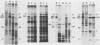Abstract
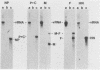
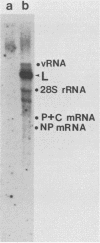
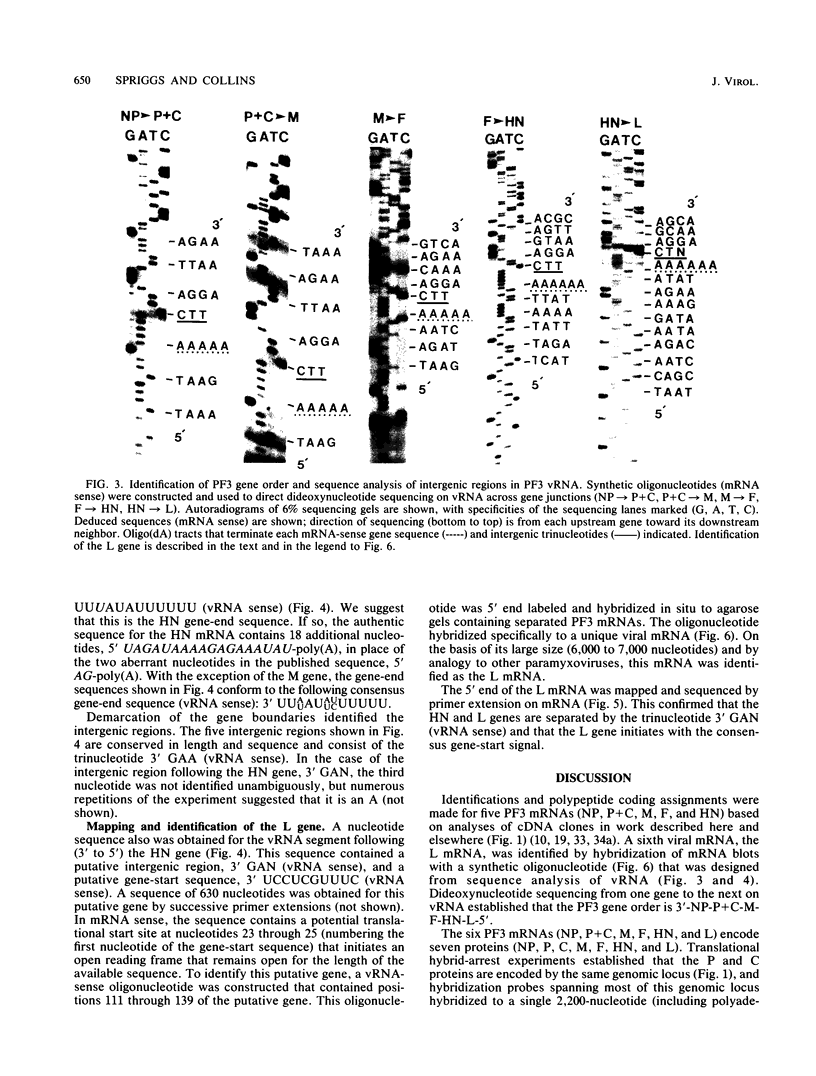
cDNA clones of mRNAs for the major nucleocapsid protein (NP), the nucleocapsid P protein plus the nonstructural C protein (P+C), and the matrix protein (M) of human parainfluenza virus type 3 (PF3) were identified by hybrid arrest and hybrid selection of in vitro translation. Previously, cDNA clones were identified and sequenced for the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein (HN) and the fusion glycoprotein (F) mRNAs (N. Elango, J. E. Coligan, R. C. Jambou, and S. Venkatesan, J. Virol. 57:481-489, 1986; M. K. Spriggs, R. A. Olmsted, S. Venkatesan, J. E. Coligan, and P. L. Collins, Virology 152:241-251, 1986). Synthetic oligonucleotides, designed from nucleotide sequences of the cDNAs, were used to direct dideoxynucleotide sequencing of gene junctions in PF3 genomic RNA (vRNA). From sequencing of vRNA, a sixth viral gene was detected and identified as the large nucleocapsid protein (L) gene by hybridization of a synthetic oligonucleotide to intracellular PF3 mRNAs separated by gel electrophoresis. The order of the six PF3 genes on vRNA was 3'-NP-P+C-M-F-HN-L-5'. The five intergenic regions consisted of the trinucleotide 3'-GAA. The PF3 genes initiated with semiconserved 10-nucleotide gene-start sequences and terminated with semiconserved 12-nucleotide gene-end sequences. The M gene terminated with an aberrant gene-end sequence; analysis of intracellular mRNA showed that this aberrant sequence correlated with a disproportionately high accumulation of readthrough mRNA. These studies showed that PF3 encodes six unique mRNAs (NP, P+C, M, F, HN, and L) that encode seven proteins (NP, P, C, M, F, HN, and L) and provided evidence of a close relationship between PF3 and Sendai (murine parainfluenza type 1) viruses.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett T., Shrimpton S. B., Russell S. E. Nucleotide sequence of the entire protein coding region of canine distemper virus polymerase-associated (P) protein mRNA. Virus Res. 1985 Nov;3(4):367–372. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90436-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellini W. J., Englund G., Rozenblatt S., Arnheiter H., Richardson C. D. Measles virus P gene codes for two proteins. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):908–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.908-919.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B., Giorgi C., Roux L., Raju R., Dowling P., Chollet A., Kolakofsky D. Sequence determination of the Sendai virus HN gene and its comparison to the influenza virus glycoproteins. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Hightower L. E., Ball L. A. Transcriptional map for Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):682–693. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.682-693.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Huang Y. T., Wertz G. W. Identification of a tenth mRNA of respiratory syncytial virus and assignment of polypeptides to the 10 viral genes. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):572–578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.572-578.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Wertz G. W., Ball L. A., Hightower L. E. Coding assignments of the five smaller mRNAs of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1024–1031. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1024-1031.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Wertz G. W. cDNA cloning and transcriptional mapping of nine polyadenylylated RNAs encoded by the genome of human respiratory syncytial virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3208–3212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling P. C., Giorgi C., Roux L., Dethlefsen L. A., Galantowicz M. E., Blumberg B. M., Kolakofsky D. Molecular cloning of the 3'-proximal third of Sendai virus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5213–5216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elango N., Coligan J. E., Jambou R. C., Venkatesan S. Human parainfluenza type 3 virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein: nucleotide sequence of mRNA and limited amino acid sequence of the purified protein. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):481–489. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.481-489.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi C., Blumberg B. M., Kolakofsky D. Sendai virus contains overlapping genes expressed from a single mRNA. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta K. C., Kingsbury D. W. Complete sequences of the intergenic and mRNA start signals in the Sendai virus genome: homologies with the genome of vesicular stomatitis virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3829–3841. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta K. C., Kingsbury D. W. Conserved polyadenylation signals in two negative-strand RNA virus families. Virology. 1982 Jul 30;120(2):518–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta K. C., Kingsbury D. W. Polytranscripts of Sendai virus do not contain intervening polyadenylate sequences. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):102–109. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90186-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. W., Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. The polypeptides of canine distemper virus: synthesis in infected cells and relatedness to the polypeptides of other morbilliviruses. Virology. 1980 Jan 30;100(2):433–449. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90534-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrler G., Compans R. W. Synthesis of mumps virus polypeptides in infected Vero cells. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):430–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Paterson R. G., Lamb R. A. Identification and predicted sequence of a previously unrecognized small hydrophobic protein, SH, of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):744–751. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.744-751.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C. H., Re G. G., Gupta K. C., Portner A., Kingsbury D. W. Expression of Sendai virus defective-interfering genomes with internal deletions. Virology. 1985 Oct 15;146(1):38–49. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jambou R. C., Elango N., Venkatesan S. Proteins associated with human parainfluenza virus type 3. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):298–302. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.298-302.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Determination by peptide mapping of the unique polypeptides in Sendai virions and infected cells. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):469–478. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90263-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters P. S., Samuel C. E. Detection of in vivo synthesis of polycistronic mRNAs of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1984 Apr 30;134(2):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B. M., Roberts B. E., Kuff E. L. Structural gene identification and mapping by DNA-mRNA hybrid-arrested cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4370–4374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Harris T. J., Lamb R. A. Analysis and gene assignment of mRNAs of a paramyxovirus, simian virus 5. Virology. 1984 Oct 30;138(2):310–323. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90354-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Harris T. J., Lamb R. A. Fusion protein of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5: nucleotide sequence of mRNA predicts a highly hydrophobic glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6706–6710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Miller J. S., Roberts B. E. Purification and mapping of specific mRNAs by hybridization-selection and cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. D., Berkovich A., Rozenblatt S., Bellini W. J. Use of antibodies directed against synthetic peptides for identifying cDNA clones, establishing reading frames, and deducing the gene order of measles virus. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):186–193. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.186-193.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K. Complete intergenic and flanking gene sequences from the genome of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):415–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90515-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda T., Hidaka Y., Kanda T., Shibuta H., Nomoto A., Iwasaki K. Sequence of 3,687 nucleotides from the 3' end of Sendai virus genome RNA and the predicted amino acid sequences of viral NP, P and C proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7317–7330. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs M. K., Olmsted R. A., Venkatesan S., Coligan J. E., Collins P. L. Fusion glycoprotein of human parainfluenza virus type 3: nucleotide sequence of the gene, direct identification of the cleavage-activation site, and comparison with other paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90388-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey D. G., Dimock K., Kang C. Y. Structural characterization of virion proteins and genomic RNA of human parainfluenza virus 3. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):761–766. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.761-766.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez A., Banerjee A. K. Cloning and gene assignment of mRNAs of human parainfluenza virus 3. Virology. 1985 Nov;147(1):177–186. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90237-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez A., Banerjee A. K. Studies on human parainfluenza virus 3: characterization of the structural proteins and in vitro synthesized proteins coded by mRNAs isolated from infected cells. Virology. 1985 May;143(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90095-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao S. G., Brunk C. F., Pearlman R. E. Hybridization of nucleic acids directly in agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jun;131(2):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler S. L., Lambert D. M., Galinski M. S., Heineke B. E., Pons M. W. Human parainfluenza virus 3: purification and characterization of subviral components, viral proteins and viral RNA. Virus Res. 1985 Nov;3(4):339–351. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90434-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler S. L., Lambert D. M., Galinski M. S., Pons M. W. Intracellular synthesis of human parainfluenza type 3 virus-specified polypeptides. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):661–664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.661-664.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde A., Morrison T. Structural and functional characterization of Newcastle disease virus polycistronic RNA species. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):71–76. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.71-76.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]