Abstract
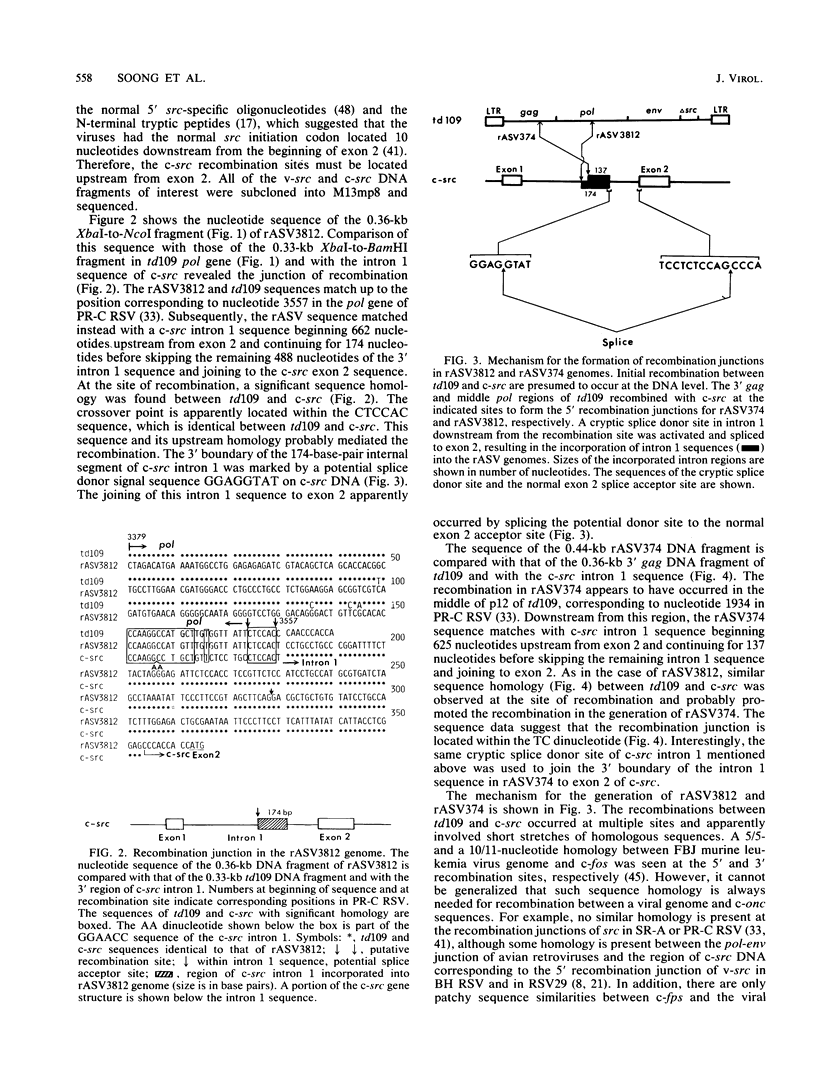
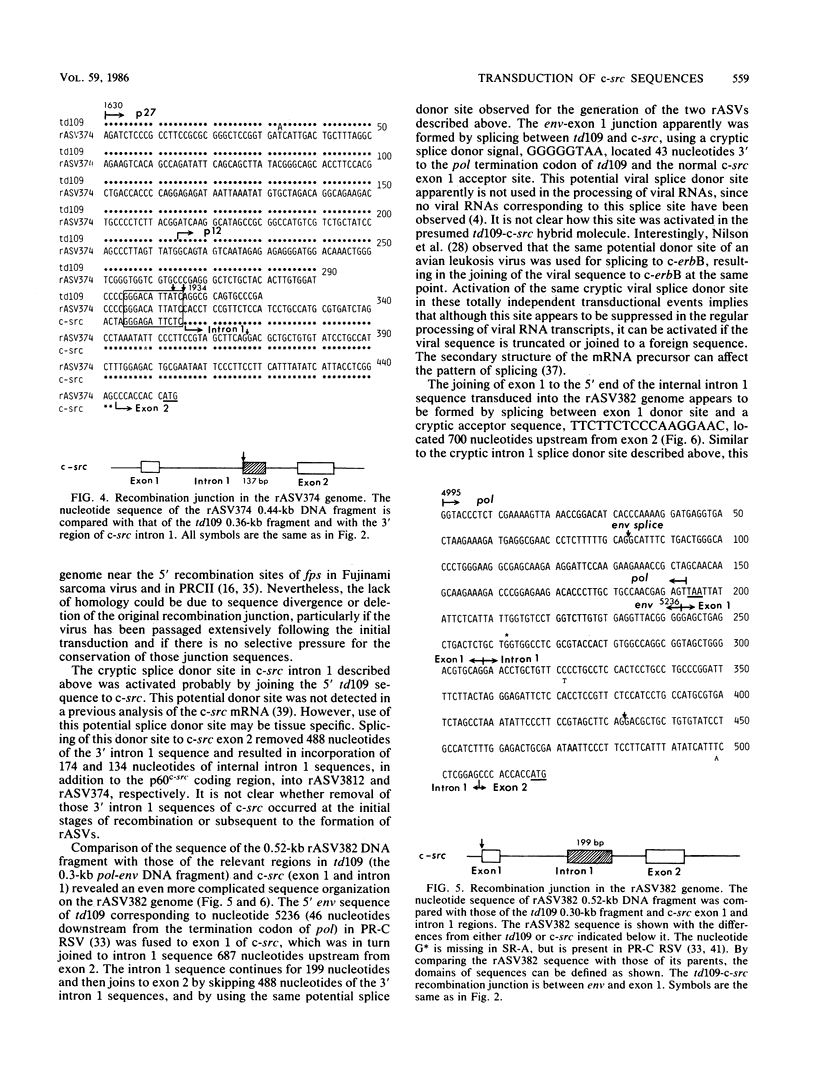
The mechanism of cellular src (c-src) transduction by a transformation-defective deletion mutant, td109, of Rous sarcoma virus was studied by sequence analysis of the recombinational junctions in three td109-derived recovered sarcoma viruses (rASVs). Our results show that two rASVs have been generated by recombination between td109 and c-src at the region between exons 1 and 2 defined previously. Significant homology between td109 and c-src sequences was present at the sites of recombination. The viral and c-src sequence junction of the third rASV was formed by splicing a cryptic donor site at the 5' region of env of td109 to exon 1 of c-src. Various lengths of c-src internal intron 1 sequences were incorporated into all three rASV genomes, which resulted from activation of potential splice donor and acceptor sites. The incorporated intron 1 sequences were absent in the c-src mRNA, excluding its being the precursor for recombination with td109 and implying that initial recombinations most likely took place at the DNA level. A potential splice acceptor site within the incorporated intron 1 sequences in two rASVs was activated and was used for the src mRNA synthesis in infected cells. The normal env mRNA splice acceptor site was used for src mRNA synthesis for the third rASV.
Full text
PDF

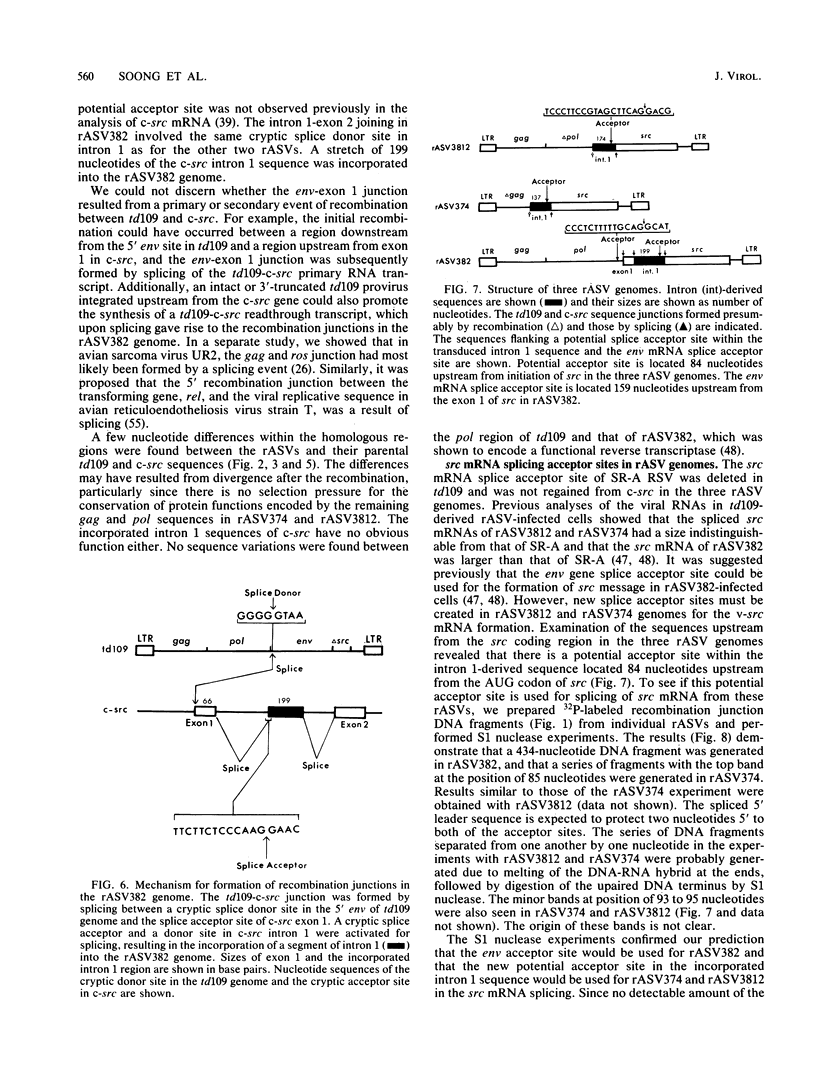


Images in this article
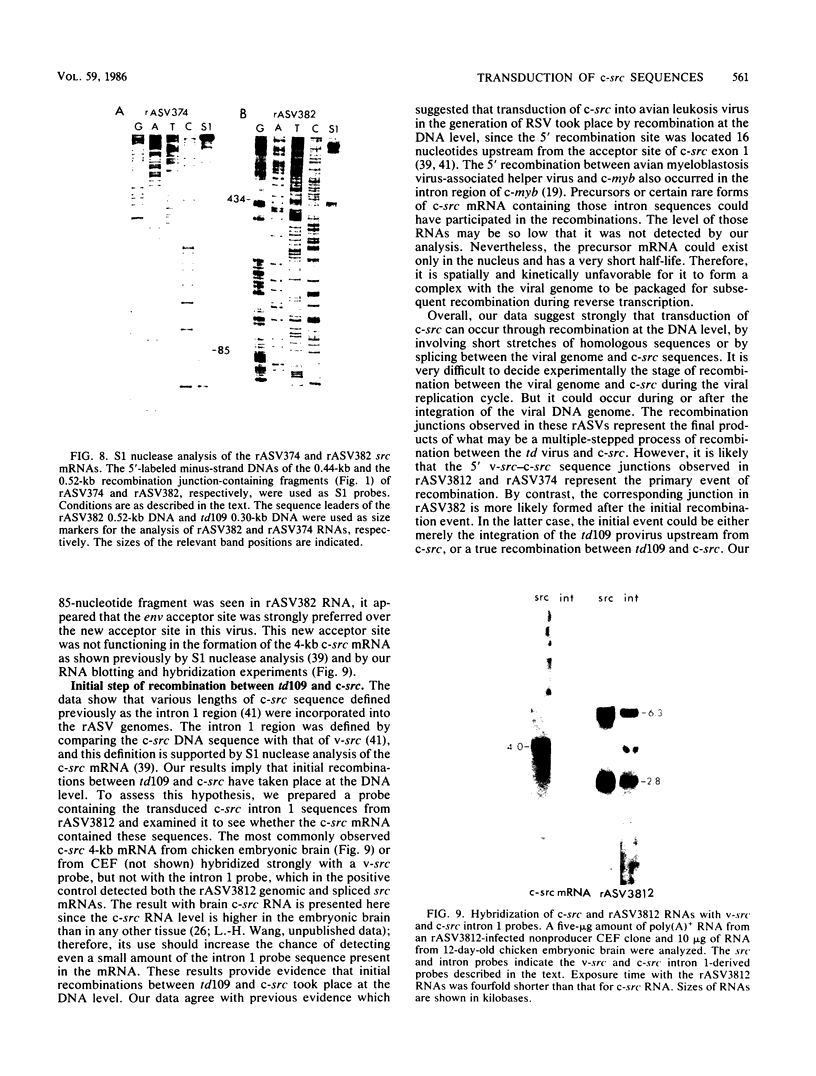
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breitbart R. E., Nguyen H. T., Medford R. M., Destree A. T., Mahdavi V., Nadal-Ginard B. Intricate combinatorial patterns of exon splicing generate multiple regulated troponin T isoforms from a single gene. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):67–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broome S., Gilbert W. Rous sarcoma virus encodes a transcriptional activator. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. J., Stoltzfus C. M. Cloning and nucleotide sequences of cDNAs spanning the splice junctions of Rous sarcoma virus mRNAs. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):969–972. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.969-972.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton P. C., Brugge J. S. Neural tissues express high levels of the cellular src gene product pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1157–1162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R., Kant J. A. Organization of the rat gamma-fibrinogen gene: alternative mRNA splice patterns produce the gamma A and gamma B (gamma ') chains of fibrinogen. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90415-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta A., Wang L. H., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Partial nucleotide sequence of Rous sarcoma virus-29 provides evidence that the original Rous sarcoma virus was replication defective. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):728–735. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.728-735.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Rogers J., Davis M., Calame K., Bond M., Wall R., Hood L. Two mRNAs can be produced from a single immunoglobulin mu gene by alternative RNA processing pathways. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90617-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enrietto P. J., Payne L. N., Wyke J. A. Analysis of the pathogenicity of transformation defective partial deletion mutants of avian sarcoma virus: characterization of recovered viruses which encode novel src specific proteins. Virology. 1983 Jun;127(2):397–411. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fradin A., Jove R., Hemenway C., Keiser H. D., Manley J. L., Prives C. Splicing pathways of SV40 mRNAs in X. laevis oocytes differ in their requirements for snRNPs. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):927–936. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90427-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern C. C., Hayward W. S., Hanafusa H. Characterization of some isolates of newly recovered avian sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):91–101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.91-101.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa H., Halpern C. C., Buchhagen D. L., Kawai S. Recovery of avian sarcoma virus from tumors induced by transformation-defective mutants. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1735–1747. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. C., Hammond C., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence and topography of chicken c-fps. Genesis of a retroviral oncogene encoding a tyrosine-specific protein kinase. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 20;181(2):175–186. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90083-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Hanafusa H. Viral and cellular src genes contribute to the structure of recovered avian sarcoma virus transforming protein. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90511-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Piatigorsky J. Alternative RNA splicing of the murine alpha A-crystallin gene: protein-coding information within an intron. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):707–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Bishop J. M. Transduction of c-myb into avian myeloblastosis virus: locating points of recombination within the cellular gene. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):565–572. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.565-572.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress M., Glaros D., Khoury G., Jay G. Alternative RNA splicing in expression of the H-2K gene. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):602–604. doi: 10.1038/306602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner T. L., Hanafusa H. DNA sequence of the Bryan high-titer strain of Rous sarcoma virus: extent of env deletion and possible genealogical relationship with other viral strains. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):549–556. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.549-556.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Muramatsu M., Ogata K. Alternative transcription and two modes of splicing results in two myosin light chains from one gene. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):333–338. doi: 10.1038/308333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckameyer W. S., Shibuya M., Hsu M. T., Wang L. H. Proto-oncogene c-ros codes for a molecule with structural features common to those of growth factor receptors and displays tissue specific and developmentally regulated expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1478–1486. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckameyer W. S., Wang L. H. Molecular cloning and characterization of avian sarcoma virus UR2 and comparison of its transforming sequence with those of other avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):914–921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.914-921.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Maroney P. A., Goodwin R. G., Rottman F. M., Crittenden L. B., Raines M. A., Kung H. J. c-erbB activation in ALV-induced erythroblastosis: novel RNA processing and promoter insertion result in expression of an amino-truncated EGF receptor. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):719–726. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvin J. D., Wang L. H. Mechanisms for the generation of src-deletion mutants and recovered sarcoma viruses: identification of viral sequences involved in src deletions and in recombination with c-src sequences. Virology. 1984 Oct 30;138(2):236–245. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G., Amara S. G., Evans R. M. Alternative RNA processing: determining neuronal phenotype. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1315–1320. doi: 10.1126/science.6089345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozek C. E., Davidson N. Drosophila has one myosin heavy-chain gene with three developmentally regulated transcripts. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):23–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90493-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Tizard R., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):853–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzbauer J. E., Tamkun J. W., Lemischka I. R., Hynes R. O. Three different fibronectin mRNAs arise by alternative splicing within the coding region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):421–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya M., Hanafusa H. Nucleotide sequence of Fujinami sarcoma virus: evolutionary relationship of its transforming gene with transforming genes of other sarcoma viruses. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):787–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya M., Wang L. H., Hanafusa H. Molecular cloning of the Fujinami sarcoma virus genome and its comparison with sequences of other related transforming viruses. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1007–1016. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1007-1016.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D. Alternative splicing caused by RNA secondary structure. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):667–676. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., Parker R. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Transduction of a cellular oncogene: the genesis of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2519–2523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Feldman R. A., Hanafusa H. DNA sequence of the viral and cellular src gene of chickens. 1. Complete nucleotide sequence of an EcoRI fragment of recovered avian sarcoma virus which codes for gp37 and pp60src. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):1–11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.1-11.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H. Structure and sequence of the cellular gene homologous to the RSV src gene and the mechanism for generating the transforming virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Curran T., Müller R., Verma I. M. Analysis of FBJ-MuSV provirus and c-fos (mouse) gene reveals that viral and cellular fos gene products have different carboxy termini. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1241–1255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne R., Breitman M. L., Moscovici C., Vogt P. K. Restitution of fibroblast-transforming ability in src deletion mutants of avian sarcoma virus during animal passage. Virology. 1979 Mar;93(2):413–426. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90245-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Beckson M., Anderson S. M., Hanafusa H. Identification of the viral sequence required for the generation of recovered avian sarcoma viruses and characterization of a series of replication-defective recovered avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):881–891. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.881-891.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H. Deletion in the 3' pol sequence correlates with aberration of RNA expression in certain replication-defective avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):446–459. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.446-459.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Duesberg P. Properties and location of poly(A) in Rous sarcoma virus RNA. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1515–1529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1515-1529.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Edelstein B., Mayer B. J. Induction of tumors and generation of recovered sarcoma viruses by, and mapping of deletions in, two molecularly cloned src deletion mutants. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):904–913. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.904-913.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Feldman R., Shibuya M., Hanafusa H., Notter M. F., Balduzzi P. C. Genetic structure, transforming sequence, and gene product of avian sarcoma virus UR1. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):258–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.258-267.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Halpern C. C., Nadel M., Hanafusa H. Recombination between viral and cellular sequences generates transforming sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5812–5816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Moscovici C., Karess R. E., Hanafusa H. Analysis of the src gene of sarcoma viruses generated by recombination between transformation-defective mutants and quail cellular sequences. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):546–556. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.546-556.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Snyder P., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Evidence for the common origin of viral and cellular sequences involved in sarcomagenic transformation. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):52–64. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.52-64.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsen K. C., Eggleton K., Temin H. M. Nucleic acid sequences of the oncogene v-rel in reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T and its cellular homolog, the proto-oncogene c-rel. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):172–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.172-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Hagenbüchle O., Schibler U. A single mouse alpha-amylase gene specifies two different tissue-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Ginder G. D., Felsenfeld G. A new method for the purification and identification of covalently closed circular DNA molcules. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Apr;5(4):1139–1152. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.4.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Ferra F., Engh H., Hudson L., Kamholz J., Puckett C., Molineaux S., Lazzarini R. A. Alternative splicing accounts for the four forms of myelin basic protein. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):721–727. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90245-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]