Abstract
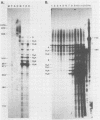
Using quantitative RNase protection assays, we have monitored the appearance of mRNAs generated during lytic infection of tightly synchronized murine cells by the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice. Our results demonstrate that transcripts from the P4 promoter can be detected prior to those from the P39 promoter, providing direct evidence for a temporal order of expression between the two parvovirus promoters.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astell C. R., Gardiner E. M., Tattersall P. DNA sequence of the lymphotropic variant of minute virus of mice, MVM(i), and comparison with the DNA sequence of the fibrotropic prototype strain. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):656–669. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.656-669.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Thomson M., Merchlinsky M., Ward D. C. The complete DNA sequence of minute virus of mice, an autonomous parvovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 25;11(4):999–1018. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.4.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Asher E., Aloni Y. Transcription of minute virus of mice, an autonomous parvovirus, may be regulated by attenuation. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):266–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.266-276.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter B. J., Rose J. A. Transcription in vivo of a defective parvovirus: sedimentation and electrophoretic analysis of RNA synthesized by adenovirus-associated virus and its helper adenovirus. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):182–199. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90253-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens K. E., Pintel D. Minute virus of mice (MVM) mRNAs predominantly polyadenylate at a single site. Virology. 1987 Oct;160(2):511–514. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Sturzenbecker L. J., Tattersall P. The autonomous parvovirus MVM encodes two nonstructural proteins in addition to its capsid polypeptides. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. Organization of nonstructural genes of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):724–732. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.724-732.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. The autonomously replicating parvoviruses of vertebrates. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:91–174. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. H., Milbrandt J. D., Greisen K. S., Hamlin J. L. Cloning of the initiation region of a mammalian chromosomal replicon. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):439–441. doi: 10.1038/302439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongeneel C. V., Sahli R., McMaster G. K., Hirt B. A precise map of splice junctions in the mRNAs of minute virus of mice, an autonomous parvovirus. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):564–573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.564-573.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labieniec-Pintel L., Pintel D. The minute virus of mice P39 transcription unit can encode both capsid proteins. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1163–1167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1163-1167.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labow M. A., Hermonat P. L., Berns K. I. Positive and negative autoregulation of the adeno-associated virus type 2 genome. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):251–258. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.251-258.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitor T. W., Joo H. S., Collett M. S. Identification and characterization of a porcine parvovirus nonstructural polypeptide. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):554–559. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.554-559.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. R., Ward D. C. Three splicing patterns are used to excise the small intron common to all minute virus of mice RNAs. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1170–1174. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1170-1174.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrali-Noy G., Spadari S., Miller-Faurès A., Miller A. O., Kruppa J., Koch G. Synchronization of HeLa cell cultures by inhibition of DNA polymerase alpha with aphidicolin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):377–387. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintel D., Dadachanji D., Astell C. R., Ward D. C. The genome of minute virus of mice, an autonomous parvovirus, encodes two overlapping transcription units. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 25;11(4):1019–1038. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.4.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd Replication process of the parvovirus H-1. I. Kinetics in a parasynchronous cell system. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):856–861. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.856-861.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd trans-Activation of parvovirus P38 promoter by the 76K noncapsid protein. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):886–889. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.886-889.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlehofer J. R., Heilbronn R., Georg-Fries B., zur Hausen H. Inhibition of initiator-induced SV40 gene amplification in SV40-transformed Chinese hamster cells by infection with a defective parvovirus. Int J Cancer. 1983 Nov 15;32(5):591–595. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910320512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl G., Gautschi M. The multiplication of parvovirus Lu3 in a synchronized culture system. I. Optimum conditions for virus replication. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;40(1):105–118. doi: 10.1007/BF01242642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P. Replication of the parvovirus MVM. I. Dependence of virus multiplication and plaque formation on cell growth. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):586–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.586-590.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennant R. W., Layman K. R., Hand R. E. Effect of cell physiological state on infection by rat virus. J Virol. 1969 Dec;4(6):872–878. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.6.872-878.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tratschin J. D., Tal J., Carter B. J. Negative and positive regulation in trans of gene expression from adeno-associated virus vectors in mammalian cells by a viral rep gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2884–2894. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakobson B., Koch T., Winocour E. Replication of adeno-associated virus in synchronized cells without the addition of a helper virus. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):972–981. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.972-981.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]