Abstract
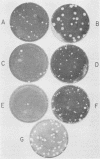
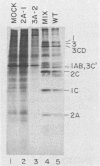
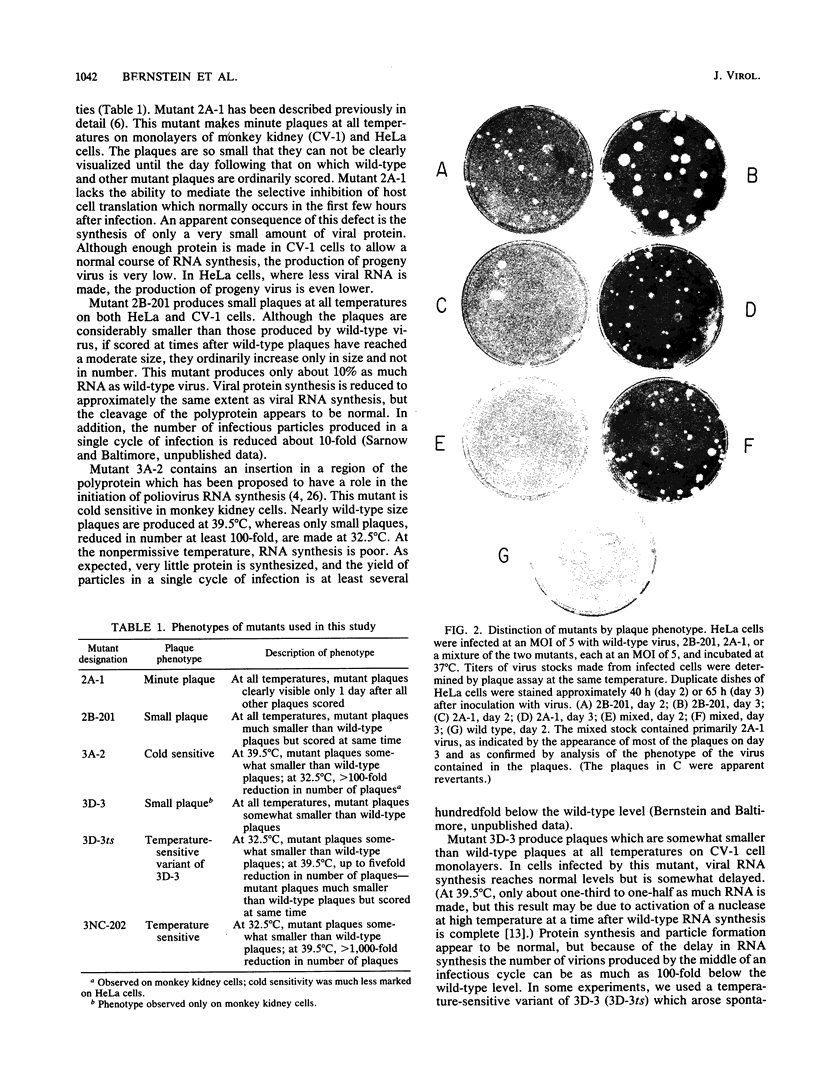
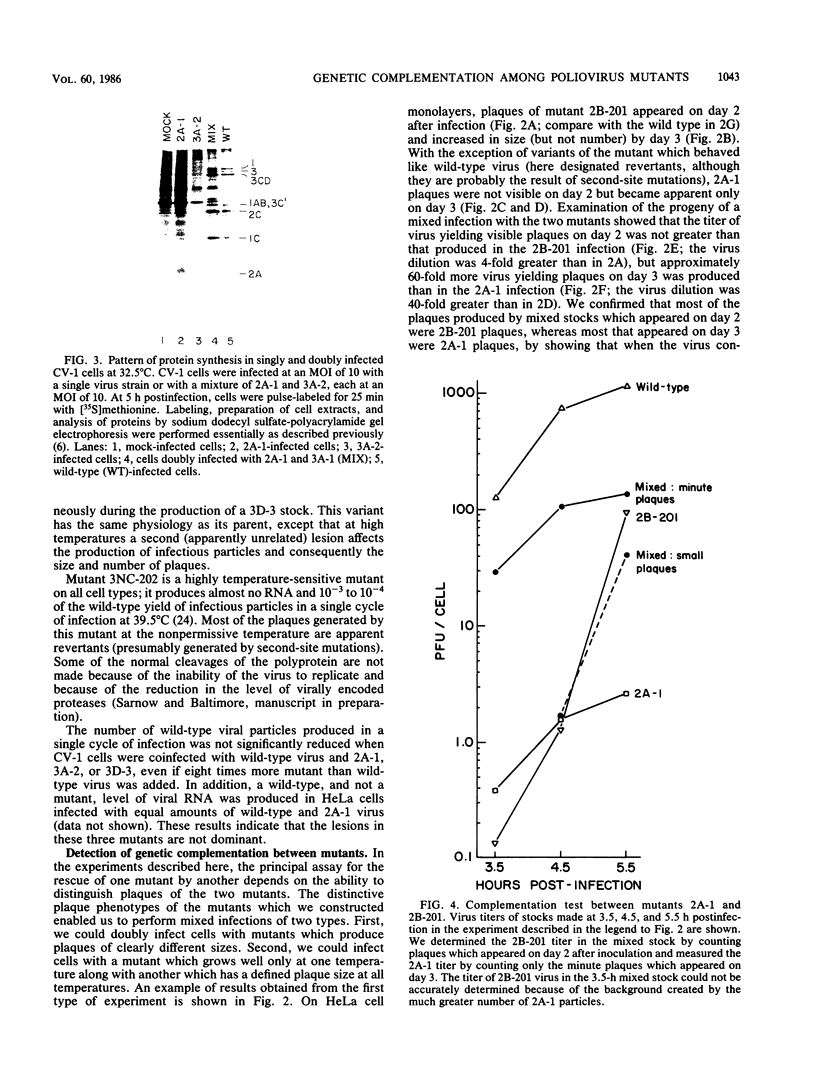
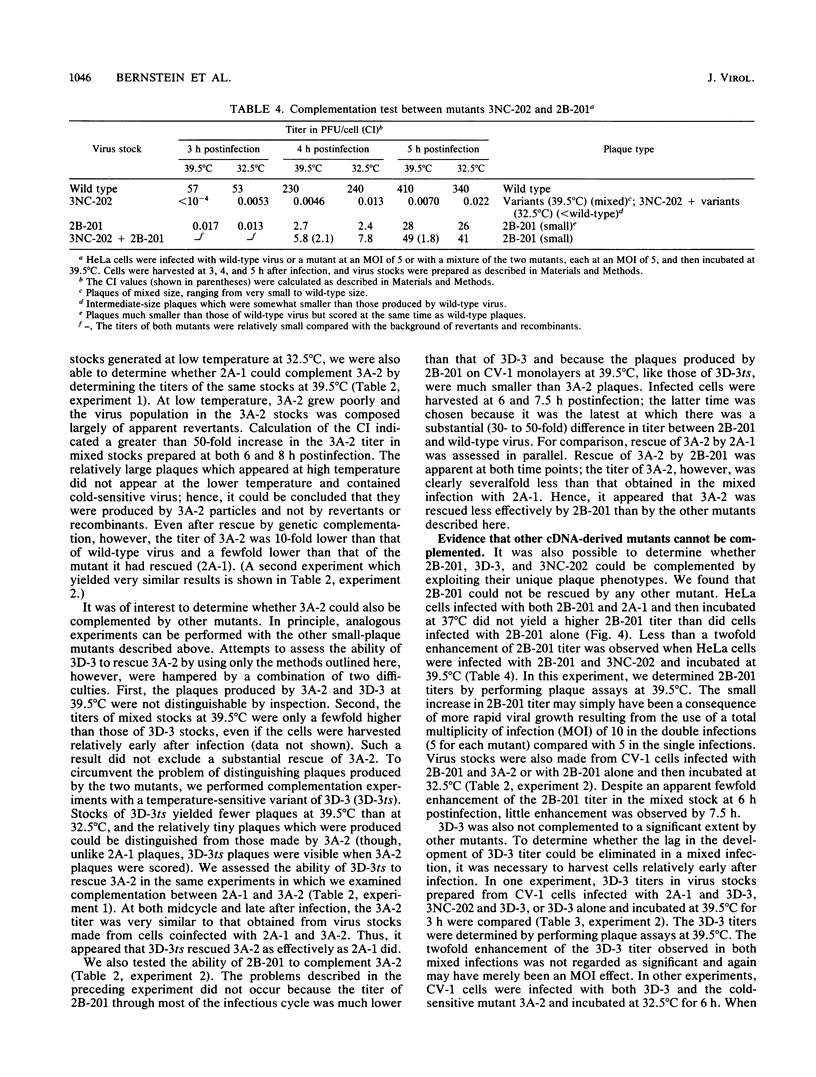
We constructed several well-defined mutations in the nonstructural portion of the poliovirus type I (Mahoney strain) genome by making small insertions in an infectious cDNA clone. The derived viral strains carrying the mutations exhibited a variety of distinct plaque phenotypes. Thus, we were able to examine genetic complementation between different pairs of mutants by comparing the yields of progeny virus in mixed and single infections. Two mutants bearing lesions in the 2A and 3A regions of the genome, which are defective in the inhibition of host cell translation and the synthesis of viral RNA, respectively, could be rescued efficiently by genetic complementation; three replication-deficient mutants containing insertions in the 2B, 3D (replicase), and 3'-untranslated regions could not. Both the 2A and 3A mutants could be rescued by each other and by all of the other mutants tested. Because yield enhancement was apparent well before the completion of a single infectious cycle, it is likely that complementation of both mutants involved early diffusion of functional products. These data provide the first unambiguous evidence that the nonstructural portion of the poliovirus genome contains multiple complementation groups. The data also suggest that certain nonstructural functions act only in cis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agut H., Bellocq C., van der Werf S., Girard M. Recombination and rescue between temperature-sensitive mutants of poliovirus type 1. Virology. 1984 Dec;139(2):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90385-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argos P., Kamer G., Nicklin M. J., Wimmer E. Similarity in gene organization and homology between proteins of animal picornaviruses and a plant comovirus suggest common ancestry of these virus families. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7251–7267. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Girard M., Darnell J. E. Aspects of the synthesis of poliovirus RNA and the formation of virus particles. Virology. 1966 Jun;29(2):179–189. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Antibodies against the chemically synthesized genome-linked protein of poliovirus react with native virus-specific proteins. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90357-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellocq C., Agut H., van der Werf S. F., Girard M. Biochemical characterization of poliovirus type 1 temperature-sensitive mutants. Virology. 1984 Dec;139(2):403–407. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90386-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Poliovirus mutant that does not selectively inhibit host cell protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2913–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond C. W., Swim H. E. Physiological characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of mengovirus. J Virol. 1975 Feb;15(2):288–296. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.2.288-296.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER P. D. RESCUE OF ONE PHENOTYPE IN MIXED INFECTIONS WITH HEAT-DEFECTIVE MUTANTS OF TYPE 1 POLIOVIRUS. Virology. 1965 Mar;25:431–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORDS C. E., HOLLAND J. J. ALTERATION OF THE SPECIES AND TISSUE SPECIFICITY OF POLIOVIRUS BY ENCLOSURE OF ITS RNA WITHIN THE PROTEIN CAPSID OF COXSACKIE B1 VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:492–495. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90192-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Baltimore D. Defective interfering particles of poliovirus. II. Nature of the defect. J Mol Biol. 1973 May 25;76(3):325–343. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90508-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D. A genetic map of poliovirus temperature-sensitive mutants. Virology. 1968 Aug;35(4):584–596. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiszman M. Y., Bucchini D., Girard M., Lwoff A. Inhibition of poliovirus RNA synthesis by supraoptimal temperatures. J Gen Virol. 1970 Feb;6(2):293–304. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-6-2-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandolf R., Hofschneider P. H. Molecular cloning of the genome of a cardiotropic Coxsackie B3 virus: full-length reverse-transcribed recombinant cDNA generates infectious virus in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4818–4822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDINKO N., HIRST G. K. Mixed infection of HeLa cells with polioviruses types 1 and 2. Virology. 1961 Jun;14:207–219. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90196-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. R., Priston A. J., Slade W. R. A genetic recombination map of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1975 Jun;27(3):355–367. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-3-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist R. E., Sullivan M., Maizel J. V., Jr Characterization of a new isolate of poliovirus defective interfering particles. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):759–769. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90129-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S., Summers D. Effects on host cell metabolism following synchronous infection with poliovirus. Virology. 1965 Dec;27(4):614–620. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90187-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. E., Diamond D. C., Emini E. A., Wimmer E. Guanidine-selected mutants of poliovirus: mapping of point mutations to polypeptide 2C. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):638–646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.638-646.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnak J. R., Phillips B. A. Picornaviral structure and assembly. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Jun;45(2):287–315. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.2.287-315.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Cloned poliovirus complementary DNA is infectious in mammalian cells. Science. 1981 Nov 20;214(4523):916–919. doi: 10.1126/science.6272391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Bernstein H. D., Baltimore D. A poliovirus temperature-sensitive RNA synthesis mutant located in a noncoding region of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):571–575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders K., King A. M. Guanidine-resistant mutants of aphthovirus induce the synthesis of an altered nonstructural polypeptide, P34. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):389–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.389-394.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Hanecak R., Dorner L. F., Wimmer E. A membrane-associated precursor to poliovirus VPg identified by immunoprecipitation with antibodies directed against a synthetic heptapeptide. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G., Hughes P. J., Mountford R. C., Minor P. D., Almond J. W. The complete nucleotide sequence of a common cold virus: human rhinovirus 14. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7859–7875. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Kohara M., Kataoka Y., Suganuma T., Omata T., Imura N., Nomoto A. Complete nucleotide sequences of all three poliovirus serotype genomes. Implication for genetic relationship, gene function and antigenic determinants. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):561–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WECKER E., LEDERHILGER G. GENOMIC MASKING PRODUCED BY DOUBLE-INFECTION OF HELA CELLS WITH HETEROTYPIC POLIOVIRUSES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Sep;52:705–709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.3.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]