Abstract
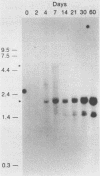
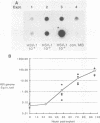
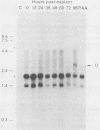
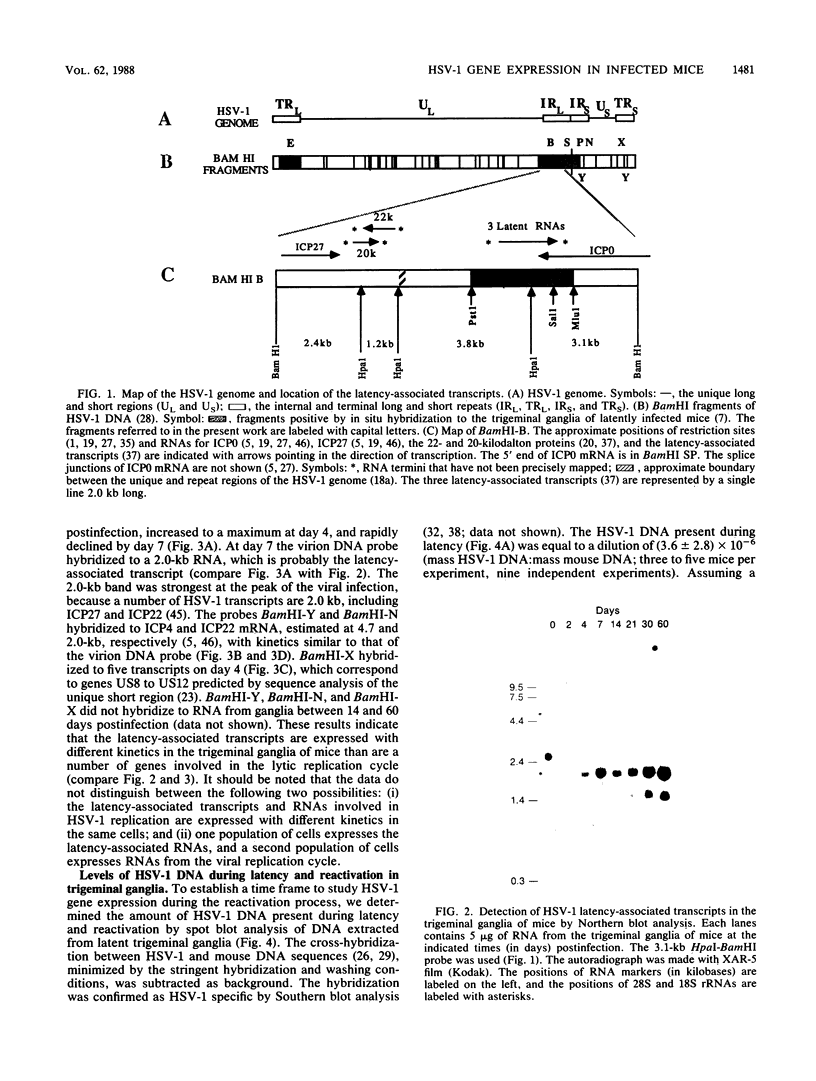
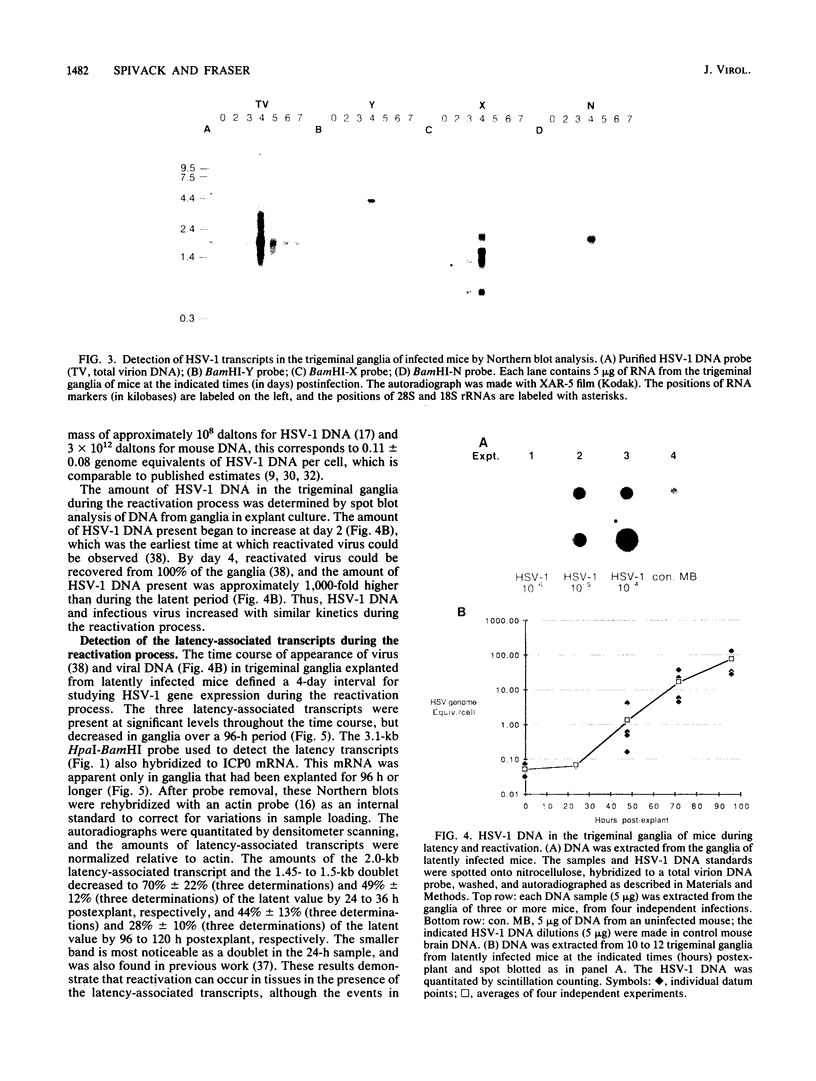
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) establishes a latent infection in the trigeminal ganglia of mice infected via the eye. In these ganglia three viral transcripts, of 2.0, 1.5, and 1.45 kilobases (kb), which are at least partially colinear, have been identified by Northern (RNA) blot analysis. These RNAs partially overlap ICPO, but are transcribed in the opposite direction (J. G. Spivack and N. W. Fraser, J. Virol. 61:3841-3847, 1987). The accumulation of these latency-associated transcripts, as well as other viral RNAs, was studied during an acute infection and the reactivation of a latent HSV-1 infection in mice. The 2.0-kb latency-associated transcript was detected in trigeminal ganglia of mice as early as 4 days postinfection, and the 1.45- and 1.5-kb RNA doublet was detected at 14 days postinfection. The levels of these latency-associated transcripts increased steadily over a 60-day period. In contrast, other HSV-1 transcripts were detected at 2 to 3 days postinfection, reached a peak on day 4, and rapidly declined below detectable levels by day 7. The data indicate that the temporal expression of the latency-associated genes during acute infection in the trigeminal ganglia of mice is different from the temporal expression of genes involved in HSV-1 replication. During the reactivation of latent HSV-1 from explanted trigeminal ganglia, the latency-associated RNAs decreased about twofold, but were present at significant levels even after HSV-1 DNA increased and infectious virus was recovered. The decrease of the latency-associated transcripts occurred when reactivation was blocked by phosphonoacetic acid or novobiocin, which suggests that this decrease may be an early event in the entry of latent HSV-1 into the viral replication cycle.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker Y., Hadar J., Tabor E., Ben-Hur T., Raibstein I., Rösen A., Darai G. A sequence in HpaI-P fragment of herpes simplex virus-1 DNA determines intraperitoneal virulence in mice. Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):255–259. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. S., Ward D. C., Prusoff W. H. Specific herpes simplex virus-induced incorporation of 5-iodo-5'-amino-2',5'-dideoxyuridine into deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 25;251(16):4833–4838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., McLauchlan J., McGeoch D. J. Orientation of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early mRNA's. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 11;7(1):77–91. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook M. L., Bastone V. B., Stevens J. G. Evidence that neurons harbor latent herpes simplex virus. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):946–951. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.946-951.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deatly A. M., Spivack J. G., Lavi E., Fraser N. W. RNA from an immediate early region of the type 1 herpes simplex virus genome is present in the trigeminal ganglia of latently infected mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3204–3208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deatly A. M., Spivack J. G., Lavi E., O'Boyle D. R., 2nd, Fraser N. W. Latent herpes simplex virus type 1 transcripts in peripheral and central nervous system tissues of mice map to similar regions of the viral genome. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):749–756. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.749-756.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstathiou S., Minson A. C., Field H. J., Anderson J. R., Wildy P. Detection of herpes simplex virus-specific DNA sequences in latently infected mice and in humans. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):446–455. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.446-455.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., Fenoglio C. M., McDougall J. K. Limited transcription of the herpes simplex virus genome when latent in human sensory ganglia. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):686–691. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.686-691.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., Fenoglio C., Shevchuk M., McDougall J. K. Detection of herpes simplex RNA in human sensory ganglia. Virology. 1979 May;95(1):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90429-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalili K., Salas C., Weinmann R. Isolation and characterization of human actin genes cloned in phage lambda vectors. Gene. 1983 Jan-Feb;21(1-2):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90142-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieff E. D., Bachenheimer S. L., Roizman B. Size, composition, and structure of the deoxyribonucleic acid of herpes simplex virus subtypes 1 and 2. J Virol. 1971 Aug;8(2):125–132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.2.125-132.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knotts F. B., Cook M. L., Stevens J. G. Pathogenesis of herpetic encephalitis in mice after ophthalmic inoculation. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jul;130(1):16–27. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch H. G., Rösen A., Ernst F., Becker Y., Darai G. Determination of the nucleotide sequence flanking the deletion (0.762 to 0.789 map units) in the genome of an intraperitoneally avirulent HSV-1 strain HFEM. Virus Res. 1987 Apr;7(2):105–115. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean A. R., Brown S. M. A herpes simplex virus type 1 variant which fails to synthesize immediate early polypeptide VmwIE63. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1339–1350. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: transcription-initiation sites and domains of alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7122–7126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Robishaw E. E., Overby L. R. Inhibition of DNA polymerase from herpes simplex virus-infected wi-38 cells by phosphonoacetic Acid. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1281–1283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1281-1283.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Rixon F. J. Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan J. L., Darby G. Herpes simplex virus latency: the cellular location of virus in dorsal root ganglia and the fate of the infected cell following virus activation. J Gen Virol. 1980 Dec;51(Pt 2):233–243. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-51-2-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K., Mounts P., Hayward G. S. Homology between mammalian cell DNA sequences and human herpesvirus genomes detected by a hybridization procedure with high-complexity probe. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90406-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. J., Rixon F. J., Everett R. D., Frame M. C., McGeoch D. J. Characterization of the IE110 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2365–2380. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Conley A. J., Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Cloning of reiterated and nonreiterated herpes simplex virus 1 sequences as BamHI fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4201–4205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puga A., Cantin E. M., Notkins A. L. Homology between murine and human cellular DNA sequences and the terminal repetition of the S component of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90407-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puga A., Rosenthal J. D., Openshaw H., Notkins A. L. Herpes simplex virus DNA and mRNA sequences in acutely and chronically infected trigeminal ganglia of mice. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):102–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon F. J., McGeoch D. J. Detailed analysis of the mRNAs mapping in the short unique region of herpes simplex virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):953–973. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock D. L., Fraser N. W. Detection of HSV-1 genome in central nervous system of latently infected mice. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):523–525. doi: 10.1038/302523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock D. L., Nesburn A. B., Ghiasi H., Ong J., Lewis T. L., Lokensgard J. R., Wechsler S. L. Detection of latency-related viral RNAs in trigeminal ganglia of rabbits latently infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3820–3826. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3820-3826.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Greene C. C., Aschman D. P., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 is an essential regulatory protein. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):796–805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.796-805.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekizawa T., Openshaw H., Wohlenberg C., Notkins A. L. Latency of herpes simplex virus in absence of neutralizing antibody: model for reactivation. Science. 1980 Nov 28;210(4473):1026–1028. doi: 10.1126/science.6254149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivack J. G., Fraser N. W. Detection of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcripts during latent infection in mice. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3841–3847. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3841-3847.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivack J. G., O'Boyle D. R., 2nd, Fraser N. W. Novobiocin and coumermycin A1 inhibit viral replication and the reactivation of herpes simplex virus type 1 from the trigeminal ganglia of latently infected mice. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3288–3291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3288-3291.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivack J. G., Prusoff W. H., Tritton T. R. Dissociation of the inhibitory effects of 2-deoxy-D-glucose on Vero cell growth and the replication of herpes simplex virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):284–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivack J. G., Prusoff W. H., Tritton T. R. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus replication by methyl daunosamine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jul;22(1):176–179. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K., Devi-Rao G. B., Cook M. L., Feldman L. T. RNA complementary to a herpesvirus alpha gene mRNA is prominent in latently infected neurons. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2434993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroop W. G., Rock D. L., Fraser N. W. Localization of herpes simplex virus in the trigeminal and olfactory systems of the mouse central nervous system during acute and latent infections by in situ hybridization. Lab Invest. 1984 Jul;51(1):27–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenser R. B., Dawson M., Ressel S. J., Dunstan M. E. Detection of herpes simplex virus mRNA in latently infected trigeminal ganglion neurons by in situ hybridization. Ann Neurol. 1982 Mar;11(3):285–291. doi: 10.1002/ana.410110309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Preston C. M., Clements J. B. Separation and characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early mRNA's. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):42–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.42-52.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]