Abstract
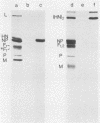
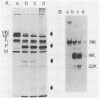
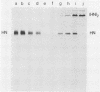
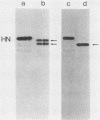
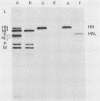
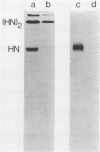
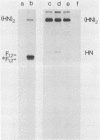
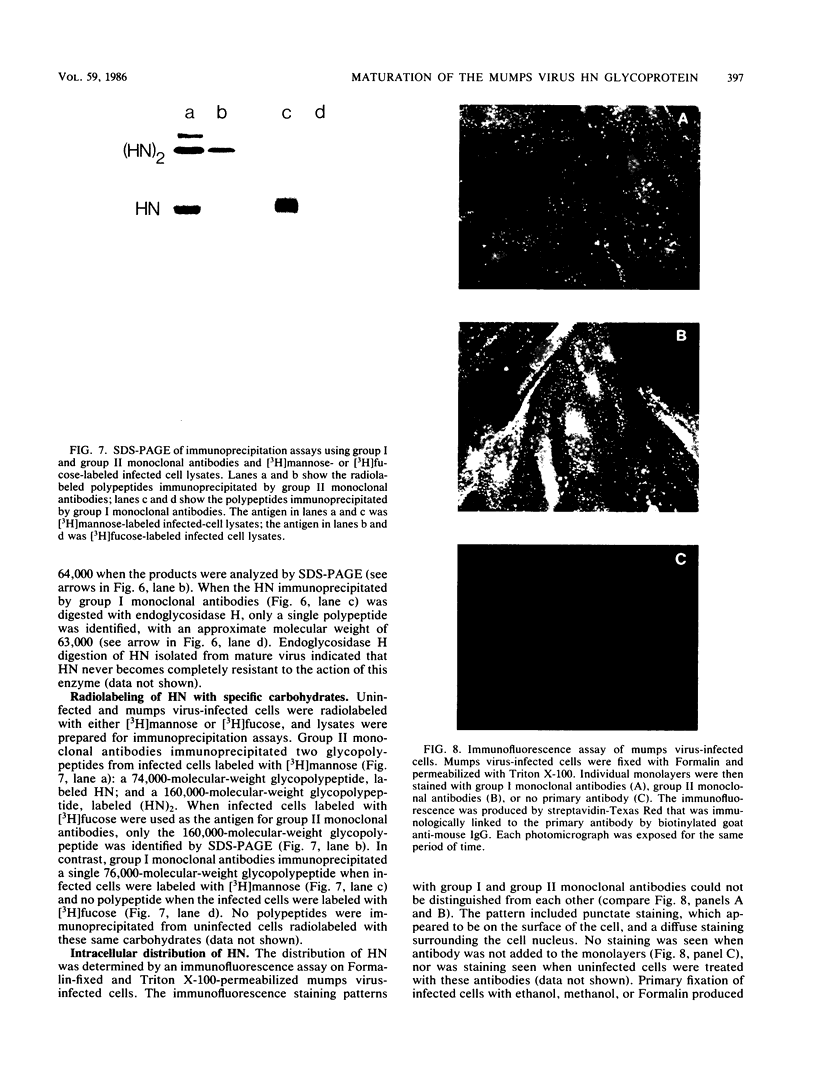
Monoclonal antibodies elicited by immunization with mumps virus glycoproteins were selected with either native or chymotrypsin-treated mumps virus in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Group I antibodies which preferentially recognized chymotrypsin-treated virus failed to recognize native mumps virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase (HN). They did react with sodium dodecyl sulfate-denatured HN and the HN chymotryptic fragments HNc2' (molecular weight, 41,000) and HNc1 (molecular weight, 32,000) after transfer to nitrocellulose paper. In contrast, group II antibodies, which preferentially recognized native virus in the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, reacted with native HN but failed to bind HN after sodium dodecyl sulfate denaturation. These two groups of monoclonal antibodies were used to define the maturation pathway of the mumps virus HN in infected cells. The HN initially appeared as a 76,000-molecular-weight polypeptide and was recognized only by group I antibodies. A truncated form of HN, HNT (molecular weight, 63,000), was synthesized in the presence of tunicamycin and was also recognized only by group I antibodies. The 76,000-molecular-weight HN was rapidly converted to a 74,000-molecular-weight polypeptide; this form of HN was recognized only by group II antibodies. The oligosaccharide side chains were modified, and intermolecular disulfide bonds were formed as HN was transported to the cell surface. The disulfide-linked oligomers of HN were direct precursors of the HN found in mature virus.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson P. H., Lee J. T. Co-translational excision of alpha-glucose and alpha-mannose in nascent vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):2245–2249. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.2245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B., Giorgi C., Roux L., Raju R., Dowling P., Chollet A., Kolakofsky D. Sequence determination of the Sendai virus HN gene and its comparison to the influenza virus glycoproteins. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Rothman J. E. Compartmentation of asparagine-linked oligosaccharide processing in the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):270–275. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabel C. A., Bergmann J. E. Processing of the asparagine-linked oligosaccharides of secreted and intracellular forms of the vesicular stomatitis virus G protein: in vivo evidence of Golgi apparatus compartmentalization. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):460–469. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H. Using recombinant DNA techniques to study protein targeting in the eucaryotic cell. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:403–445. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Kohama T., Klenk H. D. Proteolytic activation of the haemagglutinin-neuraminidase of Newcastle disease virus involves loss of a glycopeptide. J Gen Virol. 1980 Nov;51(Pt 1):207–211. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-51-1-207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R., Leavitt R., Kornfeld S., Schlesinger S. Synthesis and infectivity of vesicular stomatitis virus containing nonglycosylated G protein. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90217-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrler G., Compans R. W. Posttranslational modification and intracellular transport of mumps virus glycoproteins. J Virol. 1983 Aug;47(2):354–362. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.2.354-362.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Paterson R. G., Lamb R. A. Hemagglutinin-neuraminidase protein of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5: nucleotide sequence of the mRNA predicts an N-terminal membrane anchor. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.1-6.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. C., Ivatt R. J. Synthesis and processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:555–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza G., Rott R., Schwarz R. T. Carbohydrate-induced conformational changes of Semliki forest virus glycoproteins determine antigenicity. Virology. 1980 Apr 30;102(2):286–299. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt R., Schlesinger S., Kornfeld S. Impaired intracellular migration and altered solubility of nonglycosylated glycoproteins of vesicular stomatitis virus and Sindbis virus. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 25;252(24):9018–9023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Kong N. Glucose removal from N-linked oligosaccharides is required for efficient maturation of certain secretory glycoproteins from the rough endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1720–1729. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz D. C., Server A. C., Waxham M. N., Wolinsky J. S. Biosynthesis of mumps virus F glycoprotein: non-fusing strains efficiently cleave the F glycoprotein precursor. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jul;64(Pt 7):1457–1467. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-7-1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz D. C., Wolinsky J. S. Conversion of nonfusing mumps virus infections to fusing infections by selective proteolysis of the HN glycoprotein. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):328–340. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90501-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. The golgi apparatus: two organelles in tandem. Science. 1981 Sep 11;213(4513):1212–1219. doi: 10.1126/science.7268428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini D. D., Kreibich G., Morimoto T., Adesnik M. Mechanisms for the incorporation of proteins in membranes and organelles. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):1–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuy W., Garten W., Linder D., Klenk H. D. The carboxyterminus of the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase of Newcastle disease virus is exposed at the surface of the viral envelope. Virus Res. 1984;1(5):415–426. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe J. C., Hightower L. E. Maturation of the envelope glycoproteins of Newcastle disease virus on cellular membranes. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):947–957. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.947-957.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Server A. C., Merz D. C., Waxham M. N., Wolinsky J. S. Differentiation of mumps virus strains with monoclonal antibody to the HN glycoprotein. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):179–186. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.179-186.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. W., Hightower L. E. Identification of the P proteins and other disulfide-linked and phosphorylated proteins of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):256–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.256-267.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strous G. J., Willemsen R., van Kerkhof P., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Lodish H. F. Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein, albumin, and transferrin are transported to the cell surface via the same Golgi vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1815–1822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Marder V. J. Biosynthesis of von Willebrand protein by human endothelial cells: processing steps and their intracellular localization. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2123–2130. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolinsky J. S., Waxham M. N., Server A. C. Protective effects of glycoprotein-specific monoclonal antibodies on the course of experimental mumps virus meningoencephalitis. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):727–734. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.727-734.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Snider M. D., Porter M., Lodish H. F. Mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus blocked at different stages in maturation of the viral glycoprotein. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):417–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90478-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]