Abstract
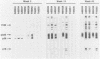
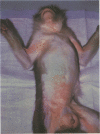
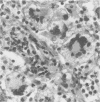
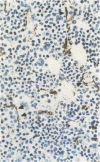
A primate lymphotropic lentivirus was isolated on the human T-cell line HuT 78 after cocultivation of a lymph node from a pig-tailed macaque (Macaca nemestrina) that had died with malignant lymphoma. This isolate, originally designated M. nemestrina immunodeficiency virus (MnIV) and now classified as simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV/Mne), was inoculated intravenously into three juvenile rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta), three juvenile pig-tailed macaques (M. nemestrina), and two juvenile baboons (Papio cynocephalus). All six macaques became viremic by 3 weeks after inoculation, whereas neither of the baboons developed viremia. One pig-tailed macaque died at 15 weeks with suppurative peritonitis secondary to ulcerative, necrotizing colitis. Immunologic abnormalities included a marked decrease in CD4+ peripheral blood lymphocytes. Although five macaques mounted an antibody response to SIV/Mne, the animal that died at 15 weeks remained antibody negative. Three other macaques (two rhesus and one pig-tailed) died 66 to 87 weeks after inoculation after exhibiting progressive weight loss, anemia, and diarrhea. Histopathologic findings at necropsy included various manifestations of immune deficiency, nephropathy, subacute encephalitis, pancreatitis, adenocarcinoma, and lymphoid atrophy. SIV/Mne could be readily isolated from the spleens and lymph nodes of all necropsied macaques, and from the cerebrospinal fluid, brains, bone marrow, livers, and pancreas of some of the animals. SIV antigens were localized by avidin-biotin immunohistochemistry to pancreatic islet cells and to bone marrow endothelial cells. The data suggest that African baboons may be resistant to infection by SIV/Mne, whereas Asian macaques are susceptible to infection with this pathogenic primate lentivirus.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskin G. B., Martin L. N., Rangan S. R., Gormus B. J., Murphey-Corb M., Wolf R. H., Soike K. F. Transmissible lymphoma and simian acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in rhesus monkeys. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Jul;77(1):127–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
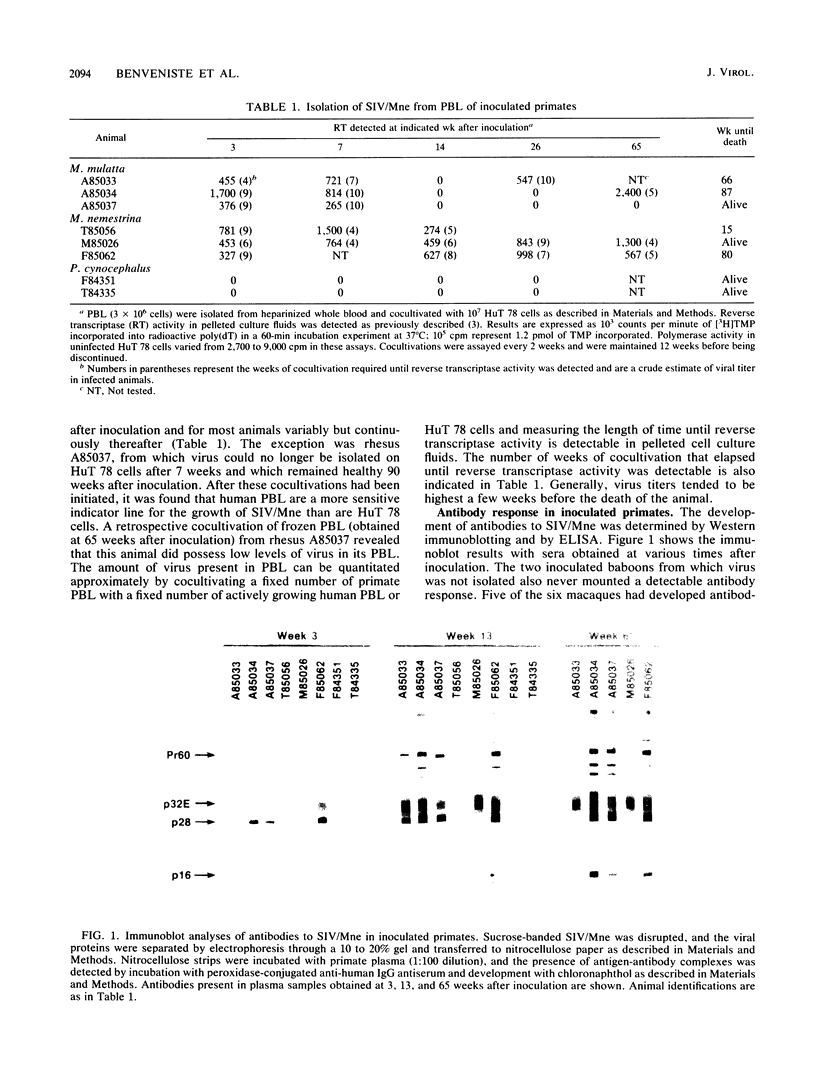
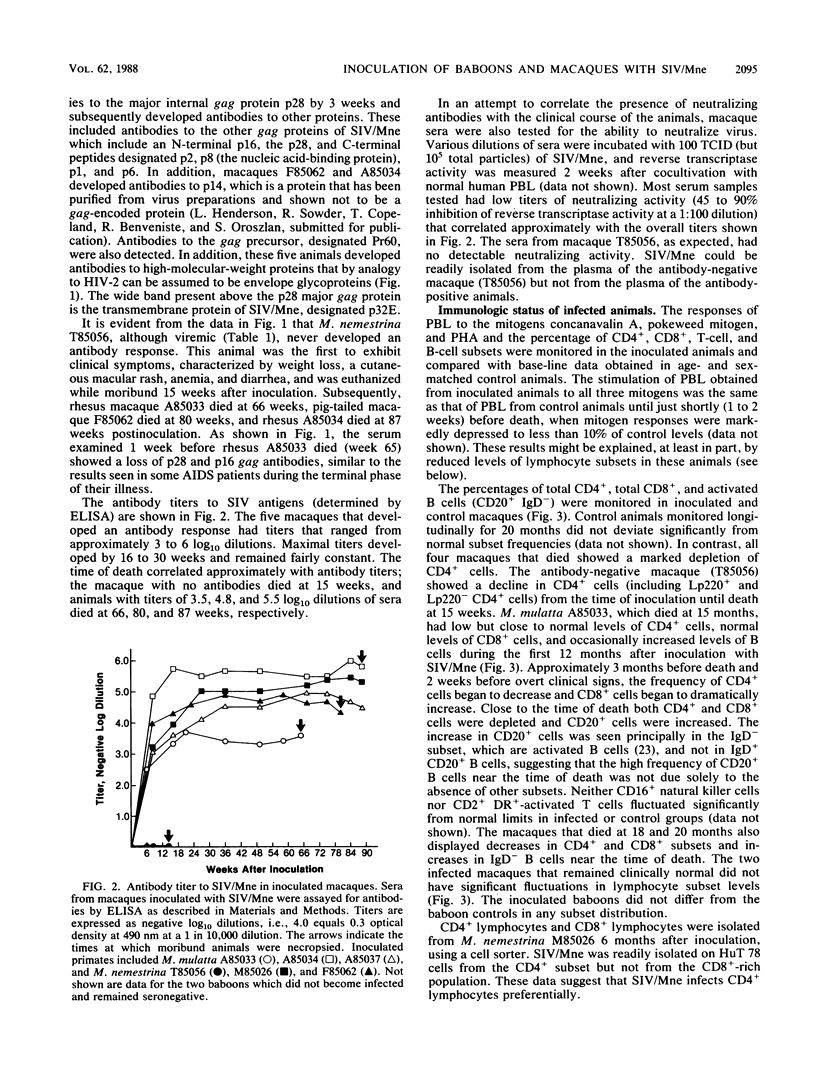
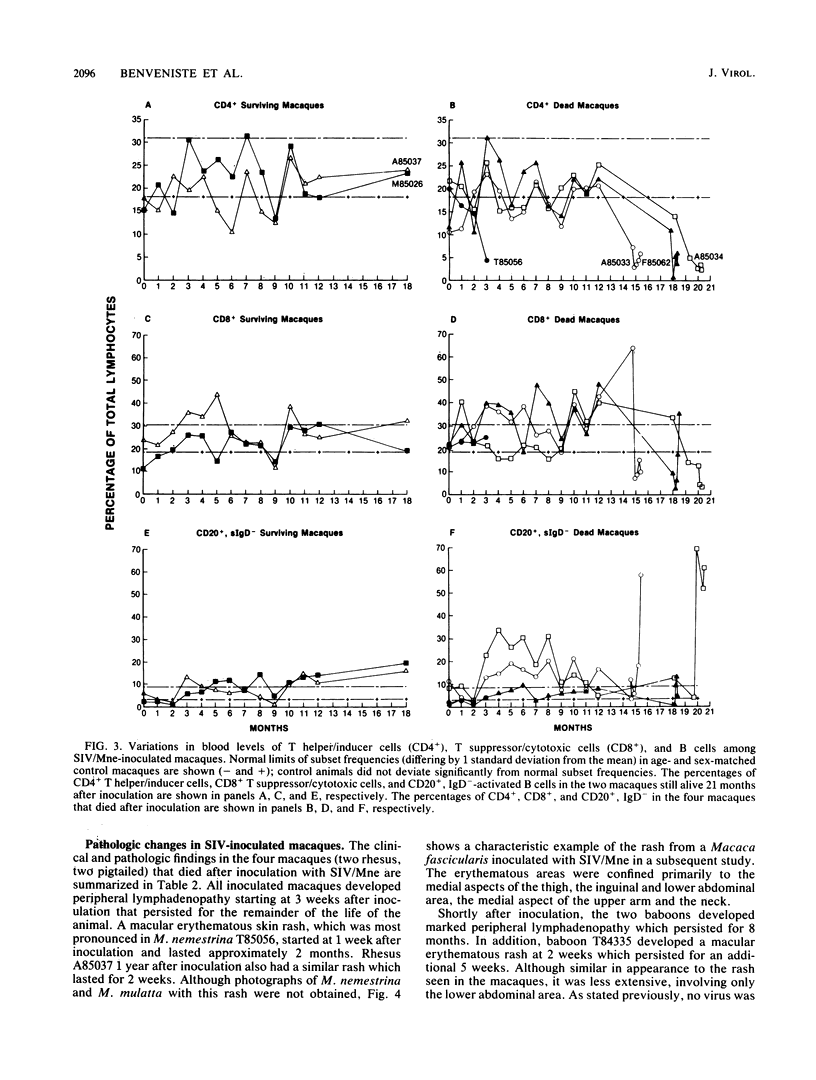
- Benveniste R. E., Arthur L. O., Tsai C. C., Sowder R., Copeland T. D., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S. Isolation of a lentivirus from a macaque with lymphoma: comparison with HTLV-III/LAV and other lentiviruses. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):483–490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.483-490.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard J. L., Baskin G. B., Murphey-Corb M., Martin L. N. Disseminated cryptosporidiosis in simian immunodeficiency virus/delta-infected rhesus monkeys. Vet Pathol. 1987 Sep;24(5):454–456. doi: 10.1177/030098588702400514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti L., Guyader M., Alizon M., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., Tiollais P., Sonigo P. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from macaque and its relationship to other human and simian retroviruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):543–547. doi: 10.1038/328543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalifoux L. V., King N. W., Daniel M. D., Kannagi M., Desrosiers R. C., Sehgal P. K., Waldron L. M., Hunt R. D., Letvin N. L. Lymphoproliferative syndrome in an immunodeficient rhesus monkey naturally infected with an HTLV-III-like virus (STLV-III). Lab Invest. 1986 Jul;55(1):43–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavel F., Guétard D., Brun-Vézinet F., Chamaret S., Rey M. A., Santos-Ferreira M. O., Laurent A. G., Dauguet C., Katlama C., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a new human retrovirus from West African patients with AIDS. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):343–346. doi: 10.1126/science.2425430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavel F., Mansinho K., Chamaret S., Guetard D., Favier V., Nina J., Santos-Ferreira M. O., Champalimaud J. L., Montagnier L. Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 infection associated with AIDS in West Africa. N Engl J Med. 1987 May 7;316(19):1180–1185. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198705073161903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel M. D., Letvin N. L., King N. W., Kannagi M., Sehgal P. K., Hunt R. D., Kanki P. J., Essex M., Desrosiers R. C. Isolation of T-cell tropic HTLV-III-like retrovirus from macaques. Science. 1985 Jun 7;228(4704):1201–1204. doi: 10.1126/science.3159089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Torre G. Ricerca al microscopio elettronico di particelle virali nel pancreas di topi normali e leucemici. Tumori. 1972 May-Jun;58(3):143–156. doi: 10.1177/030089167205800303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchini G., Gurgo C., Guo H. G., Gallo R. C., Collalti E., Fargnoli K. A., Hall L. F., Wong-Staal F., Reitz M. S., Jr Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus and its relationship to the human immunodeficiency viruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):539–543. doi: 10.1038/328539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Conjugation of antibodies with fluorochromes: modifications to the standard methods. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(3-4):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyader M., Emerman M., Sonigo P., Clavel F., Montagnier L., Alizon M. Genome organization and transactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):662–669. doi: 10.1038/326662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyorkey F., Melnick J. L., Gyorkey P. Human immunodeficiency virus in brain biopsies of patients with AIDS and progressive encephalopathy. J Infect Dis. 1987 May;155(5):870–876. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.5.870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch V., Riedel N., Kornfeld H., Kanki P. J., Essex M., Mullins J. I. Cross-reactivity to human T-lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus and molecular cloning of simian T-cell lymphotropic virus type III from African green monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9754–9758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch V., Riedel N., Mullins J. I. The genome organization of STLV-3 is similar to that of the AIDS virus except for a truncated transmembrane protein. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):307–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90283-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanki P. J., Alroy J., Essex M. Isolation of T-lymphotropic retrovirus related to HTLV-III/LAV from wild-caught African green monkeys. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):951–954. doi: 10.1126/science.2997923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanki P. J., Barin F., M'Boup S., Allan J. S., Romet-Lemonne J. L., Marlink R., McLane M. F., Lee T. H., Arbeille B., Denis F. New human T-lymphotropic retrovirus related to simian T-lymphotropic virus type III (STLV-IIIAGM). Science. 1986 Apr 11;232(4747):238–243. doi: 10.1126/science.3006256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannagi M., Kiyotaki M., Desrosiers R. C., Reimann K. A., King N. W., Waldron L. M., Letvin N. L. Humoral immune responses to T cell tropic retrovirus simian T lymphotropic virus type III in monkeys with experimentally induced acquired immune deficiency-like syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1229–1236. doi: 10.1172/JCI112706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannagi M., Yetz J. M., Letvin N. L. In vitro growth characteristics of simian T-lymphotropic virus type III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7053–7057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld H., Riedel N., Viglianti G. A., Hirsch V., Mullins J. I. Cloning of HTLV-4 and its relation to simian and human immunodeficiency viruses. Nature. 1987 Apr 9;326(6113):610–613. doi: 10.1038/326610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuritani T., Cooper M. D. Human B cell differentiation. II. Pokeweed mitogen-responsive B cells belong to a surface immunoglobulin D-negative subpopulation. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1561–1566. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Masur H., Edgar L. C., Whalen G., Rook A. H., Fauci A. S. Abnormalities of B-cell activation and immunoregulation in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1983 Aug 25;309(8):453–458. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198308253090803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., Daniel M. D., Sehgal P. K., Desrosiers R. C., Hunt R. D., Waldron L. M., MacKey J. J., Schmidt D. K., Chalifoux L. V., King N. W. Induction of AIDS-like disease in macaque monkeys with T-cell tropic retrovirus STLV-III. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):71–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2412295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber M., Smith B., Szakal A., Nelson-Rees W., Todaro G. A continuous tumor-cell line from a human lung carcinoma with properties of type II alveolar epithelial cells. Int J Cancer. 1976 Jan 15;17(1):62–70. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstine L. J., Pedersen N. C., Higgins J., Pallis K. C., Uyeda A., Marx P., Lerche N. W., Munn R. J., Gardner M. B. Seroepidemiologic survey of captive Old-World primates for antibodies to human and simian retroviruses, and isolation of a lentivirus from sooty mangabeys (Cercocebus atys). Int J Cancer. 1986 Oct 15;38(4):563–574. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910380417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphey-Corb M., Martin L. N., Rangan S. R., Baskin G. B., Gormus B. J., Wolf R. H., Andes W. A., West M., Montelaro R. C. Isolation of an HTLV-III-related retrovirus from macaques with simian AIDS and its possible origin in asymptomatic mangabeys. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):435–437. doi: 10.1038/321435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs H. D., Slichter S. J., Harker L. A., Von Behrens W. E., Clark R. A., Wedgwood R. J. The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: studies of lymphocytes, granulocytes, and platelets. Blood. 1980 Feb;55(2):243–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahwa S., Pahwa R., Good R. A., Gallo R. C., Saxinger C. Stimulatory and inhibitory influences of human immunodeficiency virus on normal B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9124–9128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts O. M., Powers J. M., Bilello J. A., Hoffman P. M. Ultrastructural changes associated with retroviral replication in central nervous system capillary endothelial cells. Lab Invest. 1987 Apr;56(4):401–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringler D. J., Hancock W. W., King N. W., Letvin N. L., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., Murphy G. F. Immunophenotypic characterization of the cutaneous exanthem of SIV-infected rhesus monkeys. Apposition of degenerative Langerhans cells and cytotoxic lymphocytes during the development of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1987 Feb;126(2):199–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose L. M., Clark E. A., Hruby S., Alvord E. C., Jr Fluctuations of T- and B-cell subsets in basic protein-induced experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) in long-tailed macaques. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Jul;44(1):93–106. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90055-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose L. M., Ginsberg A. H., Rothstein T. L., Ledbetter J. A., Clark E. A. Selective loss of a subset of T helper cells in active multiple sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7389–7393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S. M., Lane H. C., Higgins S. E., Folks T., Fauci A. S. Direct polyclonal activation of human B lymphocytes by the acquired immune deficiency syndrome virus. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1084–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.3016902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stromberg K., Benveniste R. E., Arthur L. O., Rabin H., Giddens W. E., Jr, Ochs H. D., Morton W. R., Tsai C. C. Characterization of exogenous type D retrovirus from a fibroma of a macaque with simian AIDS and fibromatosis. Science. 1984 Apr 20;224(4646):289–282. doi: 10.1126/science.6200929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C. M., Moody D. J., Stites D. P., Levy J. A. CD8+ lymphocytes can control HIV infection in vitro by suppressing virus replication. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1563–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.2431484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. M., O'Leary T. J., Baskin G. B., Benveniste R., Harris C. A., Nara P. L., Rhodes R. H. Immunohistochemical localization of human and simian immunodeficiency viral antigens in fixed tissue sections. Am J Pathol. 1987 May;127(2):199–205. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Schrier R. D., Nelson J. A., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Cellular localization of human immunodeficiency virus infection within the brains of acquired immune deficiency syndrome patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7089–7093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarchoan R., Redfield R. R., Broder S. Mechanisms of B cell activation in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and related disorders. Contribution of antibody-producing B cells, of Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells, and of immunoglobulin production induced by human T cell lymphotropic virus, type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):439–447. doi: 10.1172/JCI112595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]