Abstract
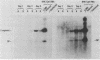
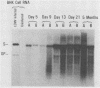
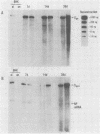
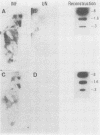
Infection of newborn mice with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) results in a lifelong persistent infection. Persistently infected animals continuously produce low levels of infectious virus and accumulate large amounts of intracellular viral nucleic acid (P. J. Southern, P. Blount, and M. B. A. Oldstone, Nature [London] 312:555-558, 1984). We have used gel electrophoresis and hybridization techniques to analyze viral RNAs that appear during the establishment and maintenance of a persistent LCMV infection in vivo to identify any role for defective and/or defective interfering RNAs. We have found a complex, heterogeneously sized population of viral RNAs in multiple independent tissues that is uniquely associated with persistent infections in vivo, but we have not yet established whether these RNAs have a causal or a consequential association with persistent infection by LCMV. Within the complex virus RNA population, full-length genomic L and S RNAs were readily detectable and represented the most abundant individual viral RNA species. RNAs apparently corresponding in size to the viral nucleoprotein and glycoprotein mRNAs could also be detected in these tissue RNA samples. The presence of glycoprotein mRNA indicates a potential mechanism of posttranscriptional regulation to account for the previously documented restriction in viral glycoprotein expression in persistently infected mice (M. B. A. Oldstone and M. J. Buchmeier, Nature (London) 300:360-362, 1982).
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auperin D. D., Romanowski V., Galinski M., Bishop D. H. Sequencing studies of pichinde arenavirus S RNA indicate a novel coding strategy, an ambisense viral S RNA. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):897–904. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.897-904.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. D., Crouch C. F., Dimmock N. J. Defective interfering Semliki Forest virus populations are biologically and physically heterogeneous. J Gen Virol. 1984 Aug;65(Pt 8):1273–1283. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-8-1273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Welsh R. M., Dutko F. J., Oldstone M. B. The virology and immunobiology of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. Adv Immunol. 1980;30:275–331. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutko F. J., Pfau C. J. Arenavirus defective interfering particles mask the cell-killing potential of standard virus. J Gen Virol. 1978 Feb;38(2):195–208. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-2-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutko F. J., Wright E. A., Pfau C. J. The RNAs of the defective interfering Pichinide virus. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jun;31(3):417–427. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-3-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Cole G. A., Monjan A. A., Nathanson N. Immunopathogenesis of acute central nervous system disease produced by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. I. Cyclophosphamide-mediated induction by the virus-carrier state in adult mice. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):860–873. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Cole G. A., Nathanson N. Immunopathogenesis of acute central nervous system disease produced by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. II. Adoptive immunization of virus carriers. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):874–889. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimenez H. B., Compans R. W. Defective interfering Tacaribe virus and persistently infected cells. Virology. 1980 Nov;107(1):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90288-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. R., Buchmeier M. J. A protein kinase activity in lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus and identification of the phosphorylated product using monoclonal antibody. Virology. 1983 Apr 30;126(2):538–547. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(83)80011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S. Defective interfering viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:101–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Dutko F. J., Pfau C. J. Determinants of spontaneous recovery and persistance in MDCK cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jul;44(1):113–122. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Pfau C. J. Viral pathogenesis and resistance to defective interfering particles. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):311–313. doi: 10.1038/283311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolakofsky D. Isolation and characterization of Sendai virus DI-RNAs. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):547–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90223-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Buchmeier M. J. Restricted expression of viral glycoprotein in cells of persistently infected mice. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):360–362. doi: 10.1038/300360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peralta L. M., Bruns M., Lehmann-Grube F. Biochemical composition of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus interfering particles. J Gen Virol. 1981 Aug;55(Pt 2):475–479. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-2-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrault J. Origin and replication of defective interfering particles. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;93:151–207. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68123-3_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popescu M., Lehmann-Grube F. Defective interfering particles in mice infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):78–83. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90407-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao D. D., Huang A. S. Interference among defective interfering particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):210–221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.210-221.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez M., Buchmeier M. J., Oldstone M. B., Lampert P. W. Ultrastructural localization of viral antigens in the CNS of mice persistently infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV). Am J Pathol. 1983 Jan;110(1):95–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanowski V., Matsuura Y., Bishop D. H. Complete sequence of the S RNA of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (WE strain) compared to that of Pichinde arenavirus. Virus Res. 1985 Sep;3(2):101–114. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh M. K., Fuller-Pace F. V., Buchmeier M. J., Southern P. J. Analysis of the genomic L RNA segment from lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):448–456. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90138-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Blount P., Oldstone M. B. Analysis of persistent virus infections by in situ hybridization to whole-mouse sections. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):555–558. doi: 10.1038/312555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Singh M. K., Riviere Y., Jacoby D. R., Buchmeier M. J., Oldstone M. B. Molecular characterization of the genomic S RNA segment from lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90323-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Levis R., Schlesinger S. Evolution of virus and defective-interfering RNAs in BHK cells persistently infected with Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):676–684. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.676-684.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Jr, Buchmeier M. J. Protein analysis of defective interfering lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus and persistently infected cells. Virology. 1979 Jul 30;96(2):503–515. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Prevention of virus-induced cerebellar diseases by defective-interfering lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Infect Dis. 1977 Sep;136(3):391–399. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.3.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., O'Connell C. M., Pfau C. J. Properties of defective lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1972 Dec;17(3):355–359. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-17-3-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Oldstone M. B. Inhibition of immunologic injury of cultured cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus: role of defective interfering virus in regulating viral antigenic expression. J Exp Med. 1977 Jun 1;145(6):1449–1468. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.6.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Pfau C. J. Determinants of lymphocytic choriomeningitis interference. J Gen Virol. 1972 Feb;14(2):177–187. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-14-2-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Zeijst B. A., Bleumink N., Crawford L. V., Swyryd E. A., Stark G. R. Viral proteins and RNAs in BHK cells persistently infected by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):262–270. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.262-270.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]