Abstract
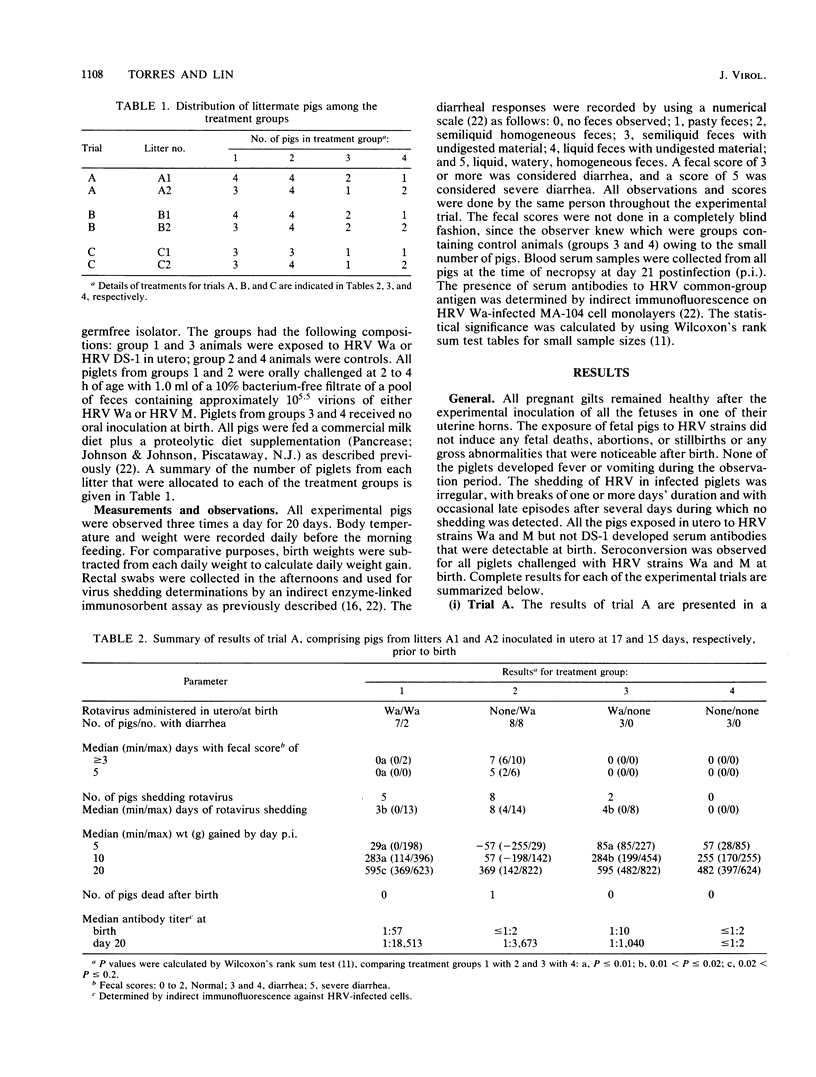
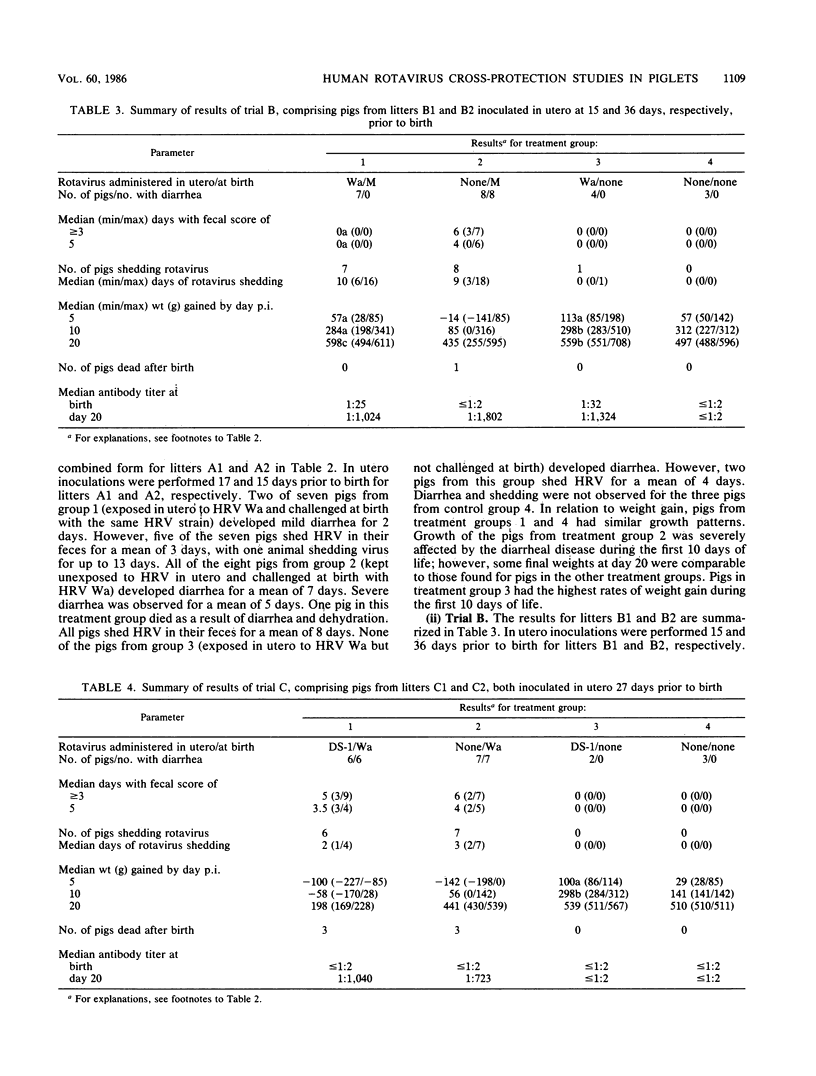
Pigs exposed in utero to human rotavirus (HRV) strain Wa serotype 1 from 15 to 36 days prior to birth responded immunologically by modifying their clinical response to neonatal oral challenge with a pathogenic dose of homologous Wa or heterologous M serotype 3 HRV. In these cases, diarrhea was prevented in 12 of 14 pigs and greatly reduced in the other two. However, fecal virus shedding was not significantly modified, since it was detected in 12 of 14 pigs. These results suggest the existence of a closer antigenic relationship between these two different HRV serotypes which may only be expressed in an in vivo test system. Exposure of fetal pigs to HRV DS-1 serotype 2 failed to cause infection or to induce any protection when pigs were challenged at birth with HRV Wa. This model for cross-protection studies in gnotobiotic piglets offers good possibilities for the evaluation of potential HRV vaccine candidates, for the in vivo study of antigenic similarities between rotavirus serotypes, and for the understanding of protective immune responses against diarrhea and virus shedding.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohl E. H., Gupta R. K., Olquin M. V., Saif L. J. Antibody responses in serum, colostrum, and milk of swine after infection or vaccination with transmissible gastroenteritis virus. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):289–301. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.289-301.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Saif L. J. Passive immunity in transmissible gastroenteritis of swine: immunoglobulin characteristics of antibodies in milk after inoculating virus by different routes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):23–32. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.23-32.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Saif L. J. Isolation and serotyping of porcine rotaviruses and antigenic comparison with other rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):105–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.105-111.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Brown J. F. Antigenic and pathogenic relationships of three bovine rotaviruses and a porcine rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jul;65(Pt 7):1151–1158. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-7-1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner G. H., Carter G. R. Response of the bovine fetus to reovirus. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1975 Dec;70(12):1463–1464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner G. H., Richardson M., Carter G. R. Prenatal immunization and protection of the newborn: ovine and bovine fetuses vaccinated with Escherichia coli antigen by the oral route and exposed to challenge inoculum at birth. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Jun;34(6):737–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delem A., Lobmann M., Zygraich N. A bovine rotavirus developed as a candidate vaccine for use in humans. J Biol Stand. 1984 Oct;12(4):443–445. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(84)80068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eydelloth R. S., Vonderfecht S. L., Sheridan J. F., Enders L. D., Yolken R. H. Kinetics of viral replication and local and systemic immune responses in experimental rotavirus infection. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):947–950. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.947-950.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaul S. K., Simpson T. F., Woode G. N., Fulton R. W. Antigenic relationships among some animal rotaviruses: virus neutralization in vitro and cross-protection in piglets. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):495–503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.495-503.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Flores J., Midthun K., Kapikian A. Z. Serotypic characterization of rotaviruses derived from asymptomatic human neonatal infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):425–430. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.425-430.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Serotypic similarity and diversity of rotaviruses of mammalian and avian origin as studied by plaque-reduction neutralization. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):694–702. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Flores J., Hoshino Y., Glass R. I., Midthun K., Gorziglia M., Chanock R. M. Rotavirus: the major etiologic agent of severe infantile diarrhea may be controllable by a "Jennerian" approach to vaccination. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):815–822. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Kim H. W., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. Approaches to immunization of infants and young children against gastroenteritis due to rotaviruses. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 May-Jun;2(3):459–469. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.3.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melbus C. A. Calf diaarhea induced by coronavirus and a reovirus-like agent. Mod Vet Pract. 1976 Sep;57(9):693–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midthun K., Greenberg H. B., Hoshino Y., Kapikian A. Z., Wyatt R. G., Chanock R. M. Reassortant rotaviruses as potential live rotavirus vaccine candidates. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):949–954. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.949-954.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomenclature of human rotaviruses: designation of subgroups and serotypes. Bull World Health Organ. 1984;62(3):501–507. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan J. F., Eydelloth R. S., Vonderfecht S. L., Aurelian L. Virus-specific immunity in neonatal and adult mouse rotavirus infection. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):917–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.917-927.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel R. B., Torres-Medina A. Effects of environmental and dietary factors on human rotavirus infection in gnotobiotic piglets. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):906–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.906-911.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Medina A., Wyatt R. G., Mebus C. A., Underdahl N. R., Kapikian A. Z. Patterns of shedding of human reovirus-like agent in gnotobiotic newborn piglets with experimentally-induced diarrhea. Intervirology. 1976;7(4-5):250–255. doi: 10.1159/000149957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underdahl N. R., Mebus C. A., Stair E. L., Twiehaus M. J. The effect of cytopathogenic transmissible gastroenteritis-like viruses and-or Escherichia coli on germfree pigs. Can Vet J. 1972 Jan;13(1):9–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., James W. D., Pittman A. L., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Definition of human rotavirus serotypes by plaque reduction assay. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):110–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.110-115.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., James W. D., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Saif L. J., Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Human rotavirus type 2: cultivation in vitro. Science. 1980 Jan 11;207(4427):189–191. doi: 10.1126/science.6243190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Mebus C. A. Induction of cross-reactive serum neutralizing antibody to human rotavirus in calves after in utero administration of bovine rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):505–508. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.505-508.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Mebus C. A., Yolken R. H., Kalica A. R., James H. D., Jr, Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Rotaviral immunity in gnotobiotic calves: heterologous resistance to human virus induced by bovine virus. Science. 1979 Feb 9;203(4380):548–550. doi: 10.1126/science.216077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zissis G., Lambert J. P., Marbehant P., Marissens D., Lobmann M., Charlier P., Delem A., Zygraich N. Protection studies in colostrum-deprived piglets of a bovine rotavirus vaccine candidate using human rotavirus strains for challenge. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):1061–1068. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


