Abstract
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) codes for at least three glycoproteins, gp350, gp220, and gp85. The two largest glycoproteins are thought to be involved in the attachment of the virus to its receptor on B cells, but despite the fact that gp85 induces neutralizing antibody, no function has been attributed to it. As an indirect approach to understanding the role of gp85 in the initiation of infection, we determined the point at which a neutralizing, monoclonal antibody that reacted with the glycoprotein interfered with virus replication. The antibody had no effect on virus binding. To examine the effect of the antibody on later stages of infection, the fusion assay of Hoekstra and colleagues (D. Hoekstra, T. de Boer, K. Klappe, and J. Wilshaut, Biochemistry 23:5675-5681, 1984) was adapted for use with EBV. The virus was labeled with a fluorescent amphiphile that was self-quenched at the high concentration obtained in the virus membrane. When the virus and cell membrane fused, there was a measurable relief of self-quenching that could be monitored kinetically. Labeling had no effect on virus binding or infectivity. The assay could be used to monitor virus fusion with lymphoblastoid lines or normal B cells, and its validity was confirmed by the use of fixed cells and the Molt 4 cell line, which binds but does not internalize the virus. The monoclonal antibody to gp85 that neutralized virus infectivity, but not a second nonneutralizing antibody to the same molecule, inhibited the relief of self-quenching in a dose-dependent manner. This finding suggests that gp85 may play an active role in the fusion of EBV with B-cell membranes.
Full text
PDF

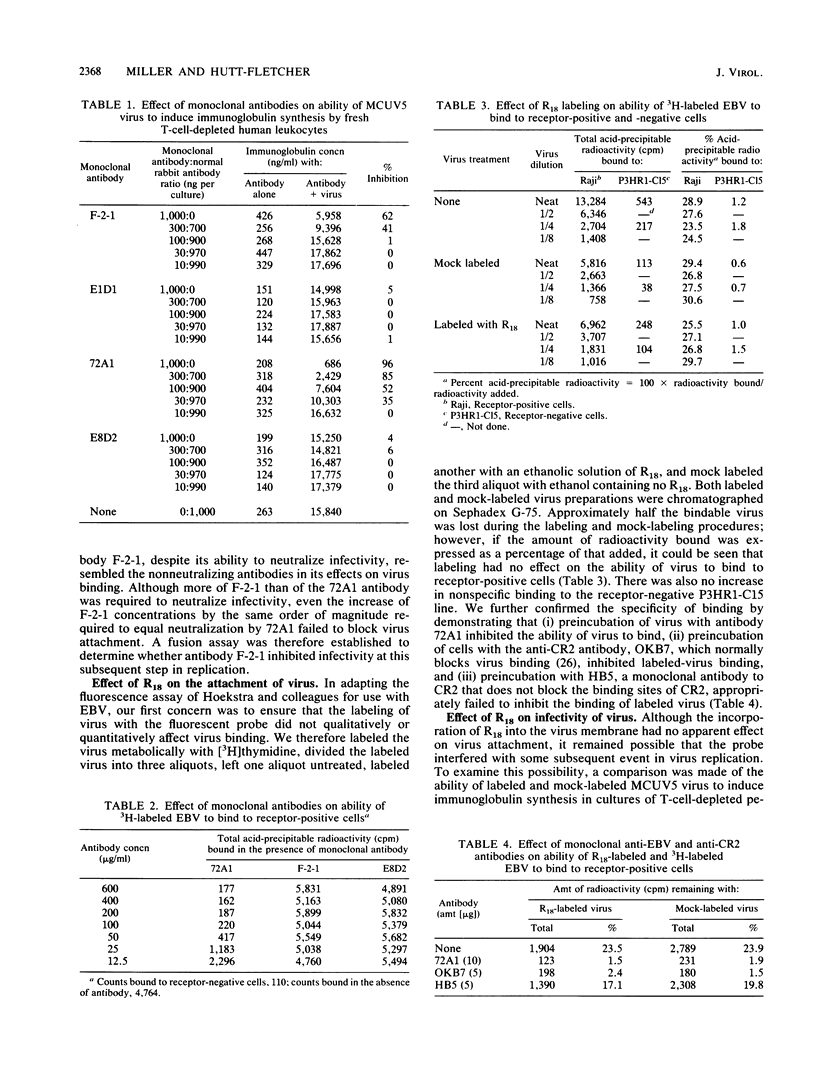
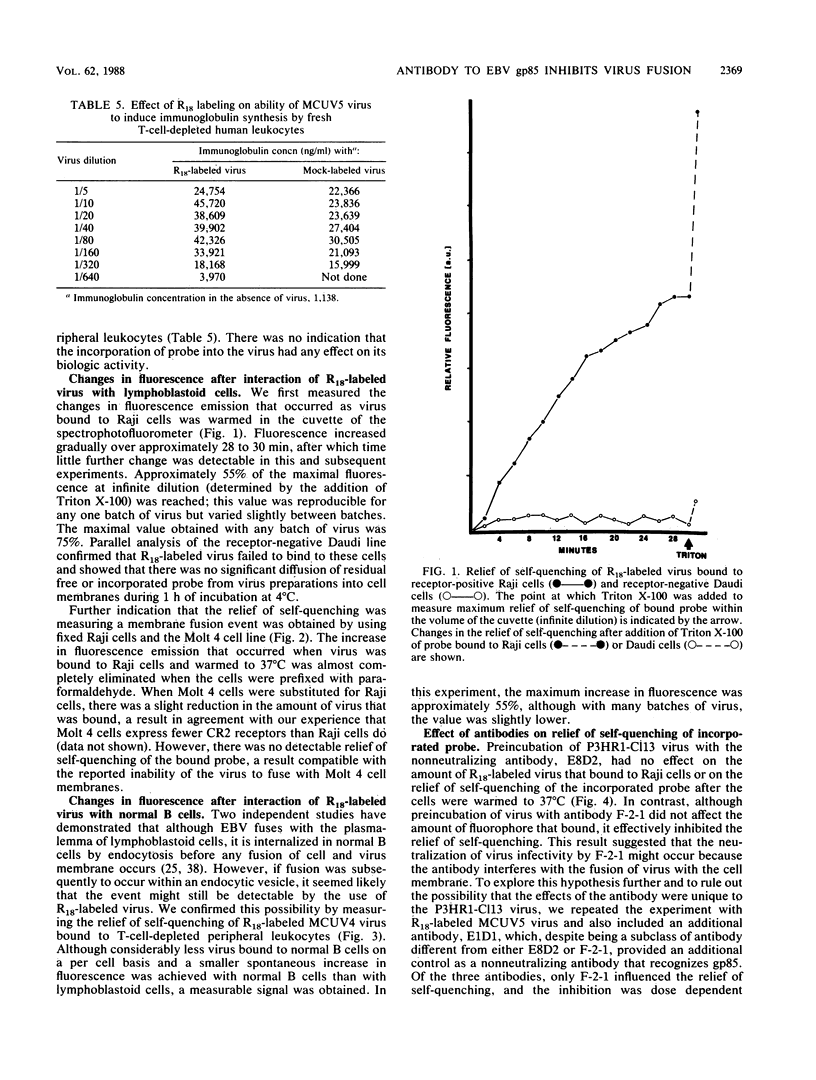
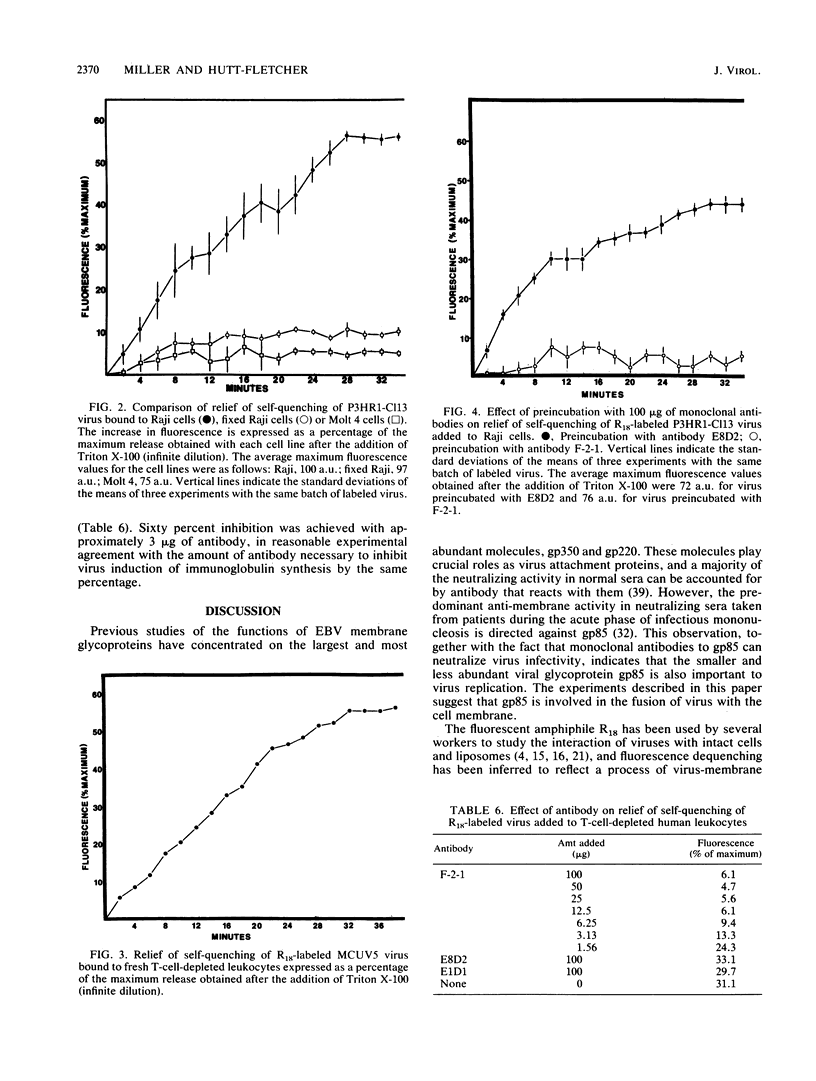


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balachandran N., Oba D. E., Hutt-Fletcher L. M. Antigenic cross-reactions among herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2, Epstein-Barr virus, and cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1125–1135. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1125-1135.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran N., Pittari J., Hutt-Fletcher L. M. Detection by monoclonal antibodies of an early membrane protein induced by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):369–375. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.369-375.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisel C., Tanner J., Matsuo T., Thorley-Lawson D., Kezdy F., Kieff E. Two major outer envelope glycoproteins of Epstein-Barr virus are encoded by the same gene. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):665–674. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.665-674.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal R., Bali-Puri A., Walter A., Covell D., Eidelman O. pH-dependent fusion of vesicular stomatitis virus with Vero cells. Measurement by dequenching of octadecyl rhodamine fluorescence. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13614–13619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges K., Harford J., Ashwell G., Klausner R. D. Fate of receptor and ligand during endocytosis of asialoglycoproteins by isolated hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):350–354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranage M. P., Smith G. L., Bell S. E., Hart H., Brown C., Bankier A. T., Tomlinson P., Barrell B. G., Minson T. C. Identification and expression of a human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein with homology to the Epstein-Barr virus BXLF2 product, varicella-zoster virus gpIII, and herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein H. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1416–1422. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1416-1422.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingeroth J. D., Weis J. J., Tedder T. F., Strominger J. L., Biro P. A., Fearon D. T. Epstein-Barr virus receptor of human B lymphocytes is the C3d receptor CR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4510–4514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller A. O., Spear P. G. Specificities of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies that inhibit adsorption of herpes simplex virus to cells and lack of inhibition by potent neutralizing antibodies. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):475–482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.475-482.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gompels U., Minson A. The properties and sequence of glycoprotein H of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1986 Sep;153(2):230–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heineman T., Gong M., Sample J., Kieff E. Identification of the Epstein-Barr virus gp85 gene. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1101–1107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1101-1107.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heston L., Rabson M., Brown N., Miller G. New Epstein-Barr virus variants from cellular subclones of P3J-HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):160–163. doi: 10.1038/295160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D., Klappe K., de Boer T., Wilschut J. Characterization of the fusogenic properties of Sendai virus: kinetics of fusion with erythrocyte membranes. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 27;24(18):4739–4745. doi: 10.1021/bi00339a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D., de Boer T., Klappe K., Wilschut J. Fluorescence method for measuring the kinetics of fusion between biological membranes. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5675–5681. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman G. J., Lazarowitz S. G., Hayward S. D. Monoclonal antibody against a 250,000-dalton glycoprotein of Epstein-Barr virus identifies a membrane antigen and a neutralizing antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2979–2983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutt-Fletcher L. M. Synergistic activation of cells by Epstein-Barr virus and B-cell growth factor. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):774–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.774-781.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller P. M., Davison A. J., Lowe R. S., Riemen M. W., Ellis R. W. Identification and sequence of the gene encoding gpIII, a major glycoprotein of varicella-zoster virus. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):526–533. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90295-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E., Klein G., Nadkarni J. S., Nadkarni J. J., Wigzell H., Clifford P. Surface IgM-kappa specificity on a Burkitt lymphoma cell in vivo and in derived culture lines. Cancer Res. 1968 Jul;28(7):1300–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapidot M., Nussbaum O., Loyter A. Fusion of membrane vesicles bearing only the influenza hemagglutinin with erythrocytes, living cultured cells, and liposomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13736–13741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Davison A. J. DNA sequence of the herpes simplex virus type 1 gene encoding glycoprotein gH, and identification of homologues in the genomes of varicella-zoster virus and Epstein-Barr virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):4281–4292. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.4281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Seigneurin J. M., Patel P., Bourkas A., Lenoir G. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus receptors, but absence of virus penetration, in cells of an Epstein-Barr virus genome-negative human lymphoblastoid T line (Molt 4). J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):816–821. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.816-821.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowada J., Onuma T., Moore G. E. Rosette-forming human lymphoid cell lines. I. Establishment and evidence for origin of thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerow G. R., Cooper N. R. Early events in the infection of human B lymphocytes by Epstein-Barr virus: the internalization process. Virology. 1984 Jan 15;132(1):186–198. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90102-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerow G. R., McNaughton M. E., Cooper N. R. Binding of monoclonal antibody to the Epstein Barr virus (EBV)/CR2 receptor induces activation and differentiation of human B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3068–3073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerow G. R., Mold C., Schwend V. K., Tollefson V., Cooper N. R. Identification of gp350 as the viral glycoprotein mediating attachment of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) to the EBV/C3d receptor of B cells: sequence homology of gp350 and C3 complement fragment C3d. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1416–1420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1416-1420.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerow G. R., Wolfert R., McNaughton M. E., Cooper N. R. Identification and characterization of the Epstein-Barr virus receptor on human B lymphocytes and its relationship to the C3d complement receptor (CR2). J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):347–351. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.347-351.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oba D. E., Hutt-Fletcher L. M. Induction of antibodies to the Epstein-Barr virus glycoprotein gp85 with a synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence in the BXLF2 open reading frame. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1108–1114. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1108-1114.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT J. V. CYTOLOGY OF BURKITT'S TUMOUR (AFRICAN LYMPHOMA). Lancet. 1964 Feb 1;1(7327):238–240. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92345-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S., Dierich M. P., Reisfeld R. A. Enhancement of sheep red blood cell human lymphocyte rosette formation by the sulfhydryl compound 2-amino ethylisothiouronium bromide. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Jan;3(3):324–333. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qualtiere L. F., Pearson G. R. Epstein-Barr virus-induced membrane antigens: immunochemical characterization of Triton X-100 solubilized viral membrane antigens from EBV-superinfected Raji cells. Int J Cancer. 1979 Jun 15;23(6):808–817. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Haffey M., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. III. Role of glycoprotein VP7(B2) in virion infectivity. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1149-1158.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seigneurin J. M., Vuillaume M., Lenoir G., De-Thé G. Replication of Epstein-Barr virus: ultrastructural and immunofluorescent studies of P3HR1-superinfected Raji cells. J Virol. 1977 Dec;24(3):836–845. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.3.836-845.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Davis D. S., Young L. S., Hutt-Fletcher L., Tedder T. F., Rickinson A. B. Human epithelial cell expression of an Epstein-Barr virus receptor. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):805–811. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strnad B. C., Schuster T., Klein R., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Witmer T., Neubauer R. H., Rabin H. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against the Epstein-Barr virus membrane antigen. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):258–264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.258-264.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J., Weis J., Fearon D., Whang Y., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus gp350/220 binding to the B lymphocyte C3d receptor mediates adsorption, capping, and endocytosis. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):203–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90216-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder T. F., Goldmacher V. S., Lambert J. M., Schlossman S. F. Epstein Barr virus binding induces internalization of the C3d receptor: a novel immunotoxin delivery system. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1387–1391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Poodry C. A. Identification and isolation of the main component (gp350-gp220) of Epstein-Barr virus responsible for generating neutralizing antibodies in vivo. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):730–736. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.730-736.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells A., Koide N., Klein G. Two large virion envelope glycoproteins mediate Epstein-Barr virus binding to receptor-positive cells. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):286–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.286-297.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



