Abstract
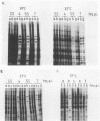
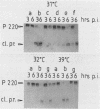
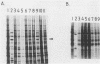
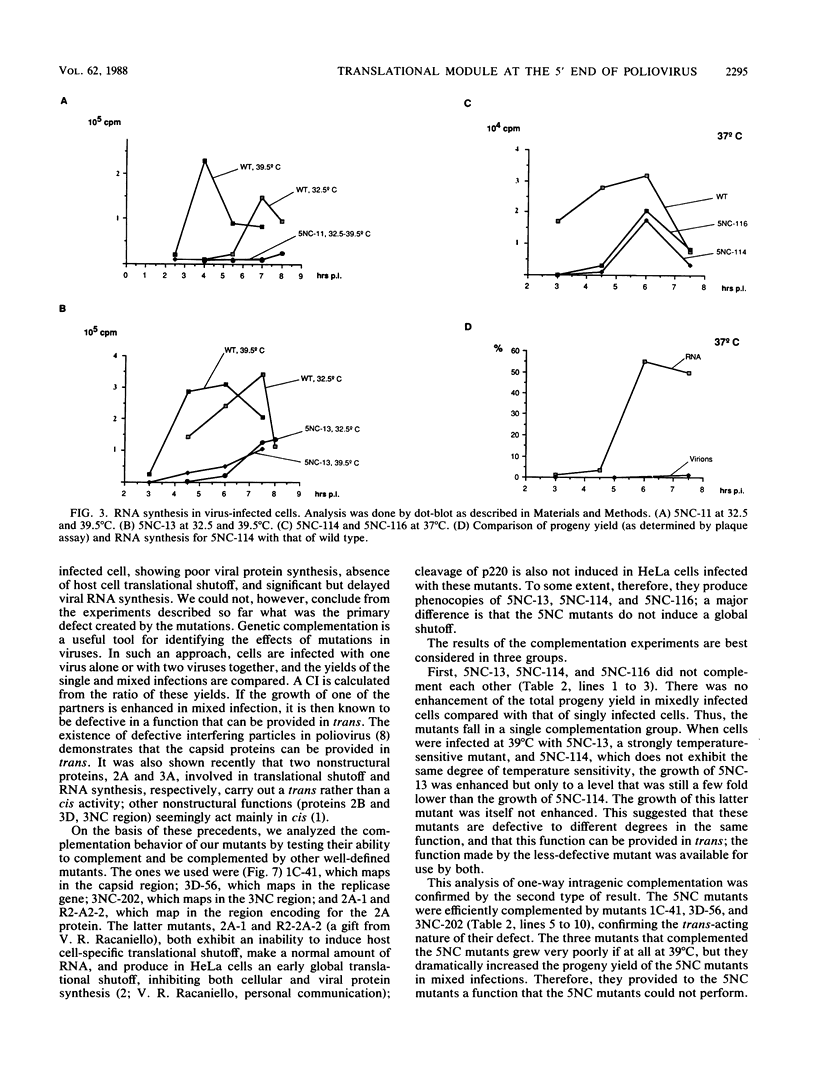
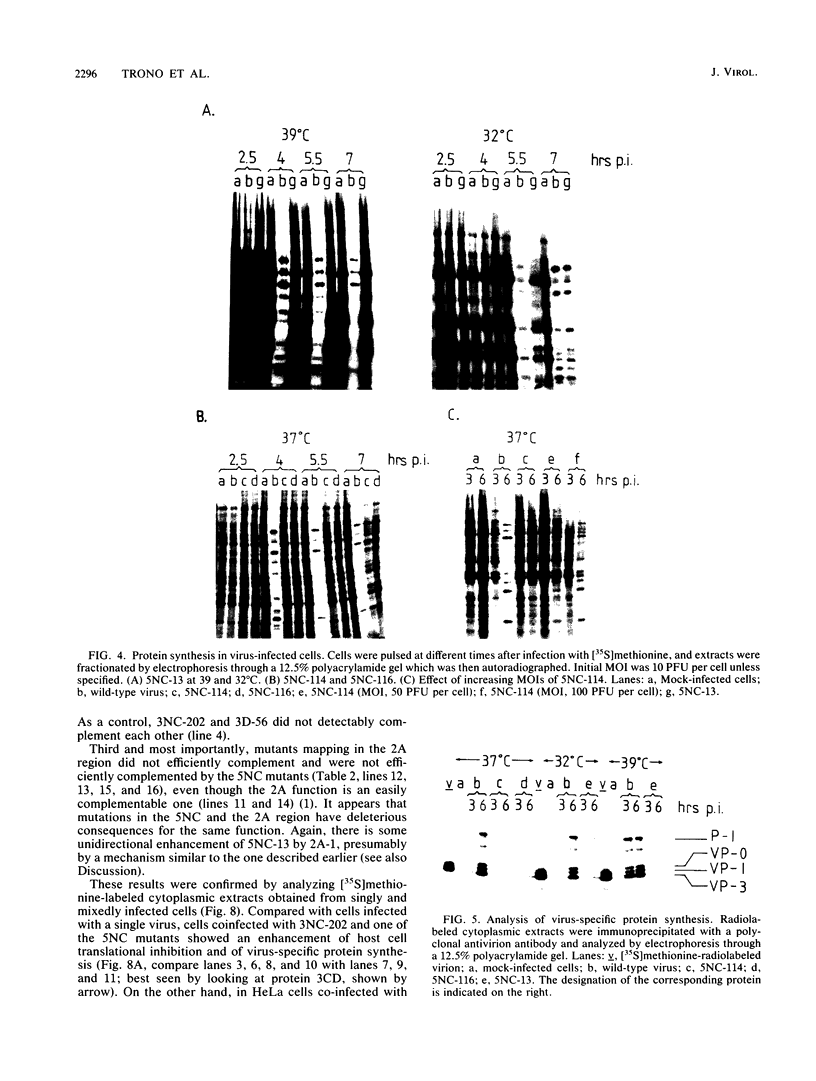
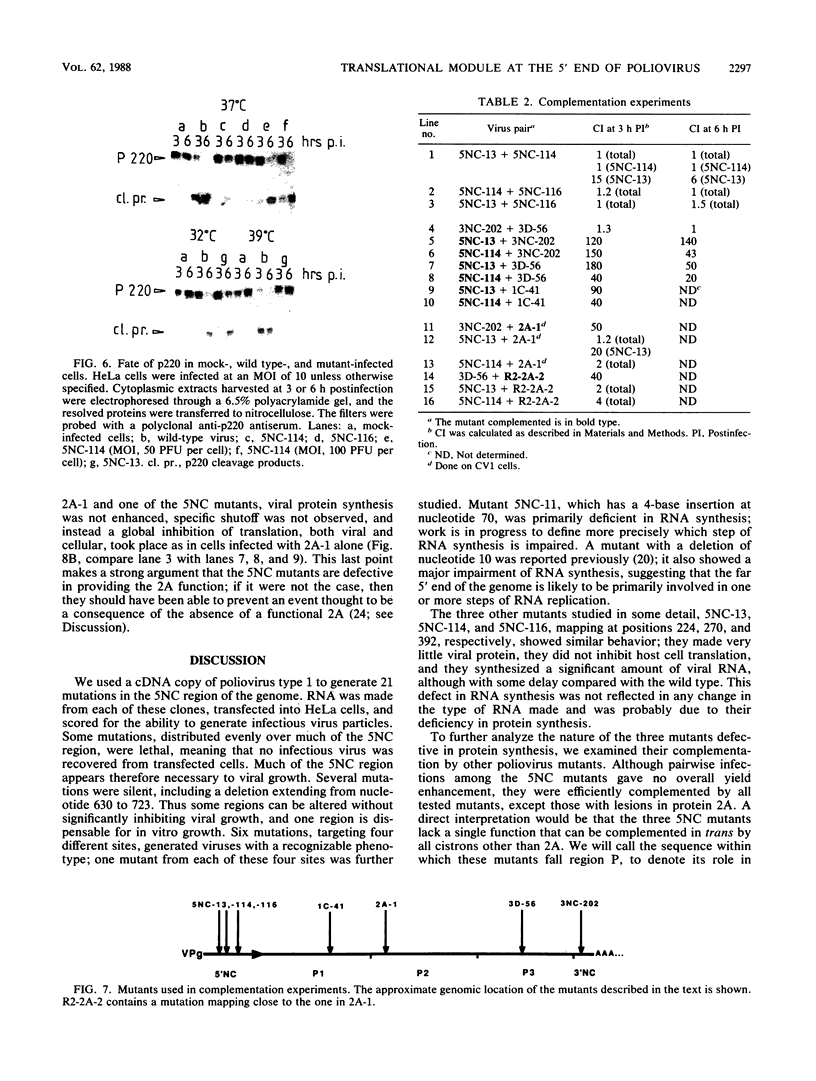
Twenty-one mutations were engineered in the 5' noncoding region of poliovirus type 1 RNA, using an infectious cDNA copy of the viral genome. RNA was made from these constructs and used to transfect HeLa cells. Viable virus was recovered from 12 of these transfection experiments, including six strains with a recognizable phenotype, mapping in four different regions. One mutant of each site was studied in more detail. Mutant 5NC-11, having a 4-base insertion at nucleotide 70, was dramatically deficient in RNA synthesis, suggesting that the far 5' end of the genome is primarily involved in one or more steps of RNA replication. Mutants 5NC-13, 5NC-114, and 5NC-116, mapping at nucleotides 224, 270, and 392, respectively, showed a similar behavior; they made very little viral protein, they did not inhibit host cell translation, and they synthesized a significant amount of viral RNA, although with some delay compared with wild type. These three mutants were efficiently complemented by all other poliovirus mutants tested, except those with lesions in protein 2A. Our results imply that these three mutants map in a region (region P) primarily involved in viral protein synthesis and that their inability to shut off host cell translation is secondary to a quantitative defect in protein 2A. The exact function of region P is still to be determined, but our data supports the hypothesis of a single functional module allowing viral protein synthesis and extending over several hundred nucleotides.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein H. D., Sarnow P., Baltimore D. Genetic complementation among poliovirus mutants derived from an infectious cDNA clone. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1040-1049.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Poliovirus mutant that does not selectively inhibit host cell protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2913–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonneau A. M., Sonenberg N. Proteolysis of the p220 component of the cap-binding protein complex is not sufficient for complete inhibition of host cell protein synthesis after poliovirus infection. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):986–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.986-991.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Dorner L. F., Larsen G. R., Wimmer E., Anderson C. W. Identification of the initiation site of poliovirus polyprotein synthesis. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1017–1028. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1017-1028.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Milburn S. C., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Hershey J. W. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis following poliovirus infection correlates with the proteolysis of a 220,000-dalton polypeptide associated with eucaryotic initiation factor 3 and a cap binding protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14806–14810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Dunn G., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Cann A. J., Stanway G., Almond J. W., Currey K., Maizel J. V., Jr Increased neurovirulence associated with a single nucleotide change in a noncoding region of the Sabin type 3 poliovaccine genome. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):548–550. doi: 10.1038/314548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett M. J., Rose J. K., Baltimore D. 5'-terminal structure of poliovirus polyribosomal RNA is pUp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):327–330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D. Defective viral particles and viral disease processes. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):325–327. doi: 10.1038/226325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuge S., Nomoto A. Construction of viable deletion and insertion mutants of the Sabin strain of type 1 poliovirus: function of the 5' noncoding sequence in viral replication. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1478–1487. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1478-1487.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Magnusson G. High efficiency polyoma DNA transfection of chloroquine treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1295–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Lee Y. F., Wimmer E. The 5' end of poliovirus mRNA is not capped with m7G(5')ppp(5')Np. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):375–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R., Sonenberg N. Cap-independent translation of poliovirus mRNA is conferred by sequence elements within the 5' noncoding region. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1103–1112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Cloned poliovirus complementary DNA is infectious in mammalian cells. Science. 1981 Nov 20;214(4523):916–919. doi: 10.1126/science.6272391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Molecular cloning of poliovirus cDNA and determination of the complete nucleotide sequence of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Meriam C. Poliovirus temperature-sensitive mutant containing a single nucleotide deletion in the 5'-noncoding region of the viral RNA. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):498–507. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90211-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Johnson V. H., Tracy S. A chimeric plasmid from cDNA clones of poliovirus and coxsackievirus produces a recombinant virus that is temperature-sensitive. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1777–1781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Regulation of translation by poliovirus. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:175–204. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svitkin Y. V., Maslova S. V., Agol V. I. The genomes of attenuated and virulent poliovirus strains differ in their in vitro translation efficiencies. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Kohara M., Kataoka Y., Suganuma T., Omata T., Imura N., Nomoto A. Complete nucleotide sequences of all three poliovirus serotype genomes. Implication for genetic relationship, gene function and antigenic determinants. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):561–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]