Table 3.
Changes in neuropeptides in the rat dentate gyrus after seizures.
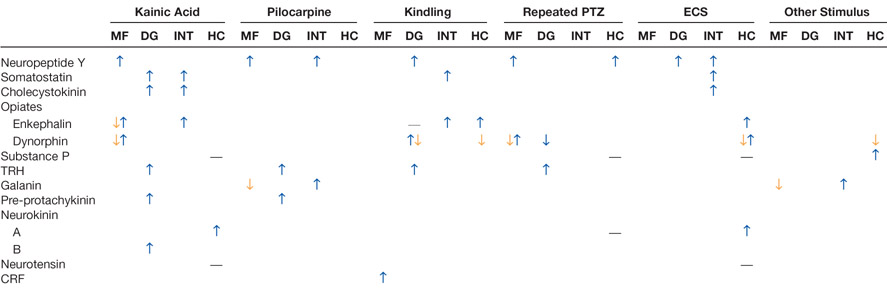 |
References for Table 3 (information from more than one study is included in each column): McGinty and others (1983, 1986); Kanamatsu and others (1986a, 1986b); Lason and others (1987); White and others (1987); Pitkanen and others (1989); Orzi and others (1990); Wanscher and others (1990); Hashimoto and Obata (1991); Xie and others (1991); Brene and others (1992); Lason and others (1992); Marksteiner and others (1992); Rosen and others (1992, 1994); Stenfors and others (1992a, 1992b); Bengzon and others (1993); Gruber and others (1993); Hong and others (1985, 1993); Kubek and others (1993); Passarelli and Orzi (1993); Kragh and others (1994); Mikkelsen and others (1994); Tonder and others (1994); Harrison and others (1995); Elmer and others (1996); Piwko and others (1996); Roder and others (1996); Sato and others (1996); Schwarzer and others (1996); Kofler and others (1997); Lurton and Cavalheiro (1997); Mazarati and others (1998); McCarthy and others (1998); Jaworska-Feil and others (1999); Pierce and others (1999); Scharfman and others (1999); Vezzani and others (1999b); Liu and others (2000); Wasterlain and others (2000).
Abbreviations: kainic acid = i.c.v. or systemic kainic acid; pilocarpine = pilocarpine or lithium/pilocarpine; PTZ = pentelenetetrazol; trauma = lesions, fluid percussive injury, or other models of trauma; ischemia = hypoxia or transient forebrain ischemia. Changes denoted reflect analysis of either the entire dentate gyrus (DG), granule cells (GC), mossy fibers (MF), hilar interneurons (INT), or hippocampus (HC).
 = increased relative to control;
= increased relative to control;
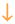 = decrease; —- = no change. Where no symbol is listed, data were unavailable. Information listed includes multiple methods (immunocytochemical, in situ hybridization, other) and different latencies after seizures.
= decrease; —- = no change. Where no symbol is listed, data were unavailable. Information listed includes multiple methods (immunocytochemical, in situ hybridization, other) and different latencies after seizures.
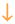
 reflects that some studies described decreases at one latency after seizures and increases at a subsequent time. Data for enkephalin include studies that examined both met-enkephalin and those that did not specify. Dynorphin data include results for dynorphin A and B and were particularly variable over time and the dorsal-ventral axis of the hippocampus. TRH = thyrotropin-releasing hormone; CRF = corticotropin-releasing factor.
reflects that some studies described decreases at one latency after seizures and increases at a subsequent time. Data for enkephalin include studies that examined both met-enkephalin and those that did not specify. Dynorphin data include results for dynorphin A and B and were particularly variable over time and the dorsal-ventral axis of the hippocampus. TRH = thyrotropin-releasing hormone; CRF = corticotropin-releasing factor.
