Abstract
The membrane phospholipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P2) is an important regulator in cell physiology. Hydrolysis of PtdIns(4,5)P2 by phospholipase C (PLC) releases two second messengers, Ins(1,4,5)P3 and diacylglycerol. To dissect the effects of PtdIns(4,5)P2 from those resulting from PLC-generated signals, a metabolically-stabilized analogue of PtdIns(4,5)P2 was required. Two analogues were designed in which the scissile O-P bond was replaced with a C-P bond that could not be hydrolyzed by PLC activity. Herein we describe the asymmetric total synthesis of the first metabolically-stabilized, phospholipase C-resistant analogues of PtdIns(4,5)P2. The key transformation was a Pd(0)-catalyzed coupling of an H-phosphite with a vinyl bromide to form the desired C-P linkage. The phosphonate analogues of PtdIns(4,5)P2 were found to be effective in restoring the sensitivity of the TRPM4 channel to Ca2+ activation.
The membrane phospholipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P2) is an important regulator of cytoskeletal organization during a plethora of cellular functions such as vesicle trafficking, endocytosis, phagocytosis, focal adhesion formation, and cell migration.1 PtdIns(4,5)P2 binds to and affects the function of many actin-binding and actin-remodeling proteins,2–4 and is a cofactor in enzyme activation.5 In addition, PtdIns(4,5)P2 regulates the activity of many ion channels and transporters.6,7 PtdIns(4,5)P2 is also the source of three second messengers: Ins(1,4,5)P3, diacylglycerol (DAG)8,9 and PtdIns(3,4,5)P3.10 In many cases, it is the decrease in PtdIns(4,5)P2, resulting from hydrolysis by phospholipase C (PLC) (Scheme 1), and not the increase in Ins(1,4,5)P3 and DAG, that constitutes the physiologically relevant signal.11,12 Hydrolysis of PtdIns(4,5)P2 causes TRP channels to lose some activity.13–19 Moreover, addition of PtdIns(4,5)P2 restores sensitivity of TRPM4 and TRPM5 to activation by Ca2+ and restores the sensitivity of TRPM8 and TRPV1 to thermal and chemical stimuli.15,16,18,19
Scheme 1.
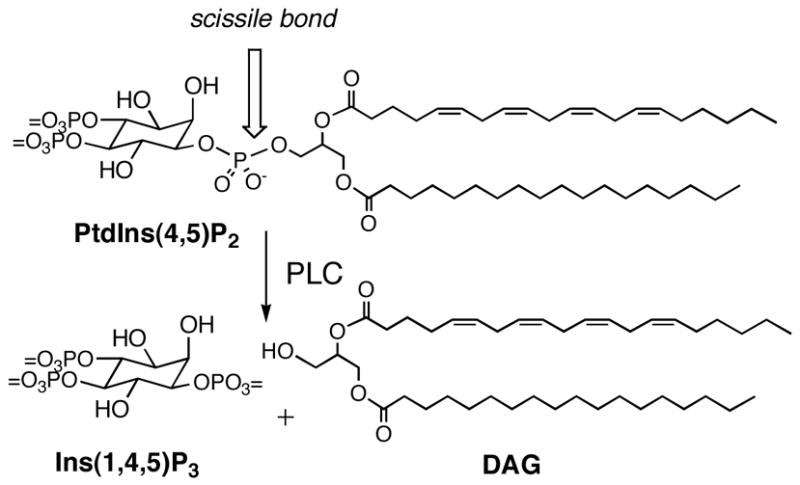
Phospholipase C catalyzes hydrolysis of PtdIns(4,5)P2 to two second messengers, Ins(1,4,5)P3 and diacylglycerol
The availability of a metabolically-stabilized analogue of PtdIns(4,5)P2, i.e., one that lacks the scissile P-O bond and thus could not be hydrolyzed by PLC activity, would have many applications in understanding the role of PtdIns(4,5)P2 in cell physiology. α-Fluoroalkylphosphonates have emerged as important non-hydrolyzable mimics for phosphoesters in the synthesis of biologically-active “unnatural products”.20–23 Herein we describe the first asymmetric total synthesis of isosteric and isoelectronic phosphonate analogues 1 – 5 of PtdIns(4,5)P2 that cannot be hydrolyzed by PLC. The synthesis employs a Pd(0) coupling not previously exploited in phospholipid or phosphoinositide synthesis. Furthermore, we demonstrate that both saturated and unsaturated α-fluorophosphonate analogues can substitute for exogenous PtdIns(4,5)P2 in restoring the sensitivity of the TRPM4 channel to Ca2+.
The synthetic sequence to the stabilized analogues 1–5 of PtdIns(4,5)P2 is illustrated in Scheme 2. A variety of attempts to connect the intermediate 924 with a fluoromethylenephosphonic acid synthon21 failed. Eventually, we turned to the Pd(0)-catalyzed coupling of a H-phosphite with a vinyl bromide in order to form the desired C-P linkage. Thus, coupling the protected inositol 9 with dibenzyl N, N-diisopropylphosphor-amidite gave the phosphoramidite intermediate 10, which was converted to H-phosphonate 11 in 76% isolated yield for two steps.25 The 1-bromo-1-fluoroolefin 7 (~ 1:1 E/Z) was 26 separately prepared via a Et2Zn-promoted olefination reaction of CBr3F/PPh3 with glyceraldehyde 6 in excellent yield.
Scheme 2.
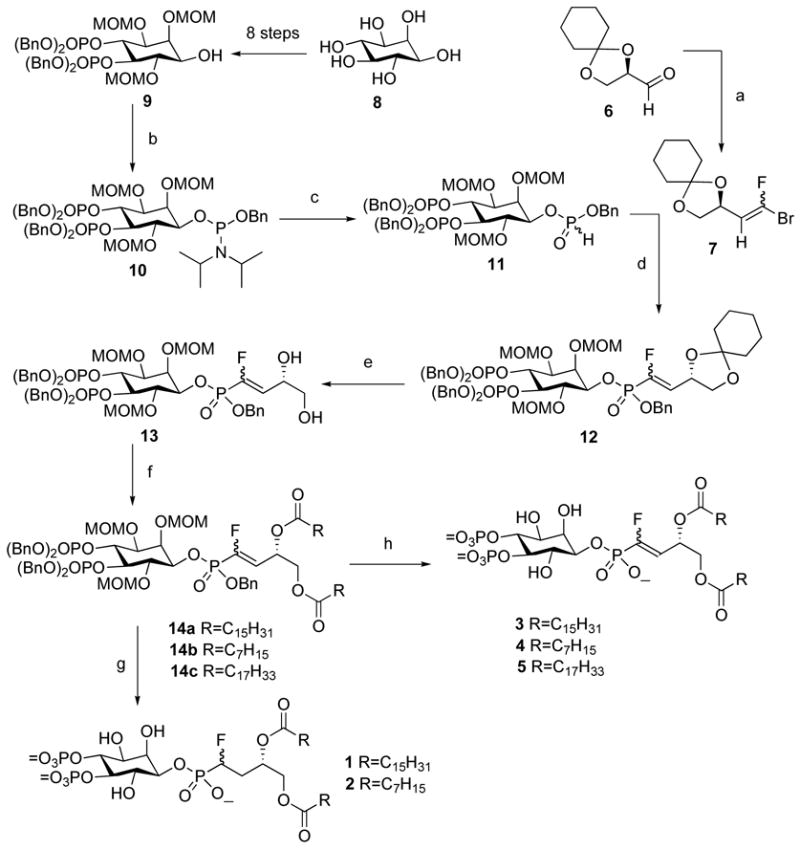
Synthesis of phosphonates 1–5a
a(a) CFBr3, PPh3, Et2Zn, THF, 76%; (b) (BnO)2P(NPr2-i)2, N,N-disopropylethylammonium ·1H-tetrazole, CH2Cl2, rt; (c) H2O, 1H-tetrazole, rt, 1h, CH2Cl2, 76% for two steps; (d) Pd(OAc)2, dppf, propylene oxide, THF, 70 °C, 62%; (e) 60% aqueous TFA, THF, 0 °C, 1 h, 86%; (f) EDCI, DMAP, fatty acid, CH2Cl2, rt; (g) H2, Pd/C, MeOH, 6h; EtSH; (h) TMBr/TMSI (5:1), rt, 1.5 h; MeOH, 1 h.
Few examples exist of Pd(0)-catalyzed formation of P-CF bonds, and in our hands only traces of coupled compound 12 and with a majority of the P-O cleaved compound 9 were obtained under standard conditions using Et3N or K2CO3 as base. It appeared that the rate of decomposition was faster than the rate of coupling for the more hindered H-phosphonate 11. To overcome this problem, we selected propylene oxide as a weak Lewis base and an effective scavenger of HBr.27 Using this modification, treatment of the H-phosphonate 11 with Pd(OAc)2/dppf/propylene oxide in THF at 70°C led to the formation of α-fluorovinylphosphonate 12 in 62% yield. Acetal 12 was selectively deprotected by treatment with 60% aqueous trifluoroacetic acid in tetrahydrofuran at 0 °C to give diol 13. Next, acylation of 13 with either octanoic acid, palmitic acid, or oleic acid provided the fully-protected phosphonates 14a, 14b and 14c in 80%, 73% and 82% yields, respectively. Hydrogenolysis of 14a a n d 14b removed the benzyl groups, and then reaction with ethanethiol removed the MOM groups to give the α-fluoromethylenephos-phonate analogues 1 and 2.28 The α-fluorovinylphosphonates 3, 4, 5 28 were obtained by deprotection of benzyl and MOM groups simultaneously with TMSBr/TMSI (5:1).
Recently, the hydrolysis of the water-soluble dioctanoyl PtdIns(4,5)P2 was found to be important in the desensitization of TRPM4 channel (activated by cytoplasmic Ca2+). Exogenous PtdIns(4,5)P2 could restore the sensitivity of TRPM4 channels to Ca2+, demonstrating that PtdIns(4,5)P2 was a general regulator for the gating of TRPM4 ion channels.15 The ability of the two dioctanoyl-PtdIns(4,5)P2 analogues 2 and 4 to restore TRPM4 currents following rundown is shown in Figure 1. Both analogues restored TRPM4 sensitivity following desensitization, but the α-fluorovinylphosphonate 4 was more potent. Indeed, the unsaturated phosphonate 4 was even more effective than the hydrolyzable dioctanoyl-PtdIns(4,5)P2 at restoring TRPM4 sensitivity. This provides further evidence that the regulation of TRPM4 by dioctanoyl-PtdIns(4,5)P2 and the ability of dioctanoyl-PtdIns(4,5)P2 to restore TRPM4 currents following rundown is not due to effects of products of PLC hydrolysis.15
Figure 1.
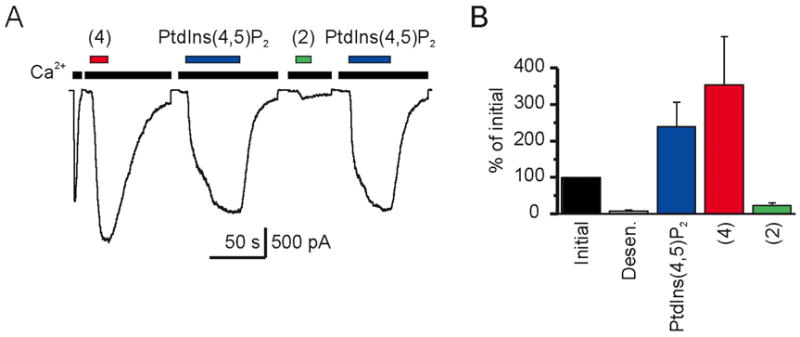
PtdIns(4,5)P2 and analogues 2 and 4 restore TRPM4 currents following desensitization. A. An excised inside-out patch from Chok1 cell expressing mouse TRPM4 (mTRPM4) shows activation and fast rundown of an inward current in the presence of 100 μM Ca2+ and recovery by dioctanoyl-PtdIns(4,5)P2 and analogues 2 and 4 (Vm = 80 mV). B. Initial magnitudes of the mTRPM4 currents, currents after rundown, and currents after recovery in response to 10 μM each of PtdIns(4,5)P2, 2, and 4 (averages, n = 8).
To determine sensitivity of TRPM4 currents to 2 and 4, we measured the effects of varying concentrations of both compounds on the recovery of TPRM4 currents in excised inside-out patches evoked in response to 100μM Ca2+ (Figure 2). Maximal recovery of TRPM4 currents was observed upon reaching 10 μM for both 2 and 4, and half-activation was observed at ~ 2 μM for both compounds, which is similar to the concentration of PtdIns(4,5)P2 that promoted half-activation of TRPM4 (6 μM).15 The difference between the effectiveness of 2 and 4 in restoring TRPM4 currents (Figure 1) appears to result from differential abilities to promote activation of the TRPM4 channel. Taken together, these data suggest that the α-fluorovinylphosphonate 4 is a biologically-active, long-lived mimic of PtdIns(4,5)P2.
Figure 2.
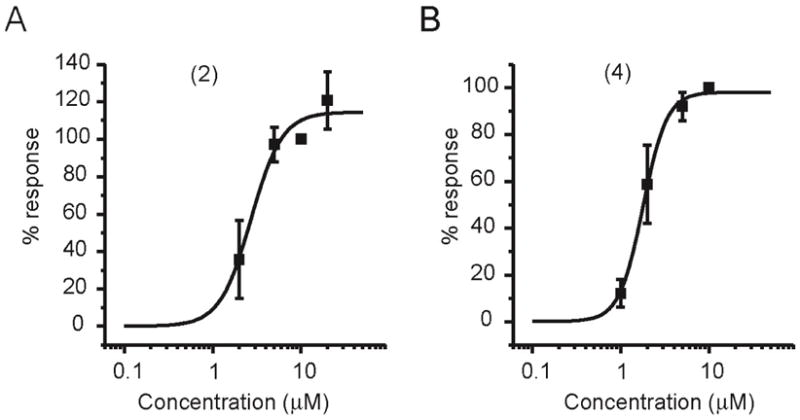
Dose-response for recovery of TRPM4 currents by 2 and 4. After TRPM4 desensitization, recovery was assessed. Data were normalized to the response to 10 μM of each analogue in the same patch. A. Averaged data (n = 5) for recovery of TRPM4 currents by 2 (EC50 = 2.7 ± 0.6 μM and nH = 2.5 ± 1.2). B. Averaged data (n = 6) for 4 (EC50 = 1.8 ± 0.1 μM and nH = 3.2 ± 0.5).
In conclusion, we developed an efficient synthesis of two non-hydrolyzable PtdIns(4,5)P2 analogues, and we showed that α-fluorovinylphosphonate 4 optimally restored the sensitivity of TRPM4 currents. These results suggest that metabolically-stabilized analogues of PtdIns(4,5)P2 will have a wide variety of applications in separating the role of the phosphoinositide per se from activities that result when Ins(1,4,5)P3, DAG, Ca2+, or other downstream signals are generated from the hydrolysis of PtdIns(4,5)P2 by PLC.
Supplementary Material
Experimental details for synthesis and characterization of new compounds, and protocols for TRPM4 channel activity measurement. This material is available free of charge via the internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
Acknowledgments
We thank the NIH (Grant NS 29632 to GDP and DC 004564 to ERL) for financial support of this work.
References
- 1.McLaughlin S, Murray D. Nature. 2005;438:605–611. doi: 10.1038/nature04398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Anderson RA, Boronenkov IV, Doughman SD, Kunz J, Loijens JC. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:9907–9910. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.15.9907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Doughman RL, Firestone AJ, Anderson RA. J Membr Biol. 2003;194:77–89. doi: 10.1007/s00232-003-2027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.McLaughlin S, Wang J, Gambhir A, Murray D. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2002;31:151–175. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.31.082901.134259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sciorra VA, Rudge SA, Wang J, McLaughlin S, Engebrecht J, Morris AJ. J Cell Biol. 2002;159:1039–1049. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200205056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hilgemann DW, Feng S, Nasuhoglu C. Sci STKE. 2001;2001:RE19. doi: 10.1126/stke.2001.111.re19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Suh BC, Hille B. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2005;15:370–378. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2005.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Berridge MJ. Nature. 1993;361:315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Berridge MJ. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cantley LC. Science. 2002;296:1655–1657. doi: 10.1126/science.296.5573.1655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Suh BC, Hille B. Neuron. 2002;35:507–520. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00790-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhang H, Craciun LC, Mirshahi T, Rohacs T, Lopes CM, Jin T, Logothetis DE. Neuron. 2003;37:963–975. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00125-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chuang HH, Prescott ED, Kong H, Shields S, Jordt SE, Basbaum AI, Chao MV, Julius D. Nature. 2001;411:957–962. doi: 10.1038/35082088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Prescott ED, Julius D. Science. 2003;300:1284–1288. doi: 10.1126/science.1083646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zhang Z, Okawa H, Wang Y, Liman ER. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:39185–39192. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M506965200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Liu D, Liman ER. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:15160–15165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2334159100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Liu B, Zhang C, Qin F. J Neurosci. 2005;25:4835–4843. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1296-05.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Liu B, Qin F. J Neurosci. 2005;25:1674–1681. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3632-04.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rohacs T, Lopes CM, Michailidis I, Logothetis DE. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:626–634. doi: 10.1038/nn1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Berkowitz DB, Bose M. J Fluorine Chem. 2001;112:13–33. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Xu Y, Prestwich GD. J Org Chem. 2003;68:5320–5330. doi: 10.1021/jo020729l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Prestwich GD, Xu Y, Qian L, Gajewiak J, Jiang G. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005;33:1357–1361. doi: 10.1042/BST0331357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Xu Y, Lee SA, Kutateladze TG, Sbrissa D, Shisheva A, Prestwich GD. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:885–897. doi: 10.1021/ja0554716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kubiak RJ, Bruzik KS. J Org Chem. 2003;68:960–968. doi: 10.1021/jo0206418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chen J, Prestwich GD. J Org Chem. 1998;63:430–431. doi: 10.1021/jo972046p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lei X, Dutheuil G, Pannecoucke X, Quirion JC. Org Lett. 2004;6:2101–2104. doi: 10.1021/ol049742d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Abbas S, Bertram RD, Hayes CJ. Org Lett. 2001;3:3365–3367. doi: 10.1021/ol0166045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Note on stereochemistry. Both compounds 1 and 2 are inseparable mixtures of diastereomers at the C-F stereocenter, and the chiral phosphorus atom is racemic. Similarly, compounds 3, 4, 5 and 12–14 are inseparable E/Z mixtures.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Experimental details for synthesis and characterization of new compounds, and protocols for TRPM4 channel activity measurement. This material is available free of charge via the internet at http://pubs.acs.org.


