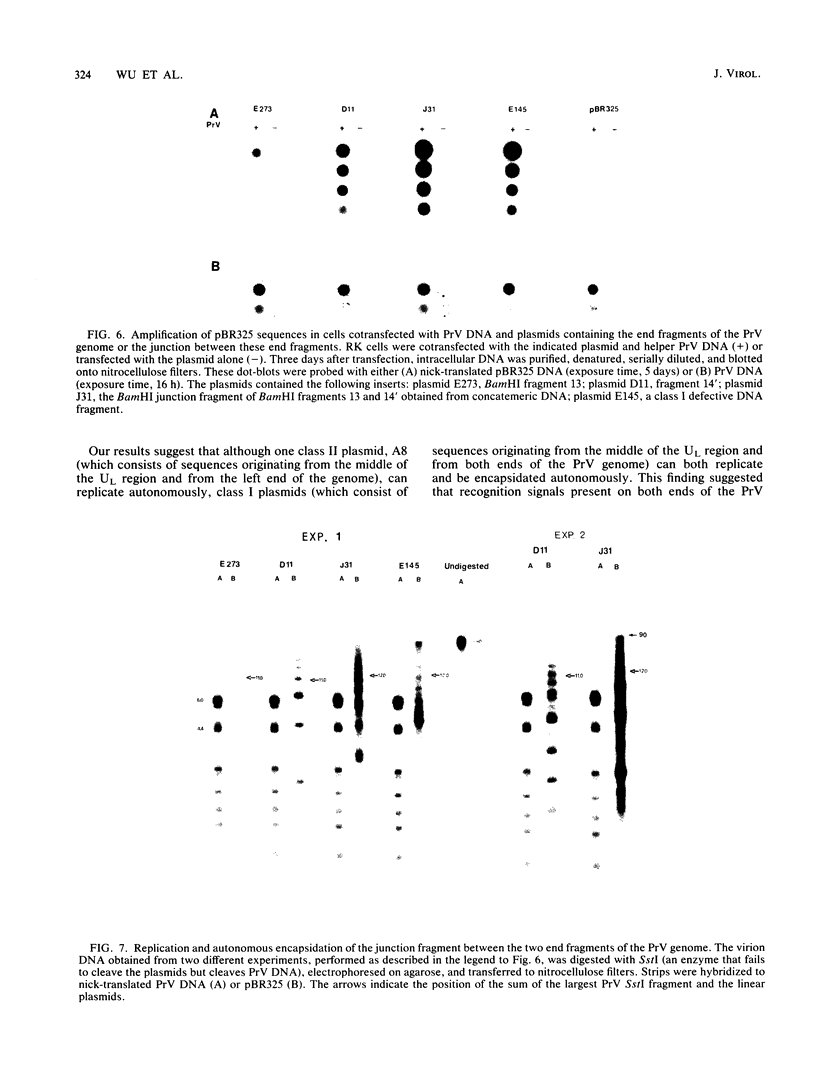
Serial passage at high multiplicity of pseudorabies virus generates defective interfering particles (DIPs) whose genomes consist at least in part of reiterations of segments of DNA in which sequences originating from different regions of the genome have become covalently linked (F. J. Rixon and T. Ben-Porat, Virology 97:151-163). To determine whether some cis functions present in these reiterated DNA sequences may be responsible for the amplification of DIP DNA, BamHI restriction fragments of this DNA were cloned. These fragments were analyzed and tested for their ability to promote the amplification of covalently linked pBR325 DNA when cotransfected into cells with helper pseudorabies virus DNA. The cloned DIP BamHI DNA fragments consisted of various combinations of sequences originating from either one or both ends as well as sequences from the middle of the unique long (UL) segment of the genome. Only plasmids with inserts consisting of segments of defective DNA originating from the middle of the UL, as well as from both ends of the genome, were able to replicate and be encapsidated autonomously. This finding indicated that signals present at both ends of the genome may be necessary for efficient cleavage-encapsidation. To confirm this observation, we constructed plasmids in which DNA segments containing an origin of replication and sequences from either one or both ends of the virus genome were linked. These experiments showed that efficient cleavage-encapsidation requires the presence of sequences derived from both ends of the genome. Two origins of replication, one at the end of the UL segment and one in the middle of the UL segment, were also identified.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker Y., Asher Y., Friedmann A., Kessler E. Circular, circular-linear and branched herpes simplex virus DNA molecules from arginine deprived cells. J Gen Virol. 1978 Dec;41(3):629–633. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-3-629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Jean J. H., Kaplan A. S. Early functions of the genome of herpesvirus. IV. Fate and translation of immediate-early viral RNA. Virology. 1974 Jun;59(2):524–531. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90462-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Kaplan A. S. A comparison of two populations of defective, interfering pseudorabies virus particles. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):471–479. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Kaplan A. S., Stehn B., Rubenstein A. S. Concatemeric forms of intracellular herpesvirus DNA. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):547–560. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90484-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Rixon F. J., Blankenship M. L. Analysis of the structure of the genome of pseudorabies virus. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90484-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Rixon F. J. Replication of herpesvirus DNA. IV: analysis of concatemers. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):61–70. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90438-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Veach R. A., Ladin B. F. Replication of herpesvirus DNA. VI. Virions containing either isomer of pseudorabies virus DNA are infectious. Virology. 1980 Apr 30;102(2):370–380. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Veach R. A. Origin of replication of the DNA of a herpesvirus (pseudorabies). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):172–175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiss M., Kobayashi I., Widner W. Separate sites for binding and nicking of bacteriophage lambda DNA by terminase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):955–959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiss M., Widner W. Bacteriophage lambda DNA packaging: scanning for the terminal cohesive end site during packaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3498–3502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. DNA sequences necessary for packaging of bacteriophage lambda DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7456–7460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean J. H., Ben-Porat T. Appearance in vivo of single-stranded complementary ends on parental herpesvirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2674–2678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN A. S., VATTER A. E. A comparison of herpes simplex and pseudorabies viruses. Virology. 1959 Apr;7(4):394–407. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaerner H. C., Maichle I. B., Ott A., Schröder C. H. Origin of two different classes of defective HSV-1 Angelotti DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1467–1478. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladin B. F., Blankenship M. L., Ben-Porat T. Replication of herpesvirus DNA. V. Maturation of concatemeric DNA of pseudorabies virus to genome length is related to capsid formation. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1151–1164. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1151-1164.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladin B. F., Ihara S., Hampl H., Ben-Porat T. Pathway of assembly of herpesvirus capsids: an analysis using DNA+ temperature-sensitive mutants of pseudorabies virus. Virology. 1982 Jan 30;116(2):544–561. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure S. C., Gold M. Intermediates in the maturation of bacteriophage lambda DNA. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure S. C., MacHattie L., Gold M. A sedimentation analysis of DNA found in Escherichia coli infected with phage lambda mutants. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa T., Matsubara K. Identification of sequences necessary for packaging DNA into lambda phage heads. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(2):267–279. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa T., Matsubara K. Lambda phage DNA sequences affecting the packaging process. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90080-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon F. J., Ben-Porat T. Structural evolution of the DNA of pseudorabies-defective viral particles. Virology. 1979 Aug;97(1):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90381-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. S., Kaplan A. S. Electron microscopic studies of the DNA of defective and standard pseudorabies virions. Virology. 1975 Aug;66(2):385–392. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90211-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnös M., Inman R. B. Position of branch points in replicating lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 14;51(1):61–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90270-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalka A., Poonian M., Bartl P. Concatemers in DNA replication: electron microscopic studies of partially denatured intracellular lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 14;64(3):541–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. G., Skalka A. Some properties of DNA from phage-infected bacteria. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Jul;49(6):127–142. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.6.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Frenkel N. The herpes simplex virus amplicon: a new eucaryotic defective-virus cloning-amplifying vector. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Frenkel N. The herpes simplex virus amplicon: analyses of cis-acting replication functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):694–698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevely W. S. Inverted repetition in the chromosome of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1977 Apr;22(1):232–234. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.1.232-234.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., McMonagle E. C., Davison A. J. Fragments from both termini of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome contain signals required for the encapsidation of viral DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 10;11(23):8205–8220. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.23.8205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J., Ogawa T. Replication of phage lambda DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:533–551. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmuza S. L., Smiley J. R. Signals for site-specific cleavage of HSV DNA: maturation involves two separate cleavage events at sites distal to the recognition sequences. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):793–802. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlazny D. A., Frenkel N. Replication of herpes simplex virus DNA: localization of replication recognition signals within defective virus genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlazny D. A., Kwong A., Frenkel N. Site-specific cleavage/packaging of herpes simplex virus DNA and the selective maturation of nucleocapsids containing full-length viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1423–1427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake R. G., Kaiser A. D., Inman R. B. Isolation and structure of phage lambda head-mutant DNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 14;64(3):519–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Spadaro A., Schaffer J. E., Murray A. W., Maxam A. M., Schaffer P. A. Cloning, sequencing, and functional analysis of oriL, a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin of DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):930–942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. A., Harper L., Ben-Porat T. Molecular basis for interference of defective interfering particles of pseudorabies virus with replication of standard virus. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):308–317. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.308-317.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]