Abstract
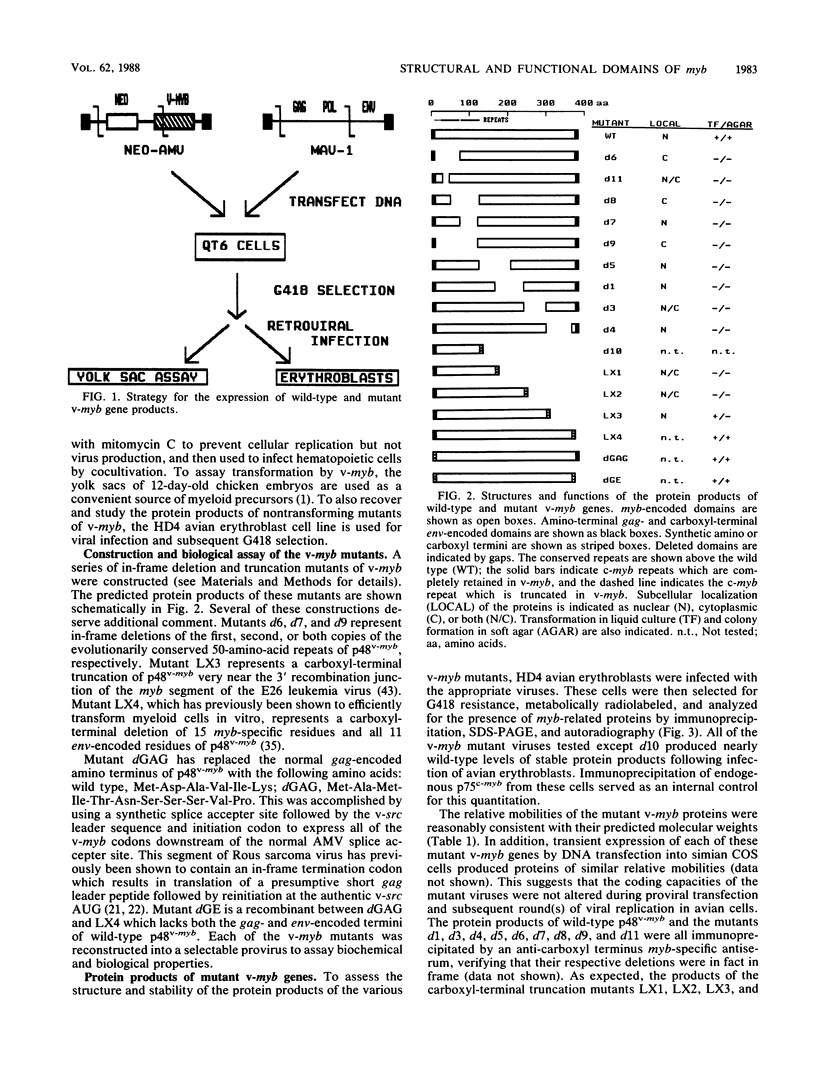
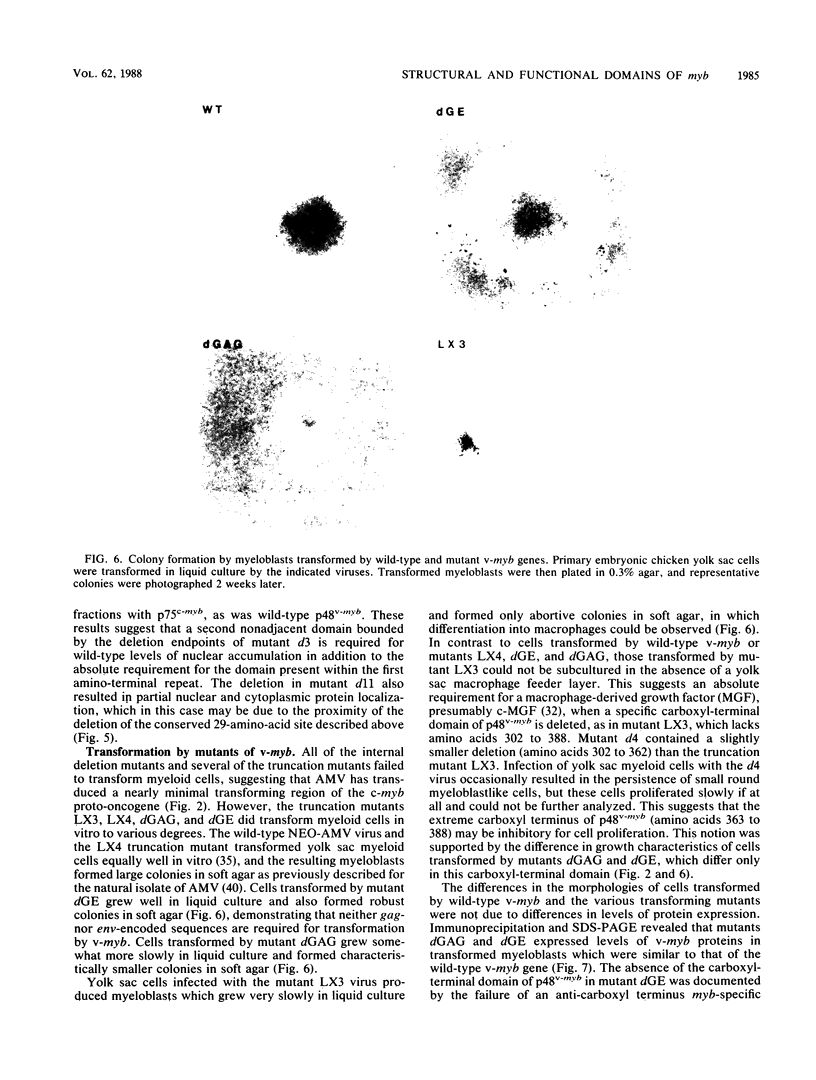
The v-myb oncogene of avian myeloblastosis virus causes acute myelomonocytic leukemia in vivo and transforms only myeloid cells in vitro. Its product, p48v-myb, is a nuclear protein of unknown function. To determine structure-function relationships for this protein, we constructed a series of deletion mutants of v-myb, expressed them in retroviral vectors, and studied their biochemical and biological properties. We used these mutants to identify two separate domains of p48v-myb which had distinct roles in its accumulation in the cell nucleus. We showed that the viral sequences which normally encode both termini of p48v-myb were dispensible for transformation. In contrast, both copies of the highly conserved v-myb amino-terminal repeat were required for transformation. We also identified a carboxyl-terminal domain of p48v-myb which was required for the growth of v-myb-transformed myeloblasts in soft agar but not for morphological transformation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALUDA M. A. Properties of cells infected with avian myeloblastosis virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:415–425. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann D. G., Souza L. M., Baluda M. A. Vertebrate DNAs contain nucleotide sequences related to the transforming gene of avian myeloblastosis virus. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):450–455. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.450-455.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Doederlein G., Freudenstein C., Graf T. Erythroblast cell lines transformed by a temperature-sensitive mutant of avian erythroblastosis virus: a model system to study erythroid differentiation in vitro. J Cell Physiol Suppl. 1982;1:195–207. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041130427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Hayman M. J., Graf T. Myeloblasts transformed by the avian acute leukemia virus E26 are hormone-dependent for growth and for the expression of a putative myb-containing protein, p135 E26. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1069–1073. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01298.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Leutz A., Kahn P., Graf T. Ts mutants of E26 leukemia virus allow transformed myeloblasts, but not erythroblasts or fibroblasts, to differentiate at the nonpermissive temperature. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):579–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90465-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Nunn M., Moscovici C., Perbal B., Baluda M., Duesberg P. H. Acute leukemia viruses E26 and avian myeloblastosis virus have related transformation-specific RNA sequences but different genetic structures, gene products, and oncogenic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3677–3681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boettiger D., Durban E. Target cells for avian myeloblastosis virus in embryonic yolk sac and relationship of cell differentiation to cell transformation. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):841–847. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.841-847.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Lampert M. A., Li A. C., Baluda M. A. Nuclear compartmentalization of the v-myb oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3017–3023. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Lampert M. A., Lipsick J. S., Baluda M. A. Avian myeloblastosis virus and E26 virus oncogene products are nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4265–4269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Lipsick J. S., Baluda M. A. Antibodies to the evolutionarily conserved amino-terminal region of the v-myb-encoded protein detect the c-myb protein in widely divergent metazoan species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4685–4689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Lipsick J. S., Reddy E. P., Baluda M. A. Identification of the leukemogenic protein of avian myeloblastosis virus and of its normal cellular homologue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2834–2838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbère-Garapin F., Horodniceanu F., Kourilsky P., Garapin A. C. A new dominant hybrid selective marker for higher eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Skalka A. M., Ju G. Endogenous avian retroviruses contain deficient promoter and leader sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2946–2950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Protein import into the cell nucleus. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:367–390. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. A., Shibuya M., Hanafusa H. Activation of the transformation potential of the cellular fps gene. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerondakis S., Bishop J. M. Structure of the protein encoded by the chicken proto-oncogene c-myb. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3677–3684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Gough N. M., Dunn A. R., de Blaquiere J. Nucleotide sequence of cDNA clones of the murine myb proto-oncogene. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2003–2008. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03884.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaney M. L., Pierce J., Parsons J. T. Site-directed mutagenesis of the gag-myc gene of avian myelocytomatosis virus 29: biological activity and intracellular localization of structurally altered proteins. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):167–176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.167-176.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Greenhouse J. J., Petropoulos C. J., Sutrave P. Adaptor plasmids simplify the insertion of foreign DNA into helper-independent retroviral vectors. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3004–3012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3004-3012.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S., Mellstrom K., Kosik E., Tamanoi F., Brugge J. Mutation of a termination codon affects src initiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1738–1746. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenuwein T., Müller R. Structure-function analysis of fos protein: a single amino acid change activates the immortalizing potential of v-fos. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):647–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90243-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Richardson W. D., Markham A. F., Smith A. E. Sequence requirements for nuclear location of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):33–38. doi: 10.1038/311033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzen A. L., Kornberg T. B., Bishop J. M. Isolation of the proto-oncogene c-myb from D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):449–456. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Bishop J. M. Transduction of c-myb into avian myeloblastosis virus: locating points of recombination within the cellular gene. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):565–572. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.565-572.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Gonda T. J., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the retroviral leukemia gene v-myb and its cellular progenitor c-myb: the architecture of a transduced oncogene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M., Moscovici M. G., Moscovici C., McGrath J. P., Levinson A. D. The product of the retroviral transforming gene v-myb is a truncated version of the protein encoded by the cellular oncogene c-myb. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):345–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90416-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Sippel A. E. Subnuclear localization of proteins encoded by the oncogene v-myb and its cellular homolog c-myb. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):62–69. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Symonds G., Evan G. I., Bishop J. M. Subcellular localization of proteins encoded by oncogenes of avian myeloblastosis virus and avian leukemia virus E26 and by chicken c-myb gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90384-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Butel J. S. Construction and characterization of an SV40 mutant defective in nuclear transport of T antigen. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):801–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90415-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leutz A., Beug H., Graf T. Purification and characterization of cMGF, a novel chicken myelomonocytic growth factor. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3191–3197. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsick J. S., Baluda M. A. The myb oncogene. Gene Amplif Anal. 1986;4:73–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsick J. S., Ibanez C. E., Baluda M. A. Expression of molecular clones of v-myb in avian and mammalian cells independently of transformation. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):267–275. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.267-275.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsick J. S., Ibanez C. E. env-encoded residues are not required for transformation by p48v-myb. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):933–936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.933-936.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsick J. S. v-myb does not prevent the expression of c-myb in avian erythroblasts. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3284–3287. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3284-3287.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majello B., Kenyon L. C., Dalla-Favera R. Human c-myb protooncogene: nucleotide sequence of cDNA and organization of the genomic locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9636–9640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moelling K., Pfaff E., Beug H., Beimling P., Bunte T., Schaller H. E., Graf T. DNA-binding activity is associated with purified myb proteins from AMV and E26 viruses and is temperature-sensitive for E26 ts mutants. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):983–990. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90358-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Gazzolo L., Moscovici M. G. Focus assay and defectiveness of avian myeloblastosis virus. Virology. 1975 Nov;68(1):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90159-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Jimenez H., Lai M. M., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Continuous tissue culture cell lines derived from chemically induced tumors of Japanese quail. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici M. G., Moscovici C. Isolation and characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant of avian myeloblastosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1421–1425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn M. F., Seeburg P. H., Moscovici C., Duesberg P. H. Tripartite structure of the avian erythroblastosis virus E26 transforming gene. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):391–395. doi: 10.1038/306391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paz-Ares J., Ghosal D., Wienand U., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. The regulatory c1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homology to myb proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activators. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3553–3558. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02684.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perbal B., Lipsick J. S., Svoboda J., Silva R. F., Baluda M. A. Biologically active proviral clone of myeloblastosis-associated virus type 1: implications for the genesis of avian myeloblastosis virus. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):240–244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.240-244.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Hoag J., Rosenberg N., Baltimore D. Protein stabilization explains the gag requirement for transformation of lymphoid cells by Abelson murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):123–132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.123-132.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosson D., Reddy E. P. Nucleotide sequence of chicken c-myb complementary DNA and implications for myb oncogene activation. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):604–606. doi: 10.1038/319604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M., Saule S., Lagrou C., Rommens C., Beug H., Graf T., Stehelin D. Three new types of viral oncogene of cellular origin specific for haematopoietic cell transformation. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):452–455. doi: 10.1038/281452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow K. E., Lautenberger J. A., Papas T. S., Baluda M. A., Perbal B., Chirikjian J. G., Reddy E. P. Nucleotide sequence of the transforming gene of avian myeloblastosis virus. Science. 1982 Jun 25;216(4553):1421–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.6283631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Potter M., Mushinski J. F., Lavu S., Reddy E. P. Activation of the c-myb locus by viral insertional mutagenesis in plasmacytoid lymphosarcomas. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1077–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.6093260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza L. M., Strommer J. N., Hillyard R. L., Komaromy M. C., Baluda M. A. Cellular sequences are present in the presumptive avian myeloblastosis virus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5177–5181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J., de Lange T., Ramsay G., Jakobovits E., Bishop J. M., Varmus H., Lee W. Definition of regions in human c-myc that are involved in transformation and nuclear localization. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1697–1709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein Y., Ihle J. N., Lavu S., Reddy E. P. Truncation of the c-myb gene by a retroviral integration in an interleukin 3-dependent myeloid leukemia cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5010–5014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







