Abstract
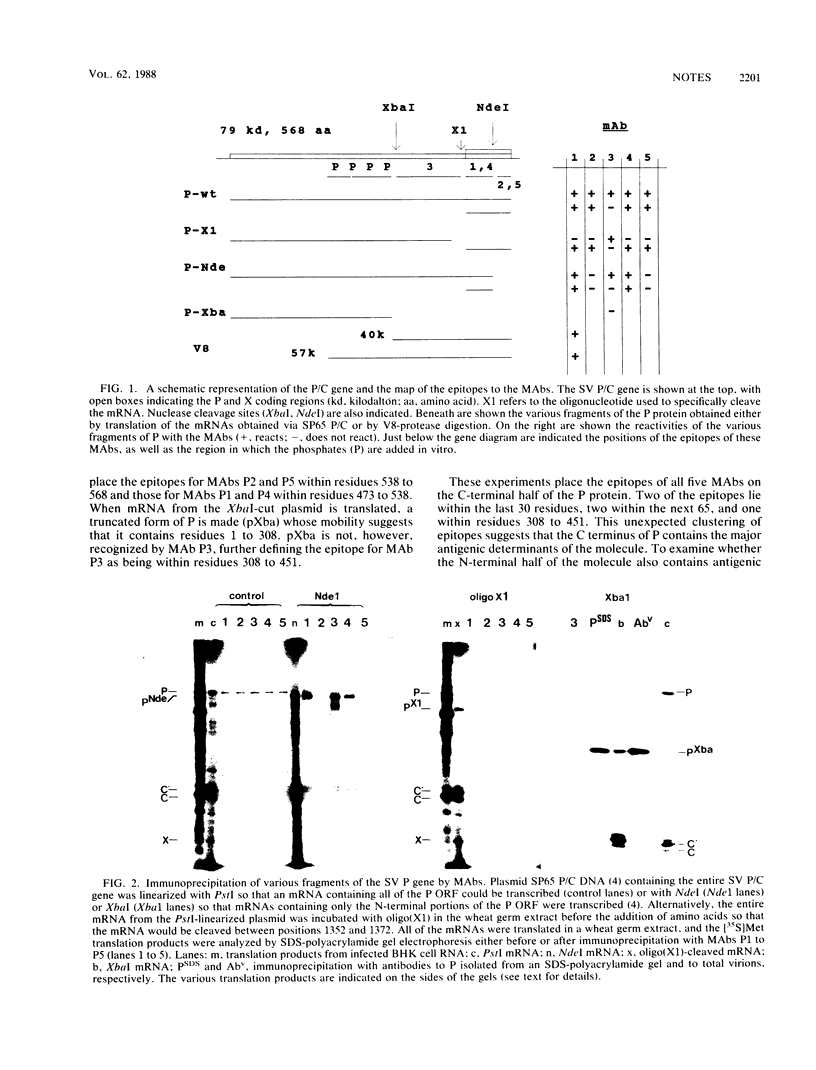
The epitopes of a panel of five monoclonal antibodies to the Sendai virus P protein were mapped by generating modified forms of the P mRNA via SP6 expression followed by in vitro translation. The epitopes were found to be clustered in the C-terminal region of the protein. Two epitopes were within the last 30 residues, two were within the next 65, and one was between residues 308 and 451 of this 568-residue-long protein. By a combination of partial proteolysis and Western immunoblotting with one of these antibodies, the sites at which phosphates are added in vitro by the virion-associated kinase were mapped to the second quarter of the molecule from the N terminus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell J. C., Prevec L. Phosphorylation sites on phosphoprotein NS of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):697–702. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.697-702.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J. A., Kolakofsky D. Identification of an additional Sendai virus non-structural protein encoded by the P/C mRNA. J Gen Virol. 1987 Sep;68(Pt 9):2515–2519. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-9-2515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J., Kolakofsky D. Ribosomal initiation from an ACG codon in the Sendai virus P/C mRNA. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):245–251. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02806.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande K. L., Portner A. Monoclonal antibodies to the P protein of Sendai virus define its structure and role in transcription. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90451-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi C., Blumberg B. M., Kolakofsky D. Sendai virus contains overlapping genes expressed from a single mRNA. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi M., Yoshida T., Nishikawa K., Naruse H., Nagai Y. Transcriptive complex of Newcastle disease virus. I. Both L and P proteins are required to constitute an active complex. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):105–117. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90322-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C. H., Kingsbury D. W. Topography of phosphate residues in Sendai virus proteins. Virology. 1982 Jul 15;120(1):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsford L., Emerson S. U. Transcriptional activities of different phosphorylated species of NS protein purified from vesicular stomatitis virions and cytoplasm of infected cells. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1097–1105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1097-1105.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A. The phosphorylation of sendai virus proteins by a virus particle-associated protein kinase. J Gen Virol. 1975 Mar;26(3):249–263. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-26-3-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Hunt T. The use of single-stranded DNA and RNase H to promote quantitative 'hybrid arrest of translation' of mRNA/DNA hybrids in reticulocyte lysate cell-free translations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6433–6451. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orvell C., Grandien M. The effects of monoclonal antibodies on biologic activities of structural proteins of Sendai virus. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2779–2787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux L., Kolakofsky D. Protein kinase associated with Sendai virions. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):545–547. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.545-547.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]