Abstract
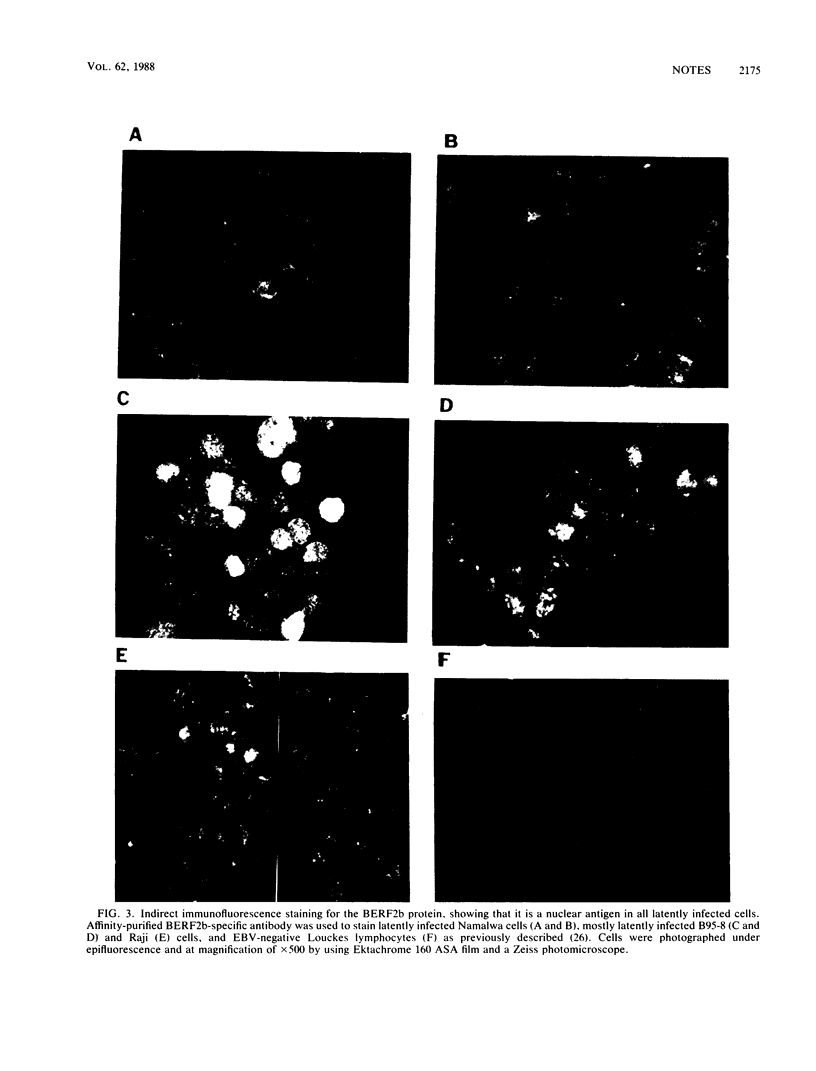
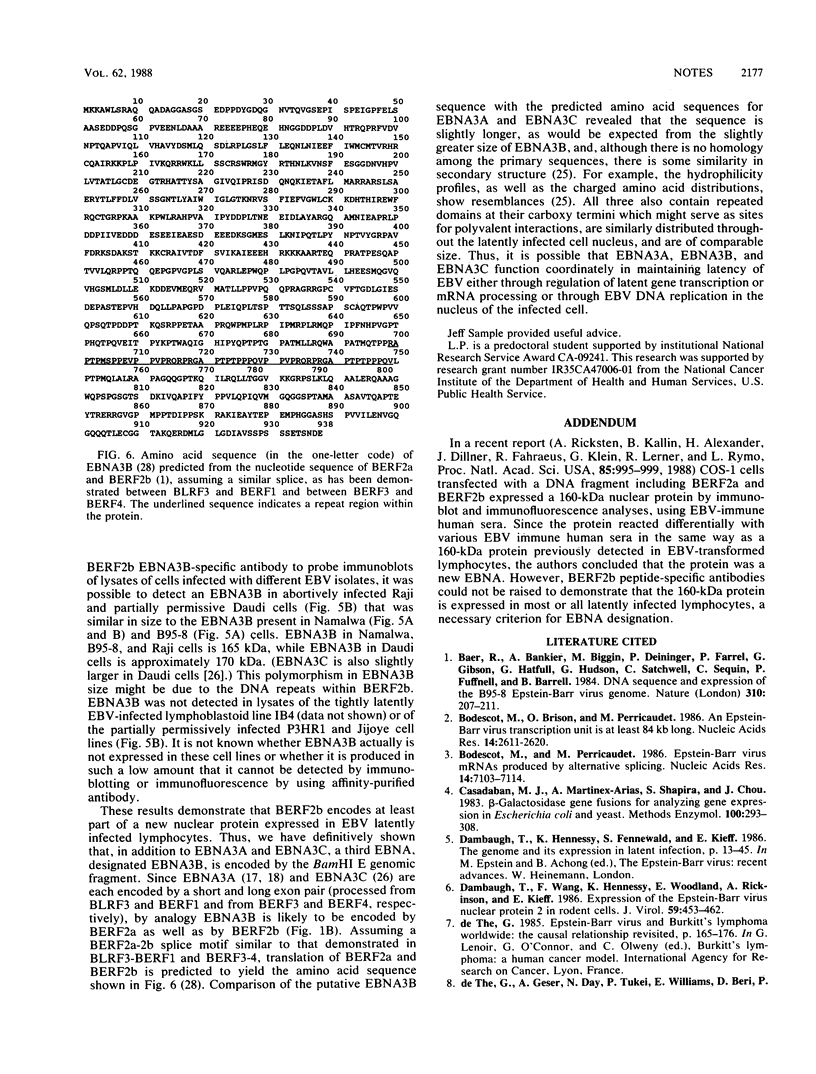
In the Epstein-Barr virus BamHI E genomic fragment, there are three distantly homologous long open reading frames, BERF1, BERF2b, and BERF4, each of which is preceded by a short open reading frame. The most leftward and most rightward short and long open reading frame pairs encode 145- and 155-kilodalton proteins in latently infected cells (EBNA3A and EBNA3C, respectively). In this report, we demonstrate that the middle long open reading frame, BERF2b, encodes part of a 165-kilodalton nuclear protein in every latently infected cell. Therefore, this protein is designated EBNA3B.
Full text
PDF



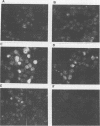
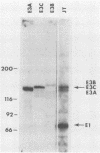
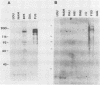
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Brison O., Perricaudet M. An Epstein-Barr virus transcription unit is at least 84 kilobases long. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2611–2620. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Perricaudet M. Epstein-Barr virus mRNAs produced by alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7103–7114. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Martinez-Arias A., Shapira S. K., Chou J. Beta-galactosidase gene fusions for analyzing gene expression in escherichia coli and yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:293–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Wang F., Hennessy K., Woodland E., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Expression of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 in rodent cells. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):453–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.453-462.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Kallin B., Alexander H., Ernberg I., Uno M., Ono Y., Klein G., Lerner R. A. An Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA5) partly encoded by the transformation-associated Bam WYH region of EBV DNA: preferential expression in lymphoblastoid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6641–6645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPSTEIN M. A., ACHONG B. G., BARR Y. M. VIRUS PARTICLES IN CULTURED LYMPHOBLASTS FROM BURKITT'S LYMPHOMA. Lancet. 1964 Mar 28;1(7335):702–703. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91524-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennewald S., van Santen V., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequence of an mRNA transcribed in latent growth-transforming virus infection indicates that it may encode a membrane protein. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):411–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.411-419.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Fennewald S., Hummel M., Cole T., Kieff E. A membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent growth-transforming infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7207–7211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Fennewald S., Kieff E. A third viral nuclear protein in lymphoblasts immortalized by Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5944–5948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Heller M., van Santen V., Kieff E. Simple repeat array in Epstein-Barr virus DNA encodes part of the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen. Science. 1983 Jun 24;220(4604):1396–1398. doi: 10.1126/science.6304878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. A second nuclear protein is encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent infection. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1238–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.2983420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. One of two Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens contains a glycine-alanine copolymer domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5665–5669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Wang F., Bushman E. W., Kieff E. Definitive identification of a member of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 3 family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5693–5697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joab I., Rowe D. T., Bodescot M., Nicolas J. C., Farrell P. J., Perricaudet M. Mapping of the gene coding for Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen EBNA3 and its transient overexpression in a human cell line by using an adenovirus expression vector. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3340–3344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3340-3344.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallin B., Dillner J., Ernberg I., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Rosén A., Henle W., Henle G., Klein G. Four virally determined nuclear antigens are expressed in Epstein-Barr virus-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1499–1503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieff E., Hennessy K., Fennewald S., Matsuo T., Dambaugh T., Heller M., Hummel M. Biochemistry of latent Epstein-Barr virus infection and associated cell growth transformation. IARC Sci Publ. 1985;(60):323–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebowitz D., Wang D., Kieff E. Orientation and patching of the latent infection membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):233–237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.233-237.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotný J., Auffray C. A program for prediction of protein secondary structure from nucleotide sequence data: application to histocompatibility antigens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):243–255. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petti L., Sample J., Wang F., Kieff E. A fifth Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein (EBNA3C) is expressed in latently infected growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1330–1338. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1330-1338.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T., Tatsumi E., Manolov G., Manolova Y., Harada S., Lipscomb H., Krueger G. Epstein-Barr virus as an etiological agent in the pathogenesis of lymphoproliferative and aproliferative diseases in immune deficient patients. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1985;27:113–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Korn L. J. A comprehensive sequence analysis program for the IBM personal computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):581–599. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Milman G., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA-1) to clustered sites in the plasmid maintenance region. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):859–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Yates J., Sugden B. A putative origin of replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus is composed of two cis-acting components. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1822–1832. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricksten A., Kallin B., Alexander H., Dillner J., Fåhraeus R., Klein G., Lerner R., Rymo L. BamHI E region of the Epstein-Barr virus genome encodes three transformation-associated nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):995–999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Hummel M., Braun D., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequences of mRNAs encoding Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins: a probable transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Petti L., Braun D., Seung S., Kieff E. A bicistronic Epstein-Barr virus mRNA encodes two nuclear proteins in latently infected, growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):945–954. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.945-954.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J., Warren N., Reisman D., Sugden B. A cis-acting element from the Epstein-Barr viral genome that permits stable replication of recombinant plasmids in latently infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de-Thé G., Geser A., Day N. E., Tukei P. M., Williams E. H., Beri D. P., Smith P. G., Dean A. G., Bronkamm G. W., Feorino P. Epidemiological evidence for causal relationship between Epstein-Barr virus and Burkitt's lymphoma from Ugandan prospective study. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):756–761. doi: 10.1038/274756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]