Abstract
Binding of the fibrinolytic proteinase plasmin (Pm) to streptokinase (SK) in a tight stoichiometric complex transforms Pm into a potent proteolytic activator of plasminogen. SK binding to the catalytic domain of Pm, with a dissociation constant of 12 pm, is assisted by SK Lys414 binding to a Pm kringle, which accounts for a 11-20-fold affinity decrease when Pm lysine binding sites are blocked by 6-aminohexanoic acid (6-AHA) or benzamidine. The pathway of SK·Pm catalytic complex formation was characterized by stopped-flow kinetics of SK and the Lys414 deletion mutant (SKΔK414) binding to Pm labeled at the active site with 5-fluorescein ([5F]FFR-Pm) and the reverse reactions by competitive displacement of [5F]FFR-Pm with active site-blocked Pm. The rate constants for the biexponential fluorescence quenching caused by SK and SKΔK414 binding to [5F]FFR-Pm were saturable as a function of SK concentration, reporting encounter complex affinities of 62-110 nm in the absence of lysine analogs and 4900-6500 and 1430-2200 nm in the presence of 6-AHA and benzamidine, respectively. The encounter complex with SKΔK414 was ∼10-fold weaker in the absence of lysine analogs but indistinguishable from that of native SK in the presence of 6-AHA and benzamidine. The studies delineate for the first time the sequence of molecular events in the formation of the SK·Pm catalytic complex and its regulation by kringle ligands. Analysis of the forward and reverse reactions supports a binding mechanism in which SK Lys414 binding to a Pm kringle accompanies near-diffusion-limited encounter complex formation followed by two slower, tightening conformational changes.
The central event in the fibrinolytic system is dissolution of fibrin clots by the serine proteinase, plasmin (Pm),2 formed by activation of the zymogen, plasminogen (Pg). The thrombolytic drug and streptococcal pathogenicity factor, streptokinase (SK) activates Pg to Pm through a unique mechanism (1, 2). SK acts by binding Pg and Pm in stoichiometric SK·Pg* and SK·Pm catalytic complexes that bind Pg as a specific substrate and proteolytically convert it into Pm by cleavage of Arg561-Val562 (1-8). The active site of Pg is conformationally induced in the catalytic SK·Pg* complex through the molecular sexuality mechanism, without the typically required proteolytic cleavage (3, 5, 6, 9-11). [Lys]Pm binds SK with ∼830-fold tighter affinity than unlabeled [Lys]Pg and with ∼3500-fold tighter affinity than fluorescently labeled [Lys]Pg (12, 13). Fluorescently labeled [Glu]Pg and [Lys]Pg analogs bind SK with ∼5-fold lower affinity than the native proteins, whereas the affinity for [Lys]Pm is unaffected by labeling. The magnitudes of the decreases in affinity induced by 6-AHA are not affected by active-site labeling.
Our equilibrium binding and steady-state kinetic studies describe a unified model for SK-Pg activation in which the conformationally activated SK·Pg* complex initially binds Pg as a specific substrate and cleaves it to Pm in a self-limiting, triggering mechanism (1, 2). Upon formation of slightly more than 1 SK eq of Pm, Pg is displaced from the SK·Pg* complex, and the much tighter SK·Pm catalytic complex is formed which propagates Pg activation through expression of a Pg binding exosite, converting the remaining free Pg to Pm in a second catalytic cycle (2).
Previous biophysical studies have shown that SK in solution behaves as independently folded domains linked by flexible segments, resulting in a highly mobile structure (14). When bound to micro-Pm (μPm), the isolated catalytic domain of Pm, however, the three SK β-grasp domains rearrange into a well defined crater-like structure surrounding the Pm active site (15). This large change in SK structure is accompanied by expression of the Pg substrate binding exosite (12).
The circulating form of the Pg zymogen, [Glu]Pg, consists of a 77-residue NH2-terminal peptide, five kringle domains (K1-K5), some of which contain lysine binding sites (LBS), and a COOH-terminal serine proteinase catalytic domain (16, 17). K1, K2, K4, and K5 exhibit varying degrees of affinity for lysine analogs and small aromatic ionic ligands (18). K1, K4, and K5 mediate Pg and Pm binding to COOH-terminal lysine residues on fibrin and to lysine and arginine residues of other proteins (19-24). The LBS located in K5 is thought to be primarily responsible for interactions with the NH2-terminal peptide in [Glu]Pg, keeping the zymogen in a spiral, compact α-conformation (25-28). Removal of the NH2-terminal peptide by Pm cleavage results in formation of [Lys]Pg, which assumes a partially extended β-conformation that is more rapidly activated by tissue-type plasminogen activator and urokinase and by the SK·Pg* and SK·Pm catalytic complexes (2, 29-32). The lysine analog 6-aminohexanoic acid (6-AHA) binds with high affinity to K1 (KD 11-13 μm) and to lower affinity sites on K4 (KD 20-60 μm) and K5 (KD 95-140 μm) based on studies of the isolated kringle domains (17, 18, 33, 34). Benzamidine binds isolated K5 with highest affinity (KD 290 μm), interacts weaker with K1 (KD 12.5 mm) and K2 (KD 33 mm), and displays insignificant affinity for K3 and K4 (18, 35, 36). Benzamidine also induces a partially extended β-conformation of [Glu]Pg but, unlike 6-AHA, does not induce the transition of [Lys]Pg to the fully extended γ-form (25, 27). The affinity of SK for native and fluorescently labeled [Glu]Pg in the compact conformation is relatively low and is unaffected by 6-AHA, whereas expression of LBS in the β-conformation of [Lys]Pg and [Lys]Pm increases affinity for SK, which is weakened ∼13-20-fold by 6-AHA in interactions mediated by the COOH-terminal Lys414 residue of SK (1, 13, 37). Pm retains significant affinity for SK when LBS interactions are blocked (KD 200-300 pm) through its interactions with the catalytic domain of Pm. LBS interactions, thus, play a critical role in formation and stabilization of the SK·Pm catalytic complex.
The present study describes the first rapid-reaction kinetics investigation of active site fluorescently labeled Pm binding to SK, characterizes the binding and conformational intermediates on the pathway, and identifies LBS-dependent steps. Stopped-flow fluorescence kinetics of SK binding to fluoresce-in-labeled [Lys]Pm identified the forward reactions of complex stabilization, whereas the reverse reactions were examined by competitive displacement of fluorescently labeled Pm from SK by unlabeled, active site-blocked Pm. Combined analysis of forward and reverse reactions allowed the sequence of elementary reaction steps of the mechanism to be delineated for the first time. Our results support the hypothesis that LBS-dependent near-diffusion-limited SK binding to form an SK·Pm encounter complex is followed by two consecutive, favorable conformational changes. The much slower competitive displacement presents as an apparent first-order process but is governed by an off-rate that is a function of the forward and reverse rate constants for the second and third steps. The conformational changes are hypothesized to reflect in part, changes in SK from its flexible conformation in solution to its ordered structure when it binds to Pm and/or a conformational change affecting the Pm catalytic site in processes that involve specific LBS interactions that are differentially affected by benzamidine and 6-AHA. Interaction of SK Lys414 with a Pm kringle contributes primarily to stabilizing the SK·Pm encounter complex in the first step of the pathway.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Protein Purification and Characterization—Human [Glu]Pg carbohydrate form 2 ([Glu]Pg2) was purified from plasma by published procedures (38, 39). Activation of 10 μm [Glu]Pg2 to [Lys]Pm2 with 90 units/ml urokinase (Calbiochem) was performed in 10 mm Mes, 10 mm Hepes, 0.15 m NaCl, 20 mm 6-AHA, and 1 mg/ml polyethylene glycol 8000 (PEG) at pH 7.4 and 25 °C. Pm was purified by affinity chromatography on soybean trypsin inhibitor-agarose (12). Pm was dialyzed against 5 mm Hepes, 0.3 m NaCl, 10 mm 6-AHA, and 1 mg/ml PEG at pH 7.0 and 4 °C. The active site of Pm (10-15 μm) was blocked with a 5-fold molar excess of d-Phe-Phe-Arg-CH2Cl (FFR-CH2Cl) in 0.1 m Hepes, 0.3 m NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 10 mm 6-AHA, 1 mg/ml PEG, pH 7.0 buffer at 25 °C for 30-60 min, reducing the initial rate of hydrolysis of d-Val-Leu-Lys-para-nitroanilide to <0.1%, as described previously (12, 13). Excess inhibitor was removed by dialysis against >250 volumes of 50 mm Hepes, 0.3 m NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, pH 7.0 at 4 °C. Native SK (Diapharma) was obtained as outdated therapeutic material and purified as described (40). The SKΔK414 mutant was prepared as described previously (37). All proteins were quick-frozen in 2-propanol/dry ice and stored at -70 °C. Protein concentrations were determined by absorbance at 280 nm using the following absorption coefficients ((mg/ml)-1cm-1) and molecular weights: Pm, 1.9 and 84,000 (39); SK and SKΔK414, 0.95 and 47,000 (41, 42). The active Pm concentration (90% of total protein) was determined by active-site titration with fluorescein mono-p-guanidinobenzoate (43).
Active-site Labeling of Pm—The active-site specific inhibitor, Nα-[(acetylthio)acetyl]-(d-Phe)-Phe-Arg-CH2Cl (ATA-FFR-CH2Cl), prepared by published procedures (44-46), was incubated at a 5-fold molar excess with 10-15 μm [Lys]Pm2 in 0.1 m Hepes, 0.3 m NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 10 mm 6-AHA, 1 mg/ml PEG, pH 7.0, at 25 °C for 60 min until inhibition was complete (<0.1% activity). Excess inhibitor was removed by dialysis against 50 mm Hepes, 0.3 m NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 1 mg/ml PEG, pH 7.0 at 4 °C. Quantitation of inhibitor incorporation measured from the amplitude of the burst reaction of NH2OH-generated thiol with 5,5′-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (46) indicated 0.8-1.4 mol thioester/mol of Pm active sites. The thiol group on the incorporated inhibitor generated by treatment of ATA-FFR-Pm with NH2OH was labeled with 5-(iodoacetamido)fluorescein to yield [5F]FFR-Pm as described (12, 13). Excess dye was removed by chromatography on Sephadex G25 superfine followed by extensive dialysis. [5F]FFR-Pm concentration and probe incorporation (87%) were determined from the probe and protein absorbance in 6 m guanidine as described (44). Proteins were homogeneous by SDS gel electrophoresis.
Stopped-flow Kinetics of SK and SKΔK414 Binding to [5F]FFR-Pm—Time traces of SK and SKΔK414 binding to [5F]FFR-Pm were acquired with an Applied Photophysics SX-18MV stopped-flow spectrofluorometer in single mixing mode. Fluorescence was measured with excitation at 500 nm and an emission cut-on filter (Melles-Griot) with 50% transmission at 515 nm. The reaction volume was 200 μl, path length was 2 mm, and experiments were performed at 25 °C. SK or SKΔK414 (0.025-15 μm) and [5F]FFR-Pm (5-20 nm) were reacted under pseudo-first order conditions (SK ≥ 5-fold over labeled Pm at the lowest concentration) in 50 mm Hepes, 0.125 m NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 1 mg/ml PEG, 1 mg/ml bovine serum albumin, 1 μm FFR-CH2Cl, pH 7.4, in the absence and presence of 50 mm 6-AHA or in 50 mm Hepes, 0.075 m NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 1 mg/ml PEG, 1 mg/ml bovine serum albumin, 1 μm FFR-CH2Cl, pH 7.4, containing 50 mm benzamidine to maintain constant ionic strength. Time traces (1000 data points) of near-complete (>95%) exponential fluorescence decreases ranged from 0.5 to 30 s, depending on the SK concentration and the presence of effector. Typically, 10 time traces were averaged for each SK concentration. Control reactions containing buffer and SK only, and buffer and [5F]FFR-Pm only, were performed to quantitate background and initial probe fluorescence, respectively, and to permit transformation of raw data into the fractional change in initial fluorescence ((Fobs - Fo)/Fo = ΔF/Fo). Averaged time traces were analyzed using Equation 1,
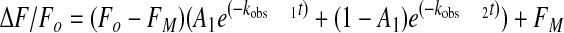 |
(Eq.1) |
where Fo is the starting fluorescence, FM is the final fluorescence, A1 is the fractional amplitude of the first exponential, (1 - A1) is the fractional amplitude of the second exponential, and kobs 1 and kobs 2 are the observed first-order rate constants. The observed pseudo-first order rate constants for each process were analyzed as a function of the total SK concentration ([SK]o) using Equation 2,
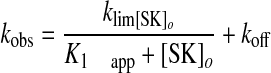 |
(Eq.2) |
where klim is the maximal value for the rate constant, K1 app is the apparent dissociation constant for the SK·Pm encounter complex, and koff is the overall reverse rate constant for binding. In addition, arrays of time traces at varying SK concentrations were analyzed simultaneously using the numerical integration programs Dynafit (47) and KinTek Explorer (KinTek Corp.), combining numerical solution of the differential equations generated from the mechanism with nonlinear least-squares analysis.
Competitive Dissociation of [5F]FFR-Pm from Its Complex with SK or SKΔK414 by FFR-Pm—Measurements were performed with an SLM 8100 spectrofluorometer or a Photon Technology International QuantaMaster 6000 fluorometer using acrylic cuvettes coated with polyethylene glycol 20,000. The excitation and emission wavelengths were 500 and 516 nm, respectively, with 4/8 nm and 2/8 nm excitation/emission band passes on the SLM and the Photon Technology International instruments, respectively. [5F]FFR-Pm (10-22 nm) was incubated with excess SK or SKΔK414 (15-100 nm) at 25 °C in the absence and presence of 50 mm 6-AHA or in buffer containing 0.075 m NaCl and 50 mm benzamidine until the fluorescence was stable (∼15 min). The reverse reaction was initiated by the addition of 100-1000 nm FFR-Pm, such that any remaining free SK was saturated with FFR-Pm, and the dissociation of SK from the SK·[5F]FFR-Pm complex by the remaining FFR-Pm was apparently first order in SK·[5F]FFR-Pm complex concentration. The increase in fluorescence was monitored until it was >90% complete, typically 4 h. Corrections were made for background scattering by subtraction of blanks containing all reactants except [5F]FFR-Pm. Corrections for instrument drift and probe photobleaching were done using cuvettes containing [5F]FFR-Pm and SK to form the complex, with the addition of buffer instead of FFR-Pm. Results expressed as ΔF/Fo versus time were fit by a single exponential to obtain estimates of koff. Least-squares fitting was performed with SCIENTIST Software (MicroMath), and the progress curves were also analyzed by numerical integration with Dynafit and Kintek Explorer. The latter program allowed simultaneous analysis of the competitive dissociation experiments and the array of forward reaction time traces at varying SK concentrations. All reported estimates of error represent ± 2 S.D. Equation 3 shows the analytical expression for koff in a 3-step binding reaction (48), rearranged as an expression of rate constants for the three steps,
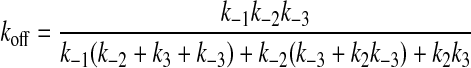 |
(Eq.3) |
Equilibrium Binding of [5F]FFR-Pm and FFR-Pm to SK and SKΔK414 in the Presence of Benzamidine—[5F]FFR-Pm was titrated with SK or SKΔK414 at 25 °C in the above-described buffer containing 50 mm benzamidine. Fluorescence titrations were performed with the Photon Technology International fluorometer at excitation and emission wavelengths of 500 and 516 nm, respectively, with 2/8-nm excitation/emission band passes. Fluorescence changes were measured after equilibration for 5-10 min. In the competitive binding experiments, SK or SKΔK414 was titrated into a mixture of labeled Pm and FFR-Pm. Concentrations of FFR-Pm were 5 and 15 nm in the titrations with SK and 10 nm in the titrations with SKΔK414. Measurements were corrected for background (≤10%) by subtraction of blanks lacking [5F]FFR-Pm. Simultaneous nonlinear least-squares fitting with SCIENTIST software was performed of the [5F]FFR-Pm titrations with SK or SKΔK414 in the absence and presence of fixed FFR-Pm concentrations by the cubic equation for tight competitive binding of a single ligand (SK or SKΔK414) to labeled ([5F]FFR-Pm) and non-labeled acceptor (FFR-Pm) (49-51). The cubic equation is an exact solution for competitive binding of one ligand to two acceptors, typically one fluorescently labeled that reports the interaction and the non-labeled competitor, under conditions where the assumption cannot be made that free and total ligand concentrations are approximately equal (49-51). This analysis gave the dissociation constant (KC) and stoichiometric factor (m) for competitive binding of SK or SKΔK414 to FFR-Pm as well as the maximum fluorescence intensity change (ΔFmax/Fo), the dissociation constant (KD), and the stoichiometric factor (n) for binding of SK or SKΔK414 to [5F]FFR-Pm (49-51).
RESULTS
Stopped-flow Kinetics of SK and SKΔK414 Binding to
[5F]FFR-Pm—Changes in fluorescein fluorescence after rapid mixing
of excess SK or SKΔK414 with [5F]FFR-Pm were biexponential in the
absence of effectors but less distinctly so in the presence of saturating (50
mm) 6-AHA or benzamidine as illustrated by the respective
logarithmic transformations of ΔF/Fo
(Figs. 1, A and
B). However, single exponential analysis of the time
traces in the presence of 6-AHA and benzamidine consistently gave poorer fits
with non-random residuals; hence, all time traces were analyzed with the
biexponential Equation 1. The first-order rate constants kobs
1 and kobs 1 for the fast and slow fluorescence
quenches increased hyperbolically with increasing SK and SKΔK414
concentration (Fig. 2). These
results support a minimal mechanism in which relatively weak initial binding
of SK occurs in the rapid mixing dead-time, with formation of a fluorescently
silent SK·Pm encounter complex with a dissociation constant
K1. This step is followed on the seconds time scale by two
distinct, resolvable conformational rearrangements tightening the SK·Pm
complex to form SK·Pm* and SK·Pm**
complexes, contributing to the fluorescence quenching, each with
characteristic amplitudes that were fitted parameters (Equation
4).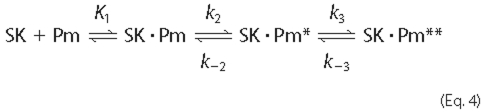
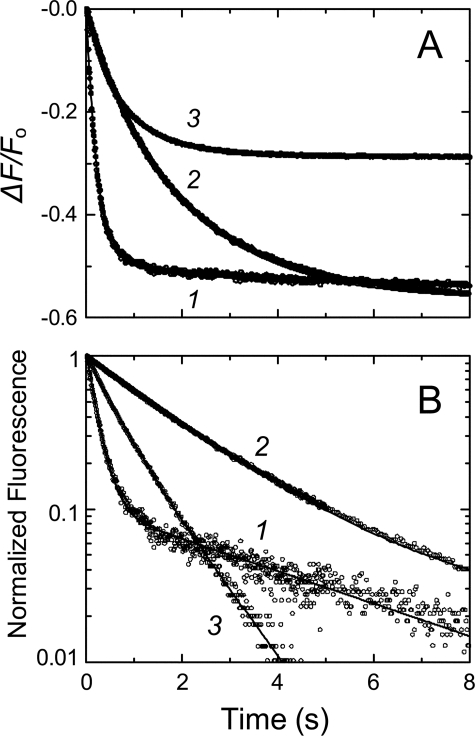
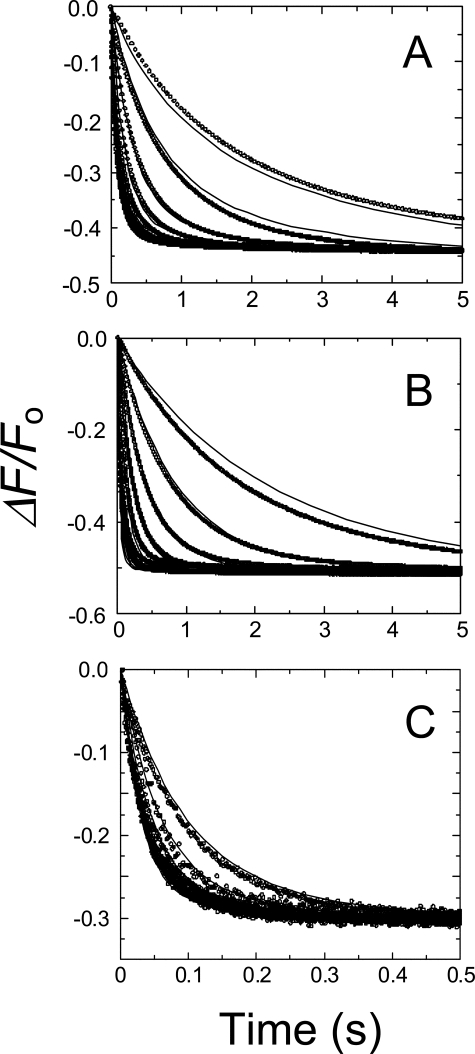
FIGURE 1.
Representative stopped-flow fluorescence traces of SK binding to [5F]FFR-Pm. A, fractional fluorescence changes (ΔF/Fo) (○) after rapid mixing of [5F]FFR-Pm and SK versus time in the absence of lysine analog (1) and in the presence of 50 mm 6-AHA (2) or 50 mm benzamidine (3). Final SK concentrations were 100, 100, and 50 nm, and [5F]FFR-Pm concentrations were 5, 20, and 10 nm, respectively. B, semilogarithmic plot of the normalized fluorescence data (○). Solid lines represent the least-squares fits of double exponentials. Stopped-flow time-traces were acquired and analyzed as described under “Experimental Procedures.”
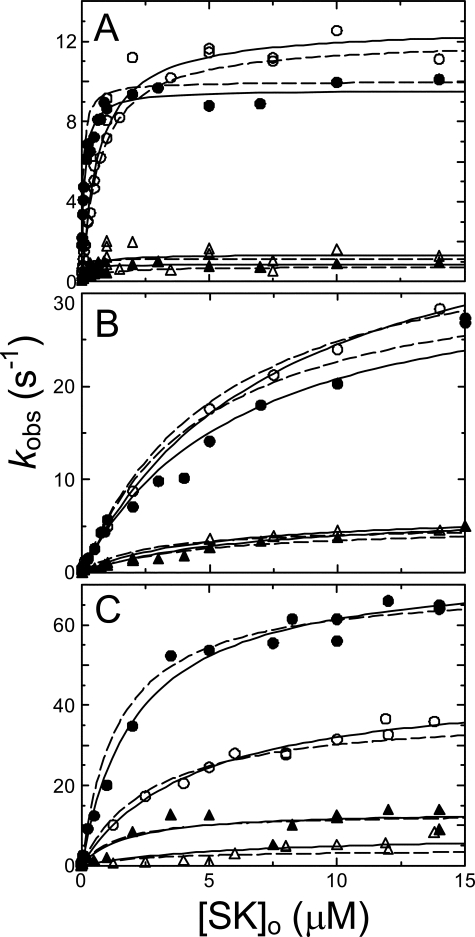
FIGURE 2.
Dependence of the kinetics of [5F]FFR-Pm binding on SK and SKΔK414 concentration. A, dependences of kobs 1 (•, SK; ○, SKΔK414) and kobs 2 (▴, SK; ▵, SKΔK414) for the first and second phases of 5-20 nm [5F]FFR-Pm binding on the total SK or SKΔK414 concentration ([SK]o) in the absence of lysine analogs. B, dependences of kobs 1 (•, SK; ○, SKΔK414) and kobs 2 (▴, SK; ▵, SKΔK414) on the total SK or SKΔK414 concentration in the presence of 50 mm 6-AHA. C, dependences of kobs 1 (•, SK; ○, SKΔK414) and kobs 2 (▴, SK; ▵, SKΔK414) on the total SK concentration in the presence of 50 mm benzamidine. Solid lines represent the least-squares fits by Equation 2, with the parameters given in Table 1. Dashed lines represent the least-squares fits using numerical integration of the reactions in Equation 4, with the parameters in Table 1. Experiments were performed and analyzed as described under “Experimental Procedures”.
Expression of the data as ΔF/Fo showed that the reactions started at zero, indicating no change associated with encounter complex formation. The hyperbolic dependence of kobs1 on SK concentration demonstrated the effect of the encounter complex (Fig. 2). K1 represents the ratio k-1/k1, with k1 and k-1 the second- and first-order rate constants for association and dissociation of the encounter complex, respectively, and k2, k-2, k3, and k-3 the first-order forward and reverse rate constants for the subsequent conformational rearrangements. K1, k2, and k3 correspond to the parameters K1 app, klim 1 and klim 2 defined by the nonlinear least-squares analysis of the kobs 1 and kobs 2 dependences on SK or SKΔK414 concentration (Fig. 2).
The fitted parameters K1 app, klim 1, and klim 2 obtained from nonlinear least squares analysis of the binding rate constants as a function of SK and SKΔK414 concentration in the absence of lysine analogs and in the presence of 6-AHA or benzamidine are given in Table 1. In the absence of lysine analogs, the encounter complex with SK was characterized by K1 app of 110 ± 20 nm, whereas the SKΔK414 mutant showed an ∼6-fold weaker interaction of 670 ± 130 nm, suggesting a distinct role of the COOH-terminal Lys414 residue in initial docking of SK with the Pm molecule. The limiting rate constants klim 1 and klim 2 for SK were comparable with those for SKΔK414 (Fig. 2A, Table 1), indicating only limited involvement of Lys414 in complex stabilization. The encounter complexes of Pm with SK and SKΔK414 in the presence of 50 mm 6-AHA displayed 59- and 12-fold weaker, identical affinities, respectively, with K1 app of 6.5 and 7.8 μm and identical rate constants for the conformational changes, suggesting the involvement of Pm kringle interactions both in initial encounter complex formation and in stabilization of the complex (Fig. 2B, Table 1). Interestingly, the rates for the conformational changes were 3-4-fold faster than in the absence of lysine analogs, reflected by higher values for klim 1 and klim 2.
TABLE 1.
Kinetic and equilibrium binding parameters for SK·Pm and SKΔK414·Pm formation
Kinetic constants determined from analysis of the forward and reverse reactions and by numerical integration are listed for Equation 4 in the absence of kringle ligands (No effector), the presence of saturating 6-AHA, and saturating benzamidine. KD,overall, calculated from the kinetic parameters and measured by fluorescence titration, and fluorescence change amplitudes (ΔFmax/Fo), determined from the kinetic analysis for the indicated species, are listed. Experiments were performed and analyzed as described under “Experimental Procedures.”
| K1 (encounter) | k2 | k−2a | k3 | k−3a | KD,overall | koff | ΔFmax/Fo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nm | s−1 | s−1 | s−1 | s−1 | pm | s−1 | % | |
| No effector | ||||||||
| SK | 62 ± 2a | 10.0 ± 0.1a | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 1.2 ± 0.1a | 0.009 ± 0.001 | 7 ± 1b | 0.0008 ± 0.0001a | SK·Pm*, −48 ± 2 |
| 110 ± 20c | 9.6 ± 0.3c | 0.9 ± 0.2c | 12 ± 4d | 0.0007 ± 0.0001b | SK·Pm**, −54 ± 2 | |||
| SKΔK414 | 720 ± 6a | 12.1 ± 0.1a | 0.29 ± 0.01 | 0.8 ± 0.1a | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 59 ± 3b | 0.0007 ± 0.0001a | SK·Pm*, −42 ± 2 |
|
670 ±
130c |
12.7 ±
0.7c |
1.4 ±
0.3c |
190 ±
40d |
0.0009 ±
0.0001c |
SK·Pm**, −45 ± 2
|
|||
| 6-AHA | ||||||||
| SK | 4900 ± 60a | 34 ± 1a | 1.07 ± 0.09 | 5.1 ± 0.2a | 0.005 ± 0.001 | 140 ± 20b | 0.0008 ± 0.0001a | SK·Pm*, −50 ± 2 |
| 6500 ± 1400b | 34 ± 1c | 6.5 ± 0.4c | 210 ± 20d | 0.0007 ± 0.0001b | SK·Pm**, −59 ± 2 | |||
| SKΔK414 | 5560 ± 50a | 39 ± 1a | 1.29 ± 0.01 | 5.0 ± 0.2a | 0.004 ± 0.001 | 140 ± 20b | 0.0008 ± 0.0001a | SK·Pm*, −45 ± 2 |
|
7800 ±
1100c |
43 ±
3c |
6.4 ±
1.2c |
350 ±
80d |
0.0008 ±
0.0001c |
SK·Pm**, −51 ± 2
|
|||
| Benzamidine | ||||||||
| SK | 1430 ± 30a | 64 ± 2a | 3.9 ± 0.8 | 17 ± 1a | 0.015 ± 0.002 | 77 ± 20b | 0.003 ± 0.001a | SK·Pm*, −26 ± 2 |
| 2200 ± 500c | 75 ± 5c | 14 ± 4c | 280 ± 160d | 0.003 ± 0.001c | SK·Pm**, −31 ± 2 | |||
| SKΔK414 | 2840 ± 20a | 39 ± 1a | 0.47 ± 0.01 | 4.0 ± 0.1a | 0.020 ± 0.001 | 170 ± 50b | 0.003 ± 0.001a | SK·Pm*, −28 ± 2 |
| 4500 ± 1500c | 46 ± 6c | 7.8 ± 1.6c | 370 ± 180d | 0.003 ± 0.001c | SK·Pm**, −31 ± 2 |
The encounter complex with SK in the presence of 50 mm benzamidine was ∼20-fold weaker than in the absence of kringle ligands, with K1 app of 2.2 μm, and even faster limiting rates of 75 and 14 s-1 for the two conformational changes. K1 app for the encounter complex with SKΔK414 was 4.5 ± 1.5 μm, comparable with that for native SK (Fig. 2C, Table 1), and klim 1 and klim 2 values of 46 ± 6 s-1 and 7.8 ± 1.6 s-1, respectively. The reverse rate constants, given by the extrapolated intercept of kobs 1 or kobs 1 at zero SK concentration, approximated zero and were too small to be determined accurately from the SK dependences.
The total amplitudes of the time traces fit by Equation 1 and by numerical analysis reflected the overall maximal fluorescence changes (ΔFmax/Fo) for SK and SKΔK414 binding to [5F]FFR-Pm and were in good agreement with previous equilibrium binding results in the absence and presence of 6-AHA (13, 37) and with results for binding in the presence of benzamidine described below (Table 1).
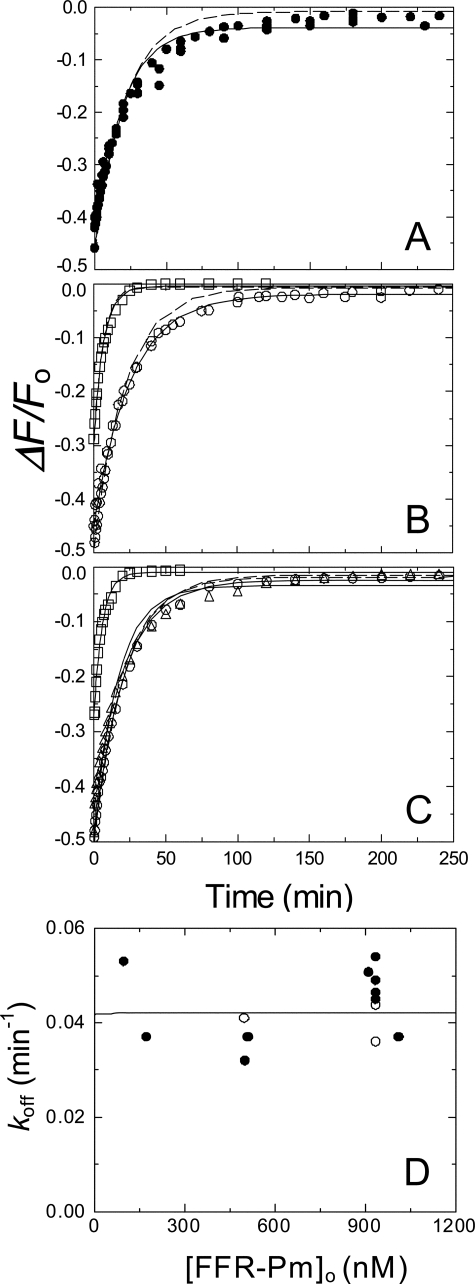
Competitive Displacement of [5F]FFR-Pm from Its Complex with SK or SKΔK414 by FFR-Pm—The addition of up to a ∼100-fold excess of unlabeled FFR-Pm to the preformed SK·[5F]FFR-Pm complex after fluorescence stabilization caused an extremely slow, apparently single exponential increase of fluorescence, approaching the initial fluorescence intensity (Fig. 3A). This process represented a slow reversal of SK or SKΔK414 binding to [5F]FFR-Pm in the final complex and parallel formation of non-fluorescent SK·FFR-Pm. The overall off-rate constant (koff) of ∼0.0008 s-1 obtained by single exponential analysis did not change throughout the investigated FFR-Pm concentration range, consistent with saturation of the slow process (Fig. 3D), and was similar for reversal of the complex with SK and SKΔK414 in the absence of effectors and the presence of 6-AHA (Figs. 3, B and C, Table 1). Benzamidine caused a ∼4-fold increase in koff both with SK and SKΔK414 (Figs. 3, B and C, Table 1).
FIGURE 3.
Kinetics of competitive dissociation of SK and SKΔK414 from the [5F]FFR-Pm complex by FFR-Pm. Increases in fluorescence after the addition of excess FFR-Pm to pre-equilibrated mixtures of [5F]FFR-Pm and SK or SKΔK414 due to dissociation of the of the SK·[5F]FFR-Pm complex. A, time courses for dissociation of the SK·[5F]FFR-Pm complex in the absence of effector (•). B, time courses in the presence of 50 mm 6-AHA (○) or 50 mm benzamidine (□). C, dissociation of the of the SKΔK414·[5F]FFR-Pm complex in the absence of effector (○), the presence of 50 mm 6-AHA (▵), or 50 mm benzamidine (□). Final concentrations of [5F]FFR-Pm, SK or SKΔK414, and FFR-Pm were 10, 100, and 910 nm, respectively. Solid lines represent the least-squares fits by a single exponential, with the parameters given in Table 1, and dashed lines represent the fits using the parameters obtained from nonlinear least-squares analysis of the mechanism in Equation 4 by numerical integration. D, the apparent off-rate as a function of increasing FFR-Pm concentration ([FFR-Pm]o). The solid line represents simulation of a hyperbola using a KD value of 12 pm and a limiting rate equal to the averaged koff value of 0.042 min-1 for reactions in the absence (•) and presence (○) of 50 mm 6-AHA. Experiments were performed and analyzed as described under “Experimental Procedures.”
Nonlinear Least-squares Analysis of the Forward and Reverse Reactions by Numerical Integration—Arrays of forward reaction time traces of [5F]FFR-Pm binding at varying SK or SKΔK414 concentrations, and time traces of the reverse reactions were analyzed simultaneously using Kintek Explorer and separately by Dynafit for the mechanism in Equation 4. For analysis of the reverse reactions, the equilibria were expanded to include competitive binding of FFR-Pm and [5F]FFR-Pm to SK. Concentrations of the various SK·[5F]FFR-Pm intermediates at the initiation of the reverse reactions were calculated iteratively using (a) the starting concentrations of SK and [5F]FFR-Pm used to form the complex, (b) the forward and reverse rate constants for complex formation of SK with [5F]FFR-Pm, and (c) the known dissociation constant for formation of the competitive, unlabeled SK·FFR-Pm complex. Formation and disappearance of each reaction species in the mechanism were simulated using the Kinetics 1.0 numerical integration program (ARSoftware).
The data were fit by the 3-step mechanism (Equation 4) using the parameter
values obtained for the SK and SKΔK414 dependences as initial estimates.
A lower limit of 5 × 108
m-1s-1 was required for the on-rate constant
k1 value as an initial estimate to obtain fitted
parameters K1, k2, and
k3 consistent with the parameters obtained from the SK
dependences and with the overall dissociation constant
KD,overall defined by Equation
5,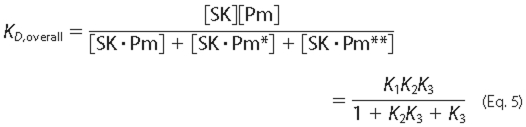
Values of k larger than 5 × 108 m-1s-1, extending into the range of the diffusion-controlled collisional limit of 109-1010m-1s-1 (52) fit the data equally well, suggesting that encounter complex formation is near-diffusion-limited.
Fitting of the displacement data by numerical integration required several iterative fits to narrow down the respective concentrations of the SK·[5F]FFR-Pm* and SK·[5F]FFR-Pm** complexes, the sum of which was equal to the concentration of [5F]FFR-Pm in the displacement reaction (9-10 nm). K1, k2, and k3 were constrained initially, to narrow down estimates for k-2 and k-3. The parameters and respective concentrations of complexes resulting in adequate fits for both forward and reverse reactions required the following two criteria to be met; KD,overall approaching the experimentally determined value in equilibrium binding measurements, and kinetics of appearance of free [5F]FFR-Pm in the reverse reaction, consistent with near-complete reversal and characterized by a rate constant comparable with koff. The final results for all fitted parameters are listed in Table 1, and the best fits for simultaneous analysis of time traces at varying SK and SKΔK414 concentrations are shown in Figs. 4 and 5. The three-step mechanism gave fitted parameters KI, k2, and k3 that were consistent with the values of K1 app, klim 1, and klim 2 obtained from the SK and SKΔK414 dependences of kobs 1 and kobs 1 using Equation 1 (Fig. 2) and KD,overall values calculated by Equation 5, in good agreement with those determined independently by equilibrium binding under all experimental conditions. The KD,overall values obtained from the numerical analysis were consistently ∼2-fold tighter because a representative subset of the time traces was used for this analysis. Simultaneous analysis of the displacement traces gave good estimates for koff, calculated by Equation 3, consistent with the apparent first-order rate constants obtained from single exponential analysis of the displacement curves (Fig. 3, Table 1). The combined fluorescence amplitudes of the SK·Pm* and SK·Pm** complexes obtained by numerical analysis (Table 1) were in good agreement with the overall maximum changes for SK and SKΔK414 binding to [5F]FFR-Pm, obtained from the time traces fit by Equation 1 and from equilibrium binding (13) and benzamidine results presented here.
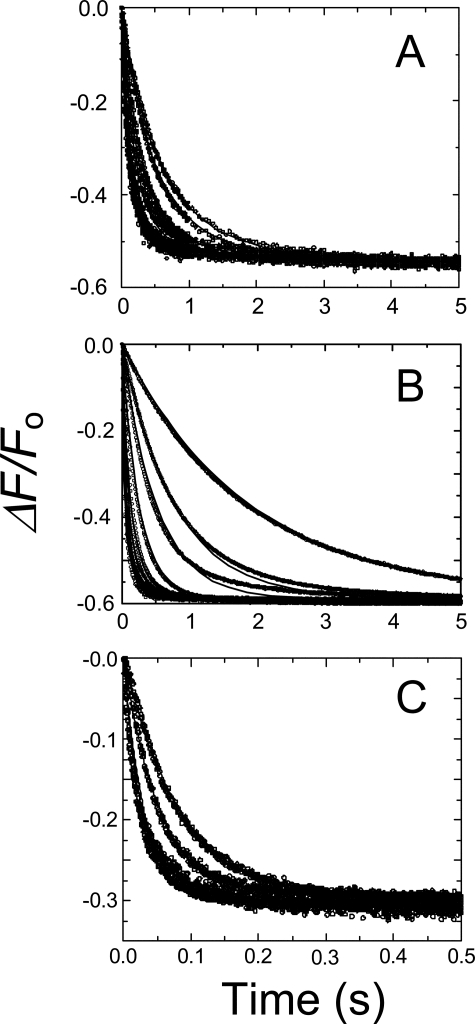
FIGURE 4.
Simultaneous fits of SK concentration and time dependences based on numerical integration. Stopped-flow time-traces of the fractional change in fluorescence (ΔF/Fo) for reactions of 10 nm [5F]FFR-Pm with 0.025, 0.030, 0.052, 0.075, 0.1, 0.2, 0.35, 0.65, 0.9, 2, 5, 7, 10, and 14 μm SK in the absence of lysine analog (A). 0.1, 0.25, 0.4, 0.9, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, and 15 μm SK in the presence of 50 mm 6-AHA (B), and 0.5, 1, 5 and 10 μm SK in the presence of 50 mm benzamidine (C). Data were collected during 0.5-30 s, until the reactions were >99% complete, and the fluorescence was stable. Data shown represent 92-99% completion of the reactions. Solid lines represent the least-squares fits to complete time traces using the mechanism in Equation 4, with the parameters listed in Table 1. Experiments were performed, and data were analyzed as described under “Experimental Procedures” and “Results.”
FIGURE 5.
Simultaneous fits of SKΔK414 concentration and time dependences based on numerical integration. Stopped-flow time-traces of the fractional change in fluorescence (ΔF/Fo) for reactions of 10 nm [5F]FFR-Pm with 0.050, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, and 14 μm SKΔK414 in the absence of lysine analog (A), 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 7.5, 10, and 14 μm SKΔK414 in the presence of 50 mm 6-AHA (B), and 1.25, 4, 6, 8, 10 and 14 μm SKΔK414 in the presence of 50 mm benzamidine (C). Data were collected during 0.5-30 s until the reactions were >99% complete, and the fluorescence was stable. Data shown represent 85-99% completion of the reactions. Solid lines represent the least-squares fits to complete time traces using the mechanism in Equation 4, with the parameters listed in Table 1. Experiments were performed and data were analyzed as described under “Experimental Procedures” and “Results.”
In the absence of effectors, KD,overall was 7 ± 1 pm for SK binding and 59 ± 3 pm for SKΔK414 binding. The ∼8-fold lower affinity of the SKΔK414 mutant was largely caused by weakening of the encounter complex, with K1 720 ± 6 nm, compared with 62 ± 2 nm for the complex with native SK. Native and mutant SK had comparable forward and reverse rate constants for the two conformational tightening steps (Table 1). Although the displacement process was apparently single-exponential, it was adequately described by the three-step mechanism using the analytical solution for expressing koff given by Equation 3 and the kinetic constants determined by numerical analysis (Table 1). The koff values determined from numerical analysis and from single exponential analysis of the displacement curves were in excellent agreement (Fig. 3, Table 1).
In the presence of 6-AHA, KD,overall for SK and SKΔK414 binding was identical, 140 ± 20 pm, and encounter complex K1 values for native and mutant SK were similar, 4900 ± 60 and 5560 ± 50 nm, respectively. This ∼8-fold weaker initial binding of the mutant compared with its binding in the absence of effectors suggested that lysine interactions other than Lys414 also contribute to initial docking. KD,overall for SK and SKΔK414 binding in the presence of benzamidine was 77 ± 20 and 170 ± 50 pm, respectively. The encounter complexes with SK and SKΔK414 in the presence of benzamidine, with K1 values of 1430 ± 30 and 2840 ± 20 nm, respectively, were ∼3.4- and 2-fold tighter than in the presence of 6-AHA, suggesting differential contributions of Pm kringles in the SK docking process. The forward rate constants k2 and k3 for the conformational changes of SK and SKΔK414 binding were ∼3-6-fold larger, and the reverse rate constant k-2 was ∼4-7-fold larger in the presence of 6-AHA, indicating release of conformational restraints, and suggesting an LBS dependence of the transition from the SK·Pm* complex to SK·Pm**. The changes in the forward and reverse rate constants in the presence of benzamidine were more complex (Table 1).
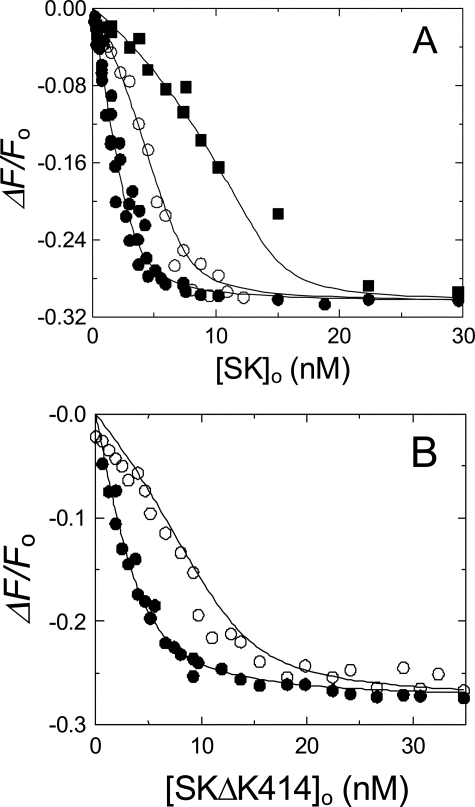
Equilibrium Binding of [5F]FFR-Pm and FFR-Pm to SK or SKΔK414 in the Presence of 50 mm Benzamidine—To characterize the effect of benzamidine on the binding kinetics, it was necessary to determine the affinity and fluorescence change for SK and SKΔK414 binding to [5F]FFR-Pm and FFR-Pm in the presence of benzamidine. Analysis of [5F]FFR-Pm titrations with SK in 50 mm benzamidine indicated that SK bound to [5F]FFR-Pm with a 1:1 stoichiometry, a dissociation constant of 280 ± 160 pm, and maximum fluorescence change of -31 ± 2% (Fig. 6A). The affinity was ∼23-fold weaker than in the absence of kringle ligands and comparable with that in the presence of saturating 6-AHA. SKΔK414 bound to [5F]FFR-Pm with a dissociation constant of 370 ± 180 pm, 2-fold weaker than in the absence of kringle ligands and indistinguishable from that in the presence of 6-AHA. Competitive binding of SK to FFR-Pm and [5F]FFR-Pm was used to determine the affinity of FFR-Pm for SK or SKΔK414 in the presence of benzamidine. Analysis of [5F]FFR-Pm titrations with SK and SKΔK414 at fixed FFR-Pm concentrations demonstrated competitive binding with dissociation constants of 130 ± 80 and 250 ± 160 pm for SK and SKΔK414 binding to FFR-Pm, respectively, about 1.5-2-fold tighter than the corresponding values obtained for labeled Pm (Fig. 6B).
FIGURE 6.
Competitive equilibrium binding of SK and SKΔK414 to [5F]FFR-Pm and FFR-Pm in the presence of benzamidine. A, the fractional change in fluorescence (ΔF/Fo) of 2.5 nm [5F]FFR-Pm in buffer containing 50 mm benzamidine plotted as a function of the total SK concentration ([SK]o) in the absence (•) and presence of 5.15 (○) and 15 nm (•) FFR-Pm. B, the fractional change in fluorescence (ΔF/Fo) of 5 nm [5F]FFR-Pm in buffer containing 50 mm benzamidine plotted as a function of the total SKΔK414 concentration ([SKΔK414]o) in the absence (•) and presence of 10 nm (○) FFR-Pm. The solid lines represent least-squares fits of the cubic equation for competitive binding, with the parameters listed under “Results” and Table 1. Fluorescence titrations were performed and analyzed as described under “Experimental Procedures.”
DISCUSSION
Rapid-reaction kinetic studies of SK binding to [5F]FFR-Pm revealed a multistep sequential binding and conformational change pathway of stable complex formation that is modulated by LBS interactions. A number of considerations are required to interpret the kinetic mechanism in the absence and presence of kringle ligands in terms of particular molecular events. On the basis of available evidence, the interdependent molecular events postulated to be involved include (a) LBS interactions mediated by SK Lys414 and a Pm kringle, (b) reorganization of the mobile domain structure of SK in solution to its defined structure when bound to the catalytic domain of Pm, (c) perturbation of the active site of Pm by SK binding that is signaled by the active site-incorporated fluorescence probe, (d) a conformational change in Pm from a partially to fully extended form induced by 6-AHA and not benzamidine, and (e) differences in the effects of benzamidine and 6-AHA arising from their preferences for binding different kringle domains.
The combined analysis of the forward and reverse reactions of SK binding to [5F]FFR-Pm supports a 3-step minimal reaction mechanism both in the absence and presence of kringle ligands (Equation 4). SK binds very tightly to native and fluorescently labeled Pm with a dissociation constant of 11-14 pm (12). High affinity is achieved in part by a ∼14-fold enhancement due to binding of the COOH-terminal Lys414 residue of SK to a Pm kringle (37). Lys414 is at the end of a 42-residue sequence that is disordered and apparently mobile in the SK·μPm crystal structure (15). The substantial remaining LBS-independent affinity of SK for native and fluorescently labeled Pm (KD 200-300 pm) is mediated by SK binding to the activated catalytic domain.
The SK-Pm binding pathway starts with near-diffusion-limited, rapid-equilibrium binding of SK to [5F]FFR-Pm to form an SK·Pm encounter complex (K1 62-110 nm) that is not accompanied by a fluorescence change. This is followed by two consecutive, favorable conformational changes on the seconds time scale, the first of these, SK·Pm*, occurring in the fast phase of the fluorescence change, and the second, SK·Pm**, reflected in the slow phase. The fluorescence amplitude coupled to the final conformational change is ∼10-12% larger than that caused by SK·Pm* formation (Table 1). These favorable steps increase the affinity of SK for Pm in succession, 67- and 133-fold over that of the encounter complex, resulting in an overall ∼9000-fold increase. In the absence of effectors, deletion of Lys414 had the largest effect on the encounter complex, weakening it 6-12-fold, while having relatively small effects on the rate constants for the conformational changes. This result indicated a major role of Lys414 in the absence of kringle ligands in promoting encounter complex formation.
The first conformational change is thought to represent binding of the three SK domains to the Pm catalytic domain accompanied by perturbation of the fluorescence probe located in the S3∼S4 substrate binding subsites. That this reflects a conformational change in Pm is supported by previous studies demonstrating changes in tripeptide substrate specificity on SK binding (12). It may also represent a fluorescence change due to the proximity of the probe to SK, where in particular, the α-domain is closest to the catalytic site in the SK·μPm complex (15). In this case, rearrangement of the SK domains accompanying binding to the catalytic domain, guided by tethering of SK through Lys414, may represent the first conformational change. Whether arrangement of the SK domains or the Pm conformational change are complete during the initial conformation change or are adjusted in the subsequent slower step characterized by the additional small fluorescence decrease is not known. That such structural flexibility of SK affects its conformation when bound to Pg and Pm is evidenced by studies of the binding of α-domain-truncated SK (53). The SK β-γ-domain fragment exhibits an increased contribution of binding energy to complex stability from LBS interactions or free energy coupling between LBS-dependent and -independent interactions with labeled [Glu]Pg, [Lys]Pg, and [Lys]Pm compared with intact SK, demonstrating the interdependence of the flexible domain interactions in forming the stable conformation of SK in the complexes (53). The conformational equilibrium constant K3 of 0.0075 based on the best-fit kinetic constants indicates that the SK·Pm** complex is the predominant species at saturating SK, consistent with the apparent single exponential reverse reaction kinetics. Whether SK·Pm* and SK·Pm** have equivalent activity in Pg activation is unknown.
The effects of 6-AHA and benzamidine on the SK-Pm binding pathway were compared because these compounds have different specificities for binding to Pg and Pm kringle domains and different effects on Pg conformation. From studies of isolated kringles, benzamidine binds with highest affinity to K5 (KD 290 μm), less tightly to K1 (KD 12.5 mm) and K2 (KD 33 mm), and not significantly to K3 or K4 (18, 35, 36). Analysis of the effects of 50 mm benzamidine on the conformations of [Glu]Pg, [Lys]Pg, K1-K5, and K1-K3 demonstrate that binding of benzamidine to K5 induces transformation of [Glu]Pg from the compact α-conformation to a partially extended β-conformation and that [Lys]Pg and K1-K5 but not K1-K3 are in similar β-conformations that are not affected by benzamidine (27). 6-AHA binds to isolated kringles, K1 (KD 11-13 μm), K4 (KD 20-60 μm), and K5 (KD 95-140 μm), with the major difference from benzamidine being the specificity for K4 (17-19, 33, 34, 54). Unlike benzamidine, 50 mm 6-AHA converts [Glu]Pg, [Lys]Pg, and K1-K5, but not K1-K3, to fully extended γ-conformations (27). The equivalent effect of 6-AHA to induce the β→γ conformational change for [Lys]Pg and K1-K5, but not K1-K3, has been concluded to be due to 6-AHA binding to K4 (27). On the basis of these studies indicating that the conformational change occurs in K1-K5, independent of the catalytic domain, Pm containing the activated catalytic domain is inferred to show a similar β→γ conformational change at saturating 6-AHA, although this has not been directly demonstrated. Rapid-reaction kinetics of the 6-AHA-induced α→γ conformational change demonstrated cooperative binding of 6-AHA to K4 and K5 of [Glu]Pg in the compact to fully extended conformational change and the absence of an effect of high affinity binding of 6-AHA to K1 (55). The β→γ conformational change was induced by ≥10 mm 6-AHA, supporting the role for relatively weak LBS in this transition (27). Studies using recombinant [Glu]Pg with selectively disabled K1, K4, or K5, however, concluded primary roles for K1 and K4 and to a lesser extent K5 in the α→γ compact to fully extended conformational change (19, 54). The precise roles of individual kringles in the conformational changes of [Glu]Pg, [Lys]Pg, and [Lys]Pm are not completely understood.
SK binding to Pm in the presence of saturating 6-AHA was characterized by 60-80-fold weaker encounter complex formation compared with the absence of kringle ligands. The binding reactions still displayed biexponential behavior, albeit less explicit than in the absence of kringle ligands, with the first conformational change accounting for most of the fluorescence decrease. Remarkably, koff for reversal of the SK binding pathway was the same as that in the absence of ligands. The two conformational changes in the presence of 6-AHA were responsible for a ∼35,000-fold increase in affinity compared with the encounter complex. The calculated and measured overall dissociation constants were not significantly different from those in the presence of benzamidine. Thus, the effects of the two kringle ligands cannot be distinguished by SK equilibrium binding affinity but show significant differences in the rate steps and amplitude of the fluorescence change. The major differences between the ligands is that 6-AHA binds to K1, K4, and K5, inducing the β→γ change in Pm conformation to the fully extended form, whereas benzamidine does not bind to K4 but binds to K1, K2, and K5 and does not induce the conformational change.
In the presence of 6-AHA, SK and SKΔK414 showed indistinguishable equilibrium and rate constants, demonstrating disengagement of Lys414 due to 6-AHA binding to K1, K4, or K5, resulting in an 8-12-fold weaker initial binding of SKΔK414 compared with binding in the absence of effectors. It is apparent that when LBS interactions mediated by K4 are disengaged, as suggested previously (27), and Pm is extended to the γ-conformation, the constraints imposed by LBS interactions and the β-conformation of Pm are released. The identity of koff in the absence of ligands and presence of 6-AHA does not necessarily suggest that the final complex is similar in both cases but that this rate constant is controlled by the forward and reverse LBS-dependent processes governed by k2, k-2, and k3, which may be equally affected by 6-AHA.
On the basis of available information, the effect of 50 mm benzamidine on SK binding to Pm can be plausibly interpreted in terms of the involvement of Lys414 of SK binding to K4, possibly influenced by K5. We cannot explicitly exclude roles for K1 and K2, which at 50 mm benzamidine would be ∼80 and ∼60% saturated, respectively, based on the published dissociation constants for isolated kringles (18, 35). The overall KD increased 20-23-fold in the presence of benzamidine, and the affinity of encounter complex formation was reduced ∼20-fold. Interestingly, compared with the results in the absence of ligands, the forward and reverse rate constants for the first conformational change increased 6.4- and 26-fold, respectively, and the overall off-rate constant increased 4-fold. Enhancement of the overall off-rate by benzamidine, predominantly controlled by k-2 and k-3, showed that the final stable complex dissociated more rapidly in the presence of benzamidine, independent of Lys414.
To characterize further the effect of Lys414 in the binding pathway in the absence and presence of 6-AHA and benzamidine, it is useful to compare the effects of Lys414 deletion on the conformational equilibrium constants, K2 and K3. In the absence of effectors, K2 and K3 are less favorable by only ∼2-fold for SKΔK414 compared with SK. K2 and K3 are essentially the same for SK and SKΔK414 in the presence of 6-AHA. By contrast, in the presence of benzamidine, K2 for SKΔK414 is ∼5-fold more favorable, and K3 is a compensating ∼5-fold less favorable than for SK. The distinctive results for SKΔK414 in benzamidine compared with 6-AHA suggest that Lys414 is not engaged in the presence of 6-AHA but is engaged in binding K4 throughout the binding pathway in the presence of benzamidine.
It is also interesting that the products of the equilibrium constants for the two conformational changes (K2K3 = k-2k-3/k2k3) are very similar for SK and SKΔK414 in the absence of effectors (11 × 10-5 and 9 × 10-5, respectively) and in the presence of either 6-AHA (3 × 10-5 and 2.6 × 10-5) or benzamidine (5.4 × 10-5 and 6.1 × 10-5). The overall conformational equilibrium constants are also not much different in the absence and presence of effectors (2-4-fold). This may reflect the relative independence of the tightening steps on the Pm β→γ conformational change or that the conformations are all extended due to interaction of Lys414 with K4 in the absence of effectors and presence of benzamidine and when K4 is occupied by 6-AHA.
There are other interpretations that cannot be excluded on the basis of the present results. In particular, K5 will be saturated with either 6-AHA or benzamidine at the concentrations used, whereas K4 will be blocked by 6-AHA but available in the presence of benzamidine. On this basis, it is possible that the differences in the rate constants in benzamidine and 6-AHA are due to occupation of K5 for both effectors in addition to Lys414 interacting with K4 in benzamidine, based on the proposal that these kringles bind 6-AHA cooperatively (55). Further studies will be required to determine which kringle binds Lys414 and to resolve the differences observed in the effects of benzamidine and 6-AHA.
The effects of benzamidine and 6-AHA also differed in the total amplitude of the fluorescence change for binding of SK and SKΔK414, which was -26-28% compared with -42-48% in the absence of ligands. This cannot be due to binding of benzamidine to the active site because it was blocked by the peptide chloromethyl ketone. The difference in amplitude appears to be specific for benzamidine, as in the presence of 6-AHA, SK binding caused a -45-50% fluorescence decrease, indistinguishable from that observed in the absence of ligands. The first conformational change in the presence of benzamidine, which contributes the majority of the fluorescence change due to SK binding, is thought to represent contact of SK with the catalytic domain, domain rearrangement, and/or a conformational change affecting the Pm active site. The different overall fluorescence change in Pm induced by SK binding in the presence of benzamidine suggests that the structure of SK bound to the catalytic domain is different, which could reflect retention of the partially extended conformation of Pm in the presence of benzamidine or blocking of K5 and maintained engagement of K4.
In summary, the present study characterizes for the first time a minimal 3-step kinetic model for the pathway of Pm binding to SK and quantitates the differential effects of LBS interactions and the conformational state of Pm on the individual steps in the pathway. Although the interaction of Pm with SK in 6-AHA and benzamidine is indistinguishable when measured by equilibrium binding, the stopped-flow results clearly indicate distinctly different, kinetically resolved behavior. The kinetics in the absence of effectors demonstrate how the conformational steps achieve ∼9000-fold tightening of binding, resulting in a stabilized complex with extremely high affinity. The model also shows that Lys414 plays an important role in establishing the initial encounter complex between Pm and SK before the conformational tightening that is relatively independent of Lys414.
Acknowledgments
We thank Malabika Laha, Sarah Stuart, Mary Beth Davis, and Sally Habib for excellent technical assistance.
This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health Grant RO1 HL056181 (NHLBI) (to P. E. B.) and RO1 HL 080018 (to I. M. V.). The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. This article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
Footnotes
The abbreviations used are: Pm, [Lys]plasmin; μPm; micro-Pm, the Pm catalytic domain; FFR-Pm, Pm inhibited with d-Phe-Phe-Arg-CH2Cl; [5F]FFR-Pm, [5-(acetamido)fluorescein]-d-Phe-Phe-Arg-Pm; SK, streptokinase; SKΔK414, SK lacking the COOH-terminal Lys414 residue; Pg, plasminogen; [Glu]Pg, intact native plasminogen; [Lys]Pg, native Pg lacking the NH2-terminal 77 residues; FFR-CH2Cl, d-Phe-Phe-Arg-CH2Cl; 6-AHA, 6-aminohexanoic acid; Pg*, nonproteolytically activated form of the plasminogen zymogen; LBS, lysine binding sites; PEG, polyethylene glycol 8000; Mes, 4-morpholineethanesulfonic acid.
References
- 1.Boxrud, P. D., Verhamme, I. M., and Bock, P. E. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279 36633-36641 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Boxrud, P. D., and Bock, P. E. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279 36642-36649 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.McClintock, D. K., and Bell, P. H. (1971) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 43 694-702 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wohl, R. C., Summaria, L., Arzadon, L., and Robbins, K. C. (1978) J. Biol. Chem. 253 1402-1407 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Reddy, K. N., and Markus, G. (1972) J. Biol. Chem. 247 1683-1691 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schick, L. A., and Castellino, F. J. (1974) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 57 47-54 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bajaj, A. P., and Castellino, F. J. (1977) J. Biol. Chem. 252 492-498 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Davidson, D. J., Higgins, D. L., and Castellino, F. J. (1990) Biochemistry 29 3585-3590 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wang, S., Reed, G. L., and Hedstrom, L. (1999) Biochemistry 38 5232-5240 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wang, S., Reed, G. L., and Hedstrom, L. (2000) Eur. J. Biochem. 267 3994-4001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Boxrud, P. D., Verhamme, I. M., Fay, W. P., and Bock, P. E. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276 26084-26089 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Boxrud, P. D., Fay, W. P., and Bock, P. E. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275 14579-14589 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Boxrud, P. D., and Bock, P. E. (2000) Biochemistry 39 13974-13981 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Damaschun, G., Damaschun, H., Gast, K., Gerlach, D., Misselwitz, R., Welfle, H., and Zirwer, D. (1992) Eur. Biophys. J. 20 355-361 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wang, X., Lin, X., Loy, J. A., Tang, J., and Zhang, X. C. (1998) Science 281 1662-1665 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Henkin, J., Marcotte, P., and Yang, H. (1991) Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 34 135-164 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ponting, C. P., Marshall, J. M., and Cederholm-Williams, S. A. (1992) Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 3 605-614 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Marti, D. N., Hu, C. K., An, S. S., von Haller, P., Schaller, J., and Llinas, M. (1997) Biochemistry 36 11591-11604 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Castellino, F. J., and McCance, S. G. (1997) Ciba Found. Symp. 212 46-60 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Christensen, U. (1985) FEBS Lett. 182 43-46 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lucas, M. A., Fretto, L. J., and McKee, P. A. (1983) J. Biol. Chem. 258 4249-4256 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wiman, B., Lijnen, H. R., and Collen, D. (1979) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 579 142-154 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bok, R. A., and Mangel, W. F. (1985) Biochemistry 24 3279-3286 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Clemmensen, I., Petersen, L. C., and Kluft, C. (1986) Eur. J. Biochem. 156 327-333 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cockell, C. S., Marshall, J. M., Dawson, K. M., Cederholm-Williams, S. A., and Ponting, C. P. (1998) Biochem. J. 333 99-105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ponting, C. P., Holland, S. K., Cederholm-Williams, S. A., Marshall, J. M., Brown, A. J., Spraggon, G., and Blake, C. C. (1992) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1159 155-161 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Marshall, J. M., Brown, A. J., and Ponting, C. P. (1994) Biochemistry 33 3599-3606 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mangel, W. F., Lin, B. H., and Ramakrishnan, V. (1990) Science 248 69-73 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hoylaerts, M., Rijken, D. C., Lijnen, H. R., and Collen, D. (1982) J. Biol. Chem. 257 2912-2919 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wohl, R. C., Summaria, L., and Robbins, K. C. (1980) J. Biol. Chem. 255 2005-2013 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Violand, B. N., Byrne, R., and Castellino, F. J. (1978) J. Biol. Chem. 253 5395-5401 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Violand, B. N., and Castellino, F. J. (1976) J. Biol. Chem. 251 3906-3912 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lerch, P. G., Rickli, E. E., Lergier, W., and Gillessen, D. (1980) Eur. J. Biochem. 107 7-13 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Markus, G., DePasquale, J. L., and Wissler, F. C. (1978) J. Biol. Chem. 253 727-732 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Thewes, T., Constantine, K., Byeon, I. J., and Llinas, M. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265 3906-3915 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Varadi, A., and Patthy, L. (1981) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 103 97-102 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Panizzi, P., Boxrud, P. D., Verhamme, I. M., and Bock, P. E. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281 26774-26778 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Deutsch, D. G., and Mertz, E. T. (1970) Science 170 1095-1096 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Castellino, F. J., and Powell, J. R. (1981) Methods Enzymol. 80 365-378 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bock, P. E., Day, D. E., Verhamme, I. M., Bernardo, M. M., Olson, S. T., and Shore, J. D. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271 1072-1080 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Taylor, F. B., Jr., and Botts, J. (1968) Biochemistry 7 232-242 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Jackson, K. W., and Tang, J. (1982) Biochemistry 21 6620-6625 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bock, P. E., Craig, P. A., Olson, S. T., and Singh, P. (1989) Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 273 375-388 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bock, P. E. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267 14963-14973 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bock, P. E. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267 14974-14981 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bock, P. E. (1993) Methods Enzymol. 222 478-503 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kuzmic, P. (1996) Anal. Biochem. 237 260-273 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tsodikov, O. V., and Record, M. T., Jr. (1999) Biophys. J. 76 1320-1329 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bock, P. E., Olson, S. T., and Björk, I. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272 19837-19845 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lindahl, P., Raub-Segall, E., Olson, S. T., and Björk, I. (1991) Biochem. J. 276 387-394 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Olson, S. T., Bock, P. E., and Sheffer, R. (1991) Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 286 533-545 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Smoluchowski, M. V. (1918) Z. Phys. Chem. 92 129-168 [Google Scholar]
- 53.Bean, R. R., Verhamme, I. M., and Bock, P. E. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280 7504-7510 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.McCance, S. G., and Castellino, F. J. (1995) Biochemistry 34 9581-9586 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Christensen, U., and Molgaard, L. (1992) Biochem. J. 285 419-425 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]