Abstract
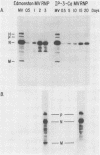
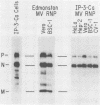
A measles virus (MV) genome originally derived from brain cells of a subacute sclerosing panencephalitis patient expressed in IP-3-Ca cells an unstable MV matrix protein and was unable to produce virus particles. Transfection of this MV genome into other cell lines did not relieve these defects, showing that they are ultimately encoded by viral mutations. However, these defects were partially relieved in a weakly infectious virus which emerged from IP-3-Ca cells and which produced a matrix protein of intermediate stability. The sequences of several cDNAs related to the unstable and intermediately stable matrix proteins showed many differences in comparison with a stable matrix protein sequence and even appreciable heterogeneity among themselves. Nevertheless, partial restoration of matrix protein stability could be ascribed to a single additional amino acid change. From an examination of additional genes, we estimated that, on average, each MV genome in IP-3-Ca cells differs from the others in 30 to 40 of its 16,000 bases. The role of extreme variability of RNA virus genomes in persistent viral infections is discussed in the context of the pathogenesis of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis and of other human diseases of suspected viral etiology.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alkhatib G., Briedis D. J. The predicted primary structure of the measles virus hemagglutinin. Virology. 1986 Apr 30;150(2):479–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baczko K., Carter M. J., Billeter M., ter Meulen V. Measles virus gene expression in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Virus Res. 1984 Oct;1(7):585–595. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90015-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baczko K., Liebert U. G., Billeter M., Cattaneo R., Budka H., ter Meulen V. Expression of defective measles virus genes in brain tissues of patients with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):472–478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.472-478.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K. Transcription and replication of rhabdoviruses. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):66–87. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.66-87.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellini W. J., Englund G., Richardson C. D., Rozenblatt S., Lazzarini R. A. Matrix genes of measles virus and canine distemper virus: cloning, nucleotide sequences, and deduced amino acid sequences. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):408–416. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.408-416.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellini W. J., Englund G., Rozenblatt S., Arnheiter H., Richardson C. D. Measles virus P gene codes for two proteins. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):908–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.908-919.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billeter M. A., Baczko K., Schmid A., Ter Meulen V. Cloning of DNA corresponding to four different measles virus genomic regions. Virology. 1984 Jan 15;132(1):147–159. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90099-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brain P., Gordon J., Willetts W. A. Rosette formation by peripheral lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):681–688. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstein T., Jacobsen L. B., Zeman W., Chen T. T. Persistent infection of BSC-1 cells by defective measles virus derived from subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1378–1382. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1378-1382.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrigan D. R., Kabacoff C. M. Identification of a nonproductive, cell-associated form of measles virus by its resistance to inhibition by recombinant human interferon. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1919–1926. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1919-1926.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter M. J., Willcocks M. M., ter Meulen V. Defective translation of measles virus matrix protein in a subacute sclerosing panencephalitis cell line. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):153–155. doi: 10.1038/305153a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Rebmann G., Baczko K., ter Meulen V., Billeter M. A. Altered ratios of measles virus transcripts in diseased human brains. Virology. 1987 Oct;160(2):523–526. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Rebmann G., Schmid A., Baczko K., ter Meulen V., Billeter M. A. Altered transcription of a defective measles virus genome derived from a diseased human brain. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):681–688. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04808.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Schmid A., Rebmann G., Baczko K., Ter Meulen V., Bellini W. J., Rozenblatt S., Billeter M. A. Accumulated measles virus mutations in a case of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis: interrupted matrix protein reading frame and transcription alteration. Virology. 1986 Oct 15;154(1):97–107. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90433-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingo E., Martínez-Salas E., Sobrino F., de la Torre J. C., Portela A., Ortín J., López-Galindez C., Pérez-Breña P., Villanueva N., Nájera R. The quasispecies (extremely heterogeneous) nature of viral RNA genome populations: biological relevance--a review. Gene. 1985;40(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingo E., Sabo D., Taniguchi T., Weissmann C. Nucleotide sequence heterogeneity of an RNA phage population. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):735–744. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörries R., ter Meulen V. Specificity of IgM antibodies in acute human coxsackievirus B infections, analysed by indirect solid phase enzyme immunoassay and immunoblot technique. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jan;64(Pt 1):159–167. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-1-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B. Antiviral antibody reacting on the plasma membrane alters measles virus expression inside the cell. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):529–530. doi: 10.1038/279529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna Y., Lenard J. Sequence alterations in temperature-sensitive M-protein mutants (complementation group III) of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):655–659. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.655-659.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Rigby P. W., Lane D. P. Negative regulation of viral enhancers in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. W., Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Measles and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis virus proteins: lack of antibodies to the M protein in patients with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):2047–2051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.2047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Grabau E. A., Jones C. L., Semler B. L. Evolution of multiple genome mutations during long-term persistent infection by vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):495–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J., Spindler K., Horodyski F., Grabau E., Nichol S., VandePol S. Rapid evolution of RNA genomes. Science. 1982 Mar 26;215(4540):1577–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.7041255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju G., Udem S., Rager-Zisman B., Bloom B. R. Isolation of a heterogeneous population of temperature-sensitive mutants of measles virus from persistently infected human lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1637–1652. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., Vanderoef R., Lenard J. Phenotypic revertants of temperature-sensitive M protein mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus: sequence analysis and functional characterization. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):256–263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.256-263.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Kristensson K., Brzosko W. J., Kapsenberg J. G. Measles virus matrix protein detected by immune fluorescence with monoclonal antibodies in the brain of patients with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):337–340. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.337-340.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeples M. E., Bratt M. A. Mutation in the matrix protein of Newcastle disease virus can result in decreased fusion glycoprotein incorporation into particles and decreased infectivity. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):81–90. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.81-90.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rammohan K. W., McFarland H. F., McFarlin D. E. Induction of subacute murine measles encephalitis by monoclonal antibody to virus haemagglutinin. Nature. 1981 Apr 16;290(5807):588–589. doi: 10.1038/290588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C., Hull D., Greer P., Hasel K., Berkovich A., Englund G., Bellini W., Rima B., Lazzarini R. The nucleotide sequence of the mRNA encoding the fusion protein of measles virus (Edmonston strain): a comparison of fusion proteins from several different paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):508–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90212-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux L., Beffy P., Portner A. Restriction of cell surface expression of Sendai virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein correlates with its higher instability in persistently and standard plus defective interfering virus infected BHK-21 cells. Virology. 1984 Oct 15;138(1):118–128. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux L., Waldvogel F. A. Instability of the viral M protein in BHK-21 cells persistently infected with Sendai virus. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):293–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90347-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands K., Grabau E., Spindler K., Jones C., Semler B., Holland J. Virus protein changes and RNA termini alterations evolving during persistent infection. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):871–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90078-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenblatt S., Eizenberg O., Ben-Levy R., Lavie V., Bellini W. J. Sequence homology within the morbilliviruses. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):684–690. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.684-690.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenblatt S., Koch T., Pinhasi O., Bratosin S. Infective substructures of measles virus from acutely and persistently infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):329–333. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.329-333.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozhon E. J., Kratochvil J. D., Lipton H. L. Analysis of genetic variation in Theiler's virus during persistent infection in the mouse central nervous system. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):16–32. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90315-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozhon E. J., Wilson A. K., Jubelt B. Characterization of genetic changes occurring in attenuated poliovirus 2 during persistent infection in mouse central nervous systems. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):137–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.137-144.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid A., Cattaneo R., Billeter M. A. A procedure for selective full length cDNA cloning of specific RNA species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):3987–3996. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.3987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard R. D., Raine C. S., Bornstein M. B., Udem S. A. Measles virus matrix protein synthesized in a subacute sclerosing panencephalitis cell line. Science. 1985 Jun 7;228(4704):1219–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.4001938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard R. D., Raine C. S., Bornstein M. B., Udem S. A. Rapid degradation restricts measles virus matrix protein expression in a subacute sclerosing panencephalitis cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7913–7917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobrino F., Dávila M., Ortín J., Domingo E. Multiple genetic variants arise in the course of replication of foot-and-mouth disease virus in cell culture. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):310–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90258-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhauer D. A., Holland J. J. Direct method for quantitation of extreme polymerase error frequencies at selected single base sites in viral RNA. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):219–228. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.219-228.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udem S. A., Cook K. A. Isolation and characterization of measles virus intracellular nucleocapsid RNA. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):57–65. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.57-65.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udem S. A. Measles virus: conditions for the propagation and purification of infectious virus in high yield. J Virol Methods. 1984 Feb;8(1-2):123–136. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(84)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler S. L., Meissner H. C. Measles and SSPE viruses: similarities and differences. Prog Med Virol. 1982;28:65–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young K. K., Heineke B. E., Wechsler S. L. M protein instability and lack of H protein processing associated with nonproductive persistent infection of HeLa cells by measles virus. Virology. 1985 Jun;143(2):536–545. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90392-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]