Table 2.
Changes in neurotrophins in the rat dentate granule cells after seizures, trauma, or ischemia.
| Epilepsy | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kainic Acid | Pilocarpine | Kindling | PTZ | ECS | Trauma | Ischemia | |
| NGF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| BDNF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| NT-3 | — |
|
|
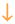 , — , — |
|
||
| NT-4 | — | ||||||
| trkA | — | — | |||||
| trkB |
|
|
|
|
|||
| trkC |
 , ,

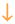
|
|
|||||
| p75 |
|
— | |||||
References for Table 2 (information from more than one study is represented in each column): Ballarin and others (1991); Ernfors and others (1991); Isackson and others (1991); Dugich-Djordjevic (1992, 1995); Bayer and Milner (1993); Bengzon and others (1992, 1993); Gall (1993); Humpel and others (1993); Merlio and others (1993); Takeda and others (1993); Arai and others (1996); Bramham and others (1996); Elmer and others (1996); Mudo and others (1995, 1996); Schmidt-Kastner and others (1995, 1996); Kornblum and others (1997); Lee and others (1997); Inoue and others (1998); Kim and others (1998); Morimoto and others (1998); Castren and others (1998); Goutan and Ferrer (1998); Rudge and others (1998); Truettner and others (1999).
Note the similarity of changes in neurotrophins after seizures induced by different mechanisms, or after trauma or ischemia. Abbreviations:
 = increased expression relative to control;
= increased expression relative to control;
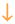 = decreased expression; — = no change;
= decreased expression; — = no change;
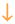 , — = some studies found no change and others demonstrated decreased expression;
, — = some studies found no change and others demonstrated decreased expression;
 ,
,

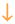 = some studies found increased expression and another found an increase followed by a decrease to control levels. Note that some of the differences between studies may be due to different methods (immunocytochemistry vs. in situ hybridization) or examination at different latencies after seizures. Where no symbol is listed, data were unavailable. PTZ = pentylenetetrazol; ECS = electroconvulsive shock; trauma = specific models of trauma used for the studies in this table were sham lesions, implantation of a dialysis probe, hilar lesion (which induced seizures as well as damage), and entorhinal cortex lesion; ischemia = models of ischemia used in this table include transient forebrain ischemia/middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neurotrophins include NGF (nerve growth factor), BDNF (brain derived neurotrophic factor), NT-3 and NT-4 (neurotrophin-3, neurotrophin-4; neurotrophin 4 is sometimes referred to as neurotrophin 4/5). trk = tyrosine kinase, the high affinity receptor class for neurotrophins (NGF binds to trkA; BDNF to trkB; NT-3 to trk A,B,C but has preference for trkC; NT-4 to trkA and B but has preference for trk B). p75 is the low affinity receptor for all neurotrophins. For p75 studies, increases occur mainly in neurons that will die. Other studies apply to changes in expression of surviving dentate granule cells after seizures, trauma, or ischemia.
= some studies found increased expression and another found an increase followed by a decrease to control levels. Note that some of the differences between studies may be due to different methods (immunocytochemistry vs. in situ hybridization) or examination at different latencies after seizures. Where no symbol is listed, data were unavailable. PTZ = pentylenetetrazol; ECS = electroconvulsive shock; trauma = specific models of trauma used for the studies in this table were sham lesions, implantation of a dialysis probe, hilar lesion (which induced seizures as well as damage), and entorhinal cortex lesion; ischemia = models of ischemia used in this table include transient forebrain ischemia/middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neurotrophins include NGF (nerve growth factor), BDNF (brain derived neurotrophic factor), NT-3 and NT-4 (neurotrophin-3, neurotrophin-4; neurotrophin 4 is sometimes referred to as neurotrophin 4/5). trk = tyrosine kinase, the high affinity receptor class for neurotrophins (NGF binds to trkA; BDNF to trkB; NT-3 to trk A,B,C but has preference for trkC; NT-4 to trkA and B but has preference for trk B). p75 is the low affinity receptor for all neurotrophins. For p75 studies, increases occur mainly in neurons that will die. Other studies apply to changes in expression of surviving dentate granule cells after seizures, trauma, or ischemia.
